Why Are Measles Cases Decreasing In The US? A Data-Driven Analysis
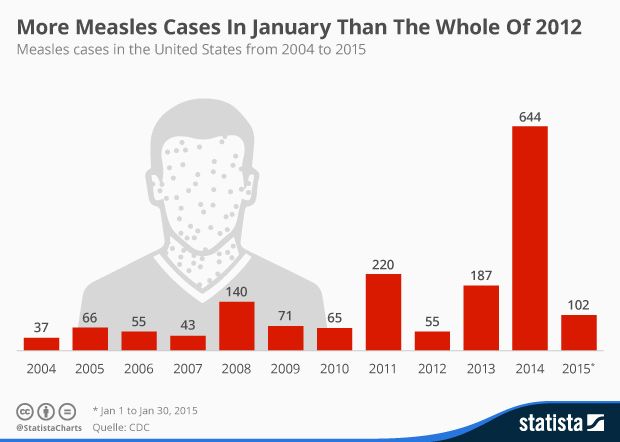
Table of Contents
The Power of Vaccination
The most significant factor behind the decreasing number of measles cases in the US is undoubtedly the widespread adoption of the measles, mumps, and rubella (MMR) vaccine. High vaccination rates have dramatically reduced the incidence and spread of this highly contagious disease.
Measles Vaccination Rates
The correlation between high vaccination rates and the decrease in measles cases is undeniable. Over the past two decades, we've witnessed a consistent rise in MMR vaccination coverage across different age groups and regions.
-
Data on vaccination rates over the past 20 years: Data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) shows a consistent increase in MMR vaccination rates among children aged 1-5, from approximately 85% in the early 2000s to over 90% in recent years. This increase has been crucial in maintaining herd immunity.
-
Comparison of vaccination rates in states with higher/lower measles case counts: States with lower MMR vaccination rates have historically experienced higher numbers of measles cases. This correlation clearly demonstrates the vaccine's effectiveness in preventing outbreaks.
-
Specific vaccination campaigns and their impact: Targeted vaccination campaigns, particularly in vulnerable communities, have played a significant role in boosting vaccination rates. These campaigns often include public education initiatives to address misconceptions and improve vaccine uptake.
Vaccine Effectiveness
The MMR vaccine boasts an extremely high effectiveness rate in preventing measles. It's crucial to address common misconceptions and highlight the scientific evidence supporting its safety and efficacy.
-
Statistics on vaccine efficacy in preventing measles: The MMR vaccine is more than 97% effective at preventing measles infection after two doses.
-
Discussion of herd immunity and its role in protecting unvaccinated individuals: Herd immunity is achieved when a high percentage of a population is immune to a disease, making it difficult for the disease to spread. This protects even those who cannot be vaccinated for medical reasons.
-
Addressing concerns about vaccine safety, citing reputable sources: Extensive research and decades of data have consistently demonstrated the MMR vaccine's safety profile. Any rare side effects are significantly outweighed by the serious risks of measles infection. Reputable sources like the CDC and the World Health Organization (WHO) provide comprehensive information addressing safety concerns.
Improved Public Health Infrastructure
Beyond vaccination, improvements in public health infrastructure have significantly contributed to the decline in measles cases in the US.
Enhanced Surveillance and Reporting
Modern disease surveillance methods enable quicker identification and containment of measles outbreaks.
-
Description of modern surveillance methods: Real-time data collection, advanced laboratory diagnostics, and rapid communication networks allow for swift responses to potential outbreaks.
-
Examples of how early detection has prevented larger outbreaks: Early identification of measles cases through improved surveillance has facilitated prompt public health interventions, such as targeted vaccination campaigns and isolation measures, effectively preventing widespread outbreaks.
-
Discussion of the role of public health agencies in outbreak response: Public health agencies like the CDC play a critical role in coordinating responses, providing resources, and disseminating information during measles outbreaks.
Increased Access to Healthcare
Improved access to healthcare, particularly vaccination services, has particularly benefited vulnerable populations.
-
Data on healthcare access and its correlation with vaccination rates: Studies show a direct correlation between improved healthcare access and higher vaccination rates, leading to lower measles incidence in underserved communities.
-
Mention of government programs aimed at improving healthcare access: Government initiatives aimed at increasing healthcare access, such as the Affordable Care Act, have indirectly contributed to higher vaccination rates.
-
Discussion of the impact of affordable healthcare on vaccination uptake: Making healthcare more affordable and accessible removes financial barriers to vaccination, leading to greater uptake among lower-income families.
Other Contributing Factors
While vaccination and improved public health infrastructure are the primary drivers, other factors have also played a role.
Improved Sanitation and Hygiene
Improved sanitation and hygiene practices contribute to reducing the spread of measles.
-
Link between improved sanitation and reduced infectious disease transmission: Better sanitation reduces the transmission of infectious diseases, including measles, by limiting exposure to contaminated environments.
-
Discuss the impact of public health education campaigns: Public health campaigns emphasizing hand hygiene and sanitation practices further reduce the risk of measles transmission.
Global Efforts to Eradicate Measles
Global efforts to eradicate measles, though primarily focused internationally, have indirectly contributed to the decline in US cases by limiting international transmission.
-
Discuss the World Health Organization's role in measles eradication: The WHO plays a vital role in coordinating global efforts to eliminate measles, including providing technical assistance and funding to countries around the world.
-
Highlight successful eradication efforts in other countries: The success of measles eradication campaigns in several countries reduces the risk of imported cases into the US.
Conclusion
The significant decrease in measles cases in the US is a result of a multi-pronged approach. High MMR vaccination rates, coupled with an improved public health infrastructure and other contributing factors, have been crucial in achieving this positive trend. The strong correlation between high vaccination rates and the decline in measles outbreaks is undeniable. Maintaining high vaccination rates is crucial to keeping measles cases decreasing in the US. Protect yourself and your community – get vaccinated today! Visit the CDC website ([link to CDC website]) for more information on measles prevention and vaccination.

Featured Posts
-
 French Open 2025 Borges Triumphs Over Injured Ruud
May 30, 2025
French Open 2025 Borges Triumphs Over Injured Ruud
May 30, 2025 -
 French Open How French Player Support Impacts Visiting Competitors
May 30, 2025
French Open How French Player Support Impacts Visiting Competitors
May 30, 2025 -
 Savvato 10 5 Ti Na Deite Stin Tileorasi
May 30, 2025
Savvato 10 5 Ti Na Deite Stin Tileorasi
May 30, 2025 -
 Sporting Cp Boss Blocks Manchester United Transfer
May 30, 2025
Sporting Cp Boss Blocks Manchester United Transfer
May 30, 2025 -
 Ilaiyaraajas London Symphony Triumph Rajinikanths Acknowledgment
May 30, 2025
Ilaiyaraajas London Symphony Triumph Rajinikanths Acknowledgment
May 30, 2025
