Understanding The Recent Spike In Bitcoin Mining Difficulty And Hashrate
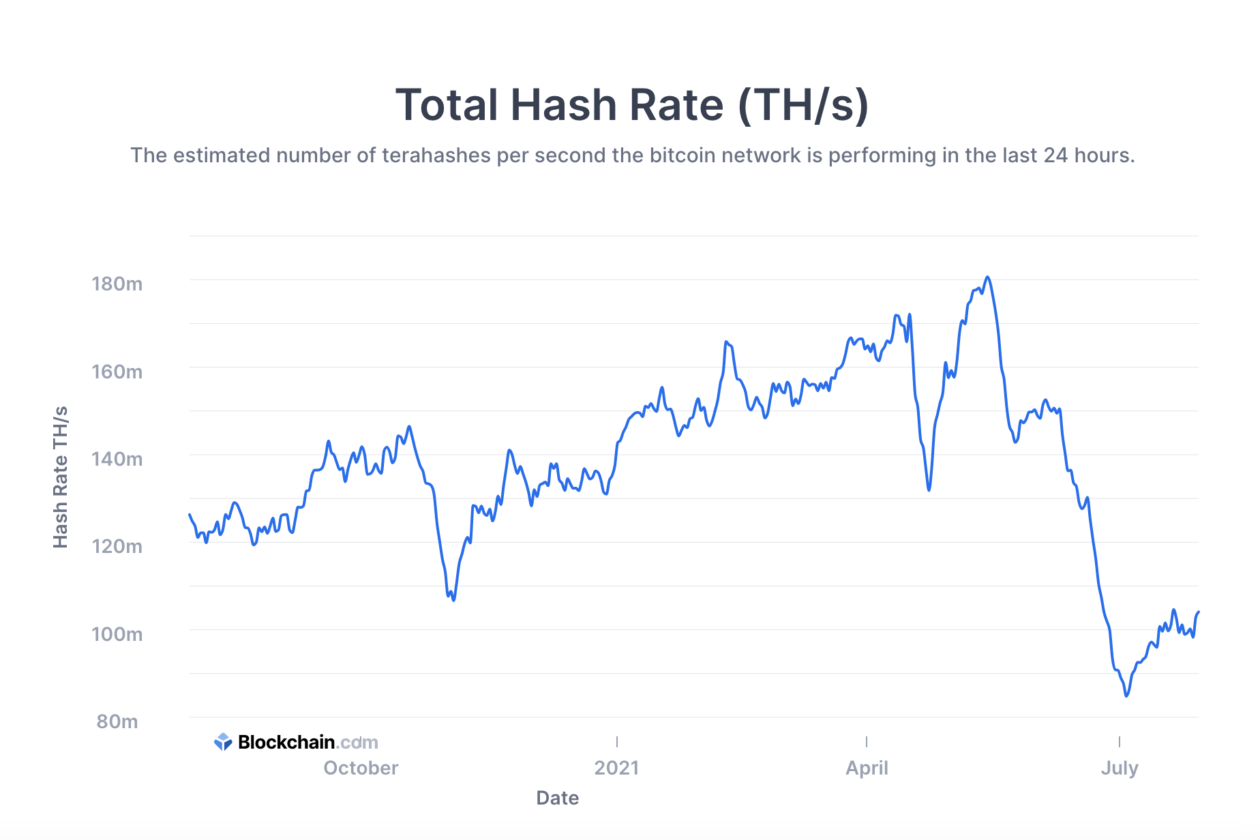
Table of Contents
First, let's clarify some key terms. Bitcoin mining difficulty refers to a measure of how computationally difficult it is to find a valid block and add it to the Bitcoin blockchain. This difficulty automatically adjusts every 2016 blocks (approximately every two weeks) to maintain a consistent block time of around 10 minutes. Hashrate, on the other hand, represents the total computational power dedicated to Bitcoin mining across the entire network, measured in hashes per second. A higher hashrate indicates more miners contributing their processing power to the network.
Factors Contributing to the Increased Bitcoin Mining Difficulty
Several interconnected factors have driven the recent surge in Bitcoin mining difficulty.
The Role of Increased Hashrate
The most direct cause of increased Bitcoin mining difficulty is a rise in the network's hashrate. As more mining power joins the network, the probability of finding a valid block increases. To maintain the target block time of approximately 10 minutes, the network automatically adjusts the mining difficulty upwards. This ensures the blockchain remains secure and operates consistently.
- New Mining Farms: The establishment of large-scale mining operations, particularly in regions with favorable energy costs, significantly boosts the overall hashrate.
- More Efficient ASICs: The development and deployment of more powerful and energy-efficient Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) allow miners to solve cryptographic puzzles faster, leading to a higher hashrate.
- Lower Energy Costs: Access to cheap electricity, such as hydroelectric or geothermal power, makes Bitcoin mining more profitable, encouraging increased participation and boosting the hashrate.
According to data from [cite reputable source, e.g., blockchain.com], the Bitcoin hashrate has increased by Y% (replace Y with actual percentage) in the last Z months (replace Z with timeframe), directly correlating with the recent difficulty adjustment.
Impact of Bitcoin Price on Mining Activity
The price of Bitcoin is a crucial factor influencing miner participation and, consequently, the hashrate. When the price of Bitcoin rises, mining becomes more profitable, attracting new miners and incentivizing existing ones to maintain or increase their operations.
