Understanding High Stock Market Valuations: A BofA Perspective
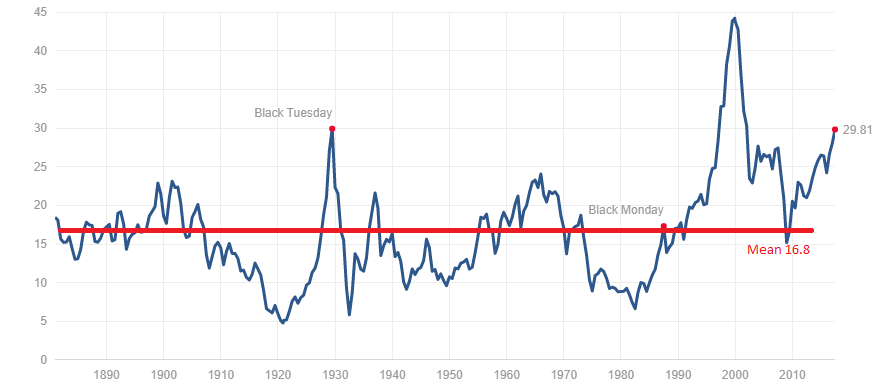
Table of Contents
Key Valuation Metrics and Their Limitations
Understanding high stock market valuations requires a careful examination of various metrics. While no single metric paints a complete picture, a combination offers a more comprehensive assessment.
Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E)
The Price-to-Earnings ratio (P/E) is a fundamental valuation metric calculated by dividing a company's stock price by its earnings per share (EPS). A higher P/E ratio generally suggests investors are willing to pay more for each dollar of earnings, potentially indicating higher growth expectations or perceived lower risk.
However, the P/E ratio has limitations:
- Industry Variations: P/E ratios vary significantly across industries. Comparing the P/E of a technology company to that of a utility company can be misleading without considering industry-specific growth rates and risk profiles.
- Accounting Practices: Different accounting standards and practices can influence reported earnings, impacting the accuracy of the P/E ratio.
- Misleading Simplicity: A high P/E ratio alone doesn't necessarily signal overvaluation. It could reflect strong future growth prospects. Conversely, a low P/E might indicate undervaluation or hidden risks.
For a more nuanced perspective, analysts often consider the cyclically adjusted price-to-earnings ratio (CAPE), which smooths out earnings fluctuations over a longer period (typically 10 years).
Other Important Valuation Metrics
While the P/E ratio is widely used, relying solely on it is risky when assessing high stock market valuations. Other crucial metrics include:
- Price-to-Sales (P/S): This ratio compares a company's market capitalization to its revenue. It's particularly useful for companies with negative earnings.
- Price-to-Book (P/B): This ratio compares a company's market capitalization to its book value (assets minus liabilities). It's often used to assess value in asset-heavy industries.
- Dividend Yield: This metric represents the annual dividend per share relative to the stock price. It's particularly relevant for income-oriented investors.
By comparing these metrics across sectors and against historical data, investors gain a more holistic understanding of market valuations and identify potential overvalued or undervalued sectors. Remember, no single metric provides a complete picture; a comprehensive analysis is crucial.
Macroeconomic Factors Influencing Valuations
High stock market valuations are not solely determined by company-specific factors. Broad macroeconomic conditions significantly influence market sentiment and pricing.
Interest Rates and Monetary Policy
Interest rates and monetary policy exert a considerable influence on stock valuations. Generally, lower interest rates stimulate borrowing and investment, pushing stock prices higher. Conversely, rising interest rates can make bonds more attractive, potentially leading to lower stock valuations.
BofA analysts closely monitor interest rate trends and central bank actions. The current interest rate environment, characterized by [insert BofA's current assessment of the interest rate environment, e.g., gradual increases], influences their view on the sustainability of current high stock market valuations. Past periods of quantitative easing (QE) have demonstrably inflated asset prices, and future policy shifts could significantly impact market dynamics.
