Why Excessive Heat Warnings Are Often Missing From Weather Forecasts
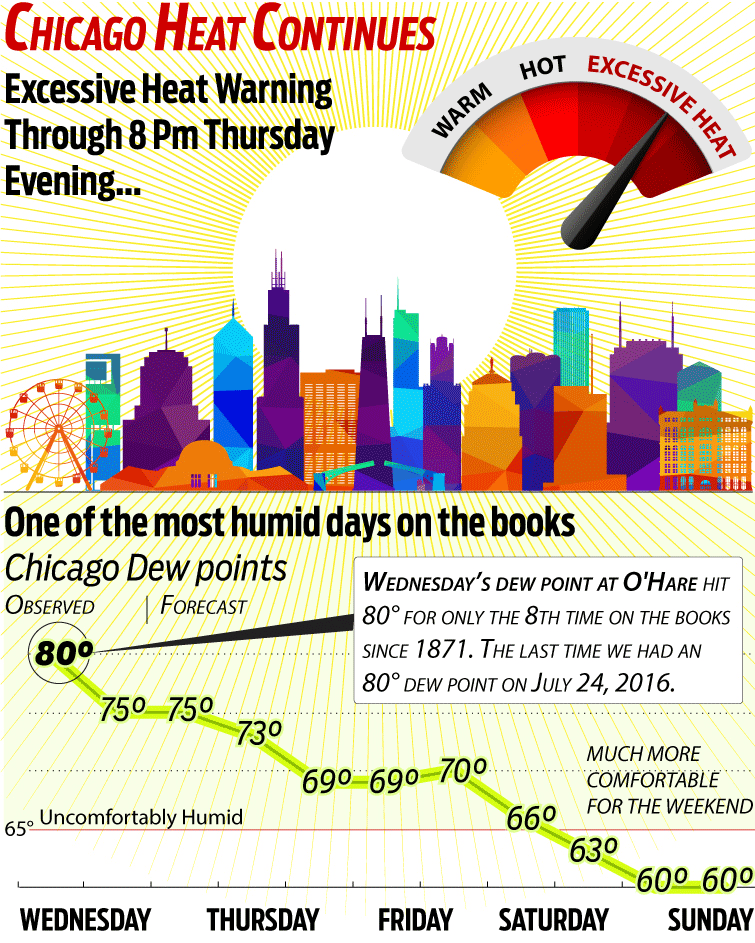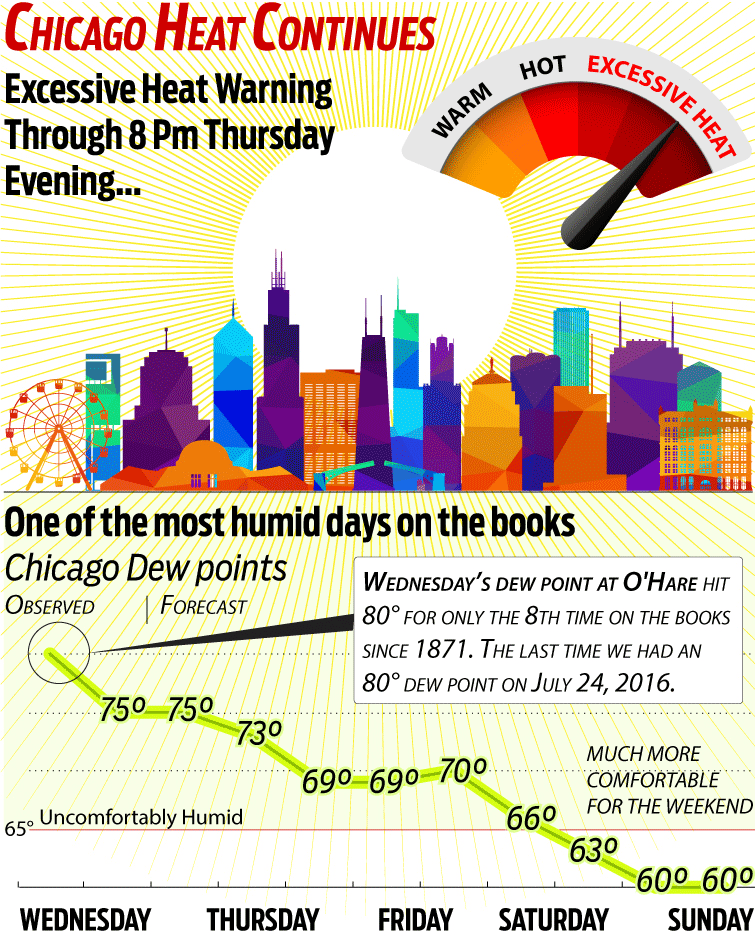
Table of Contents
Limited Technological Capabilities
Accurately predicting extreme heat events is far more complex than forecasting other severe weather phenomena. The challenges lie in the intricacies of atmospheric modeling and accurately predicting localized heat pockets, often referred to as "heat islands."