- Economics of Bitcoin Mining: Miner profitability depends on the delicate balance between the Bitcoin price, electricity costs, and the cost of mining hardware. A higher Bitcoin price makes mining more profitable, even with increased mining difficulty.
- Electricity Costs: Regions with low electricity costs have a competitive advantage in Bitcoin mining, making them hubs for large mining operations.
[Insert a chart/graph here visually depicting the correlation between Bitcoin price and hashrate over a relevant timeframe. Source the data clearly.]
Technological Advancements in Mining Hardware
The continuous development of more efficient ASICs plays a significant role in driving up the hashrate. These specialized chips are designed specifically for Bitcoin mining, offering superior performance compared to general-purpose hardware.
- ASIC Manufacturers: Companies like [mention specific ASIC manufacturers] are constantly innovating, releasing new generations of ASICs with improved hash rates and energy efficiency.
- Improved ASICs and Hashrates: These advancements allow miners to solve cryptographic hashes at a faster rate, directly contributing to the increased hashrate and subsequent difficulty adjustments. Newer ASICs often utilize more advanced manufacturing processes (e.g., smaller node sizes) leading to significant performance gains.
Implications of the Increased Difficulty and Hashrate
The recent increase in Bitcoin mining difficulty and hashrate has several significant implications.
Network Security and Decentralization
A higher hashrate significantly strengthens the Bitcoin network's security. It makes 51% attacks – where a malicious actor controls more than half of the network's hashrate to manipulate the blockchain – exponentially more difficult and expensive to execute.
- 51% Attacks: The cost and difficulty of launching a 51% attack increase proportionally with the network's hashrate.
- Decentralization: A high and distributed hashrate promotes decentralization, making the Bitcoin network more resistant to censorship and single points of failure.
Impact on Mining Profitability
While a higher hashrate initially leads to increased mining revenue for all participants, the subsequent difficulty adjustment can impact profitability. Less efficient miners or those with higher electricity costs may find their operations less profitable, potentially leading some to exit the market.
- Profitability Factors: Mining profitability depends on the interplay between Bitcoin price, electricity costs, hardware costs (including depreciation), and mining difficulty.
- Market Adjustment: As difficulty increases, less profitable miners may be forced to shut down, leading to a natural market adjustment and stabilization of the hashrate.
Environmental Concerns
The increased energy consumption associated with Bitcoin mining remains a concern. The growing hashrate translates to higher energy demand, prompting ongoing discussions around sustainable mining practices.
- Renewable Energy: The industry is increasingly adopting renewable energy sources to reduce its carbon footprint.
- Sustainable Mining: Initiatives promoting energy-efficient mining hardware and renewable energy sources are gaining traction.
Conclusion: Understanding the Future of Bitcoin Mining Difficulty and Hashrate
The recent spike in Bitcoin mining difficulty and hashrate reflects a complex interplay between technological advancements, economic incentives, and environmental concerns. The increased hashrate strengthens network security, but also impacts mining profitability and energy consumption. Predicting the future trend is challenging; however, continued technological innovation and fluctuating Bitcoin prices will likely continue to influence the hashrate and subsequent difficulty adjustments. Whether the growth continues at the current pace depends on many factors, including the development of more efficient ASICs, the price of Bitcoin, and the regulatory landscape.
To stay informed about the evolving dynamics of Bitcoin mining difficulty and hashrate, follow reputable sources such as [mention reputable sources, e.g., blockchain.com, CoinMetrics], and engage in further research. Understanding these key metrics is crucial for anyone interested in the future of Bitcoin. Stay updated on the latest trends in Bitcoin mining difficulty and hashrate to navigate this dynamic landscape successfully.

Featured Posts
-
 Preempt The Ps 5 Price Increase Your Guide To Buying Now
May 08, 2025
Preempt The Ps 5 Price Increase Your Guide To Buying Now
May 08, 2025 -
 Auto Dealers Intensify Fight Against Ev Sales Requirements
May 08, 2025
Auto Dealers Intensify Fight Against Ev Sales Requirements
May 08, 2025 -
 Next Pope Cardinals Review Candidate Profiles
May 08, 2025
Next Pope Cardinals Review Candidate Profiles
May 08, 2025 -
 Py Ays Ayl Ke Dwran Lahwr Myn Askwlwn Ke Awqat Kar Myn Tbdyly
May 08, 2025
Py Ays Ayl Ke Dwran Lahwr Myn Askwlwn Ke Awqat Kar Myn Tbdyly
May 08, 2025 -
 Ahsan Urges Tech Adoption To Boost Pakistans Global Trade
May 08, 2025
Ahsan Urges Tech Adoption To Boost Pakistans Global Trade
May 08, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Star Wars Andor A Look At Tony Gilroys Creative Vision
May 08, 2025
Star Wars Andor A Look At Tony Gilroys Creative Vision
May 08, 2025 -
 Tony Gilroys Positive Andor Experience A Star Wars Success Story
May 08, 2025
Tony Gilroys Positive Andor Experience A Star Wars Success Story
May 08, 2025 -
 Andor Showrunner Tony Gilroy Reflects On Production
May 08, 2025
Andor Showrunner Tony Gilroy Reflects On Production
May 08, 2025 -
 Andor Season 2 Your Pre Viewing Guide
May 08, 2025
Andor Season 2 Your Pre Viewing Guide
May 08, 2025 -
 Everything You Need To Know Before Andor Season 2 Airs
May 08, 2025
Everything You Need To Know Before Andor Season 2 Airs
May 08, 2025