Economic Growth and Inflation
The relationship between economic growth, inflation, and stock market valuations is complex. Strong economic growth, coupled with controlled inflation, generally supports higher valuations. However, runaway inflation can erode corporate earnings and investor confidence, leading to market corrections.
BofA's projections for economic growth and inflation are [insert BofA's projections here, e.g., moderate growth with contained inflation]. These projections influence their assessment of whether current high stock market valuations are justified or represent a potential bubble.
Geopolitical Risks and Uncertainty
Geopolitical events introduce uncertainty and volatility into the market. Trade wars, political instability, and unexpected global crises can significantly impact investor sentiment and stock prices.
BofA assesses geopolitical risks and their potential impact on market valuations. [Insert specific examples of geopolitical risks and BofA's assessment. E.g., "The ongoing trade tensions between major economies could dampen global growth and negatively affect corporate profits, thereby impacting valuations."]. Historical precedents demonstrate how significant geopolitical events can lead to short-term market corrections or even longer-term shifts in valuations.
BofA's Perspective on Current High Stock Market Valuations
BofA's analysis of current high stock market valuations considers both potential risks and opportunities.
Potential Risks
High valuations inherently carry risks:
- Market Corrections: Periods of overvaluation often precede market corrections, where prices decline sharply.
- Potential Bubbles: In extreme cases, high valuations can indicate speculative bubbles, prone to sudden and dramatic collapses.
BofA assesses the likelihood of these risks based on their macroeconomic analysis and valuation metrics. [Insert BofA's assessment of the likelihood of these risks, e.g., "While certain sectors appear overvalued, a broad market crash is deemed unlikely based on current economic indicators."]. Strategies to mitigate these risks include diversification and careful portfolio construction.
Potential Opportunities
Despite the risks, high valuations don't necessarily exclude opportunities:
- Sector-Specific Opportunities: While the overall market might appear expensive, some sectors or individual companies may be undervalued relative to their growth potential.
- Strategic Investing: Active management and strategic investment approaches, such as value investing or contrarian strategies, can identify opportunities even in a high-valuation environment.
BofA's research identifies [insert specific examples of sectors or strategies BofA believes hold potential, e.g., "certain technology sub-sectors with strong growth trajectories"]. A diversified portfolio and a long-term investment horizon are vital to navigate these potentially volatile conditions.
Conclusion
Understanding high stock market valuations requires a nuanced approach, considering multiple valuation metrics and macroeconomic factors. This article, offering a BofA perspective, highlights the importance of analyzing key metrics like the P/E ratio while acknowledging their limitations. We've explored the influence of interest rates, economic growth, and geopolitical risks on market valuations. While high valuations present potential risks, BofA's analysis also reveals opportunities for strategic investors. Remember to always conduct thorough research and consider consulting a financial advisor before making investment decisions related to high stock market valuations. Learn more about navigating the complexities of high stock market valuations by exploring further resources from Bank of America.

Featured Posts
-
 Ontario Considers Permanent Gas Tax Cut And Highway 407 East Toll Removal
May 16, 2025
Ontario Considers Permanent Gas Tax Cut And Highway 407 East Toll Removal
May 16, 2025 -
 Ontarios Honda Ev Plant A 15 Billion Project Facing Delays
May 16, 2025
Ontarios Honda Ev Plant A 15 Billion Project Facing Delays
May 16, 2025 -
 Bronson Reacts Jaylen Brown Confuses Him With Luke Combs
May 16, 2025
Bronson Reacts Jaylen Brown Confuses Him With Luke Combs
May 16, 2025 -
 Antisemitische Beleidigung Und Hetze In Berlin Kind Von Unbekannten Angegriffen
May 16, 2025
Antisemitische Beleidigung Und Hetze In Berlin Kind Von Unbekannten Angegriffen
May 16, 2025 -
 Portland Timbers Lose To San Jose Earthquakes 4 1 Final Score
May 16, 2025
Portland Timbers Lose To San Jose Earthquakes 4 1 Final Score
May 16, 2025