H3: Difficulty in Predicting Extreme Heat
- Lack of high-resolution data: Current weather models often lack the detailed data needed to pinpoint areas experiencing extreme heat with precision. This is especially true in urban areas where microclimates significantly impact temperature.
- Limitations in predicting heat islands: Urban heat islands, where temperatures are significantly higher than surrounding rural areas, are difficult to model accurately. The complex interaction between buildings, infrastructure, and vegetation makes precise prediction challenging.
- Difficulty in forecasting heat index accurately: The heat index, which combines temperature and humidity to reflect the perceived air temperature, is difficult to predict with complete accuracy, leading to potential underestimation of the actual heat risk.
H3: Data Gaps and Reporting Limitations
Insufficient weather stations, particularly in rural and sparsely populated areas, contribute to incomplete data sets. This limits the ability to accurately assess and predict localized extreme heat events.
- Uneven distribution of weather stations: Many regions, especially in developing countries, lack a sufficient network of weather stations to provide comprehensive data on temperature and humidity.
- Reliance on outdated technology: Some weather stations still rely on outdated technology, limiting the accuracy and timeliness of data collection.
- Lack of real-time data from specific locations: The absence of real-time data from vulnerable populations, such as those living in low-income neighborhoods or rural communities, further compounds the problem.
Prioritization of Other Weather Events
Severe weather events like hurricanes, tornadoes, and blizzards often overshadow the threat of excessive heat in both media coverage and resource allocation within meteorological agencies.
H3: Focus on More Immediate Threats
- Resource allocation to high-impact events: Meteorological services often prioritize resources towards events perceived as more immediate and life-threatening, like hurricanes or tornadoes, leaving less capacity for focused heat wave monitoring and warning systems.
- Public perception of heat as a less immediate danger: Many people underestimate the dangers of excessive heat, viewing it as a less immediate threat than other severe weather events. This perception can influence the allocation of resources and the prioritization of warnings.
- Limited media coverage of heat waves: Heat waves often receive less media attention compared to other severe weather events, despite their significant impact on public health.
H3: Lack of Public Awareness and Preparedness
The public's understanding of heat-related dangers and preparedness measures plays a crucial role in the effectiveness of heat warnings. A lack of awareness minimizes the perceived urgency for these warnings.
- Need for improved public education campaigns: More effective public health campaigns are crucial to educate individuals about heatstroke, its symptoms, and preventative measures.
- Highlighting the dangers of heatstroke: Public awareness campaigns must clearly communicate the potentially fatal consequences of heatstroke and the importance of taking protective action.
- Emphasizing personal preventative measures: Promoting individual preventative measures, such as staying hydrated, seeking shade, and limiting strenuous activity during peak heat hours, is essential in mitigating the impact of extreme heat.
Institutional and Policy Challenges
Insufficient funding and inconsistent warning systems further hinder the effectiveness of Excessive Heat Warnings.
H3: Underfunding of Meteorological Services
Limited funding hampers the development and implementation of advanced prediction models and warning systems.
- Budgetary constraints hindering technological upgrades: Many meteorological services lack the funding to invest in advanced technology, such as high-resolution weather sensors and sophisticated predictive models.
- Lack of investment in research and development of heat wave prediction models: Further research and development are needed to improve the accuracy of heat wave prediction models and to better understand the complex factors contributing to extreme heat events.
H3: Lack of Standardized Warning Systems
Inconsistent criteria and dissemination methods across different regions and countries lead to inconsistencies in heat warnings.
- Variations in heat index thresholds: Different regions may use different thresholds for issuing heat warnings, leading to inconsistencies in warning levels.
- Differences in warning dissemination methods: The methods used to disseminate heat warnings vary across different regions, leading to potential disparities in the reach and effectiveness of warnings.
- Inconsistent use of terminology: The use of inconsistent terminology in heat warnings can cause confusion and hinder public understanding of the risks involved.
Conclusion
The absence of timely and effective Excessive Heat Warnings is a critical public health issue resulting from a complex interplay of technological limitations, prioritization challenges, and institutional shortcomings. Improving the accuracy and dissemination of heat alerts requires a multi-faceted approach. We need improved data collection, advanced prediction models, increased public awareness, and better resource allocation. Demand better and more consistent Excessive Heat Warnings from your local meteorological services. Contact your representatives and advocate for improved funding and technology to better protect communities from the dangers of extreme heat. Let's work together to ensure that everyone has access to accurate and timely heat wave warnings, saving lives and preventing heat-related illnesses.

Featured Posts
-
 Dansk Chef Under Kritik Stjerne Beskylder For Mangel Pa Respekt
May 30, 2025
Dansk Chef Under Kritik Stjerne Beskylder For Mangel Pa Respekt
May 30, 2025 -
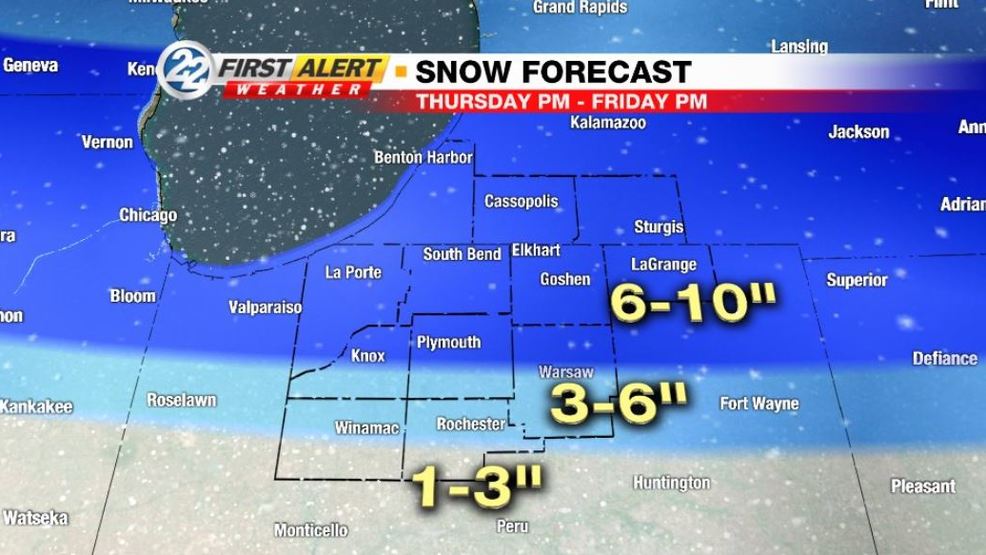 Snow Alert Significant Snow Accumulation In Western Manitoba
May 30, 2025
Snow Alert Significant Snow Accumulation In Western Manitoba
May 30, 2025 -
 311 Heat Related Deaths In England A Call For Improved Public Health Strategies
May 30, 2025
311 Heat Related Deaths In England A Call For Improved Public Health Strategies
May 30, 2025 -
 Cape Cod Red Tide Emergency What You Need To Know
May 30, 2025
Cape Cod Red Tide Emergency What You Need To Know
May 30, 2025 -
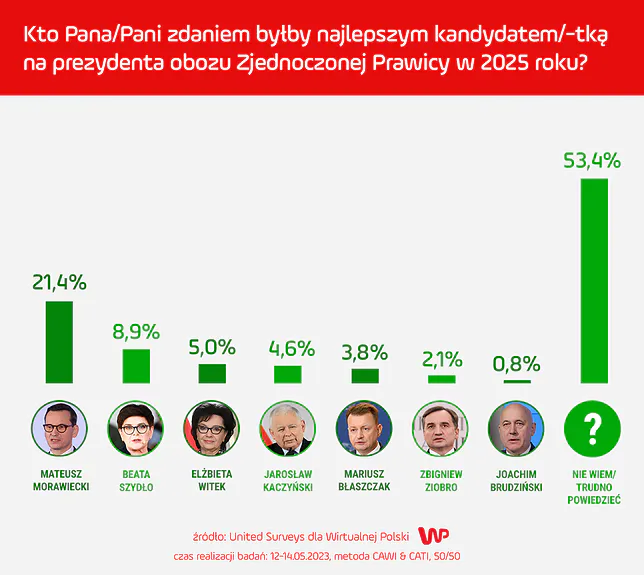 Wybory Prezydenckie 2025 Niespotykana Kampania Mentzena
May 30, 2025
Wybory Prezydenckie 2025 Niespotykana Kampania Mentzena
May 30, 2025
