AI And The Illusion Of Learning: Guiding Principles For Ethical Use
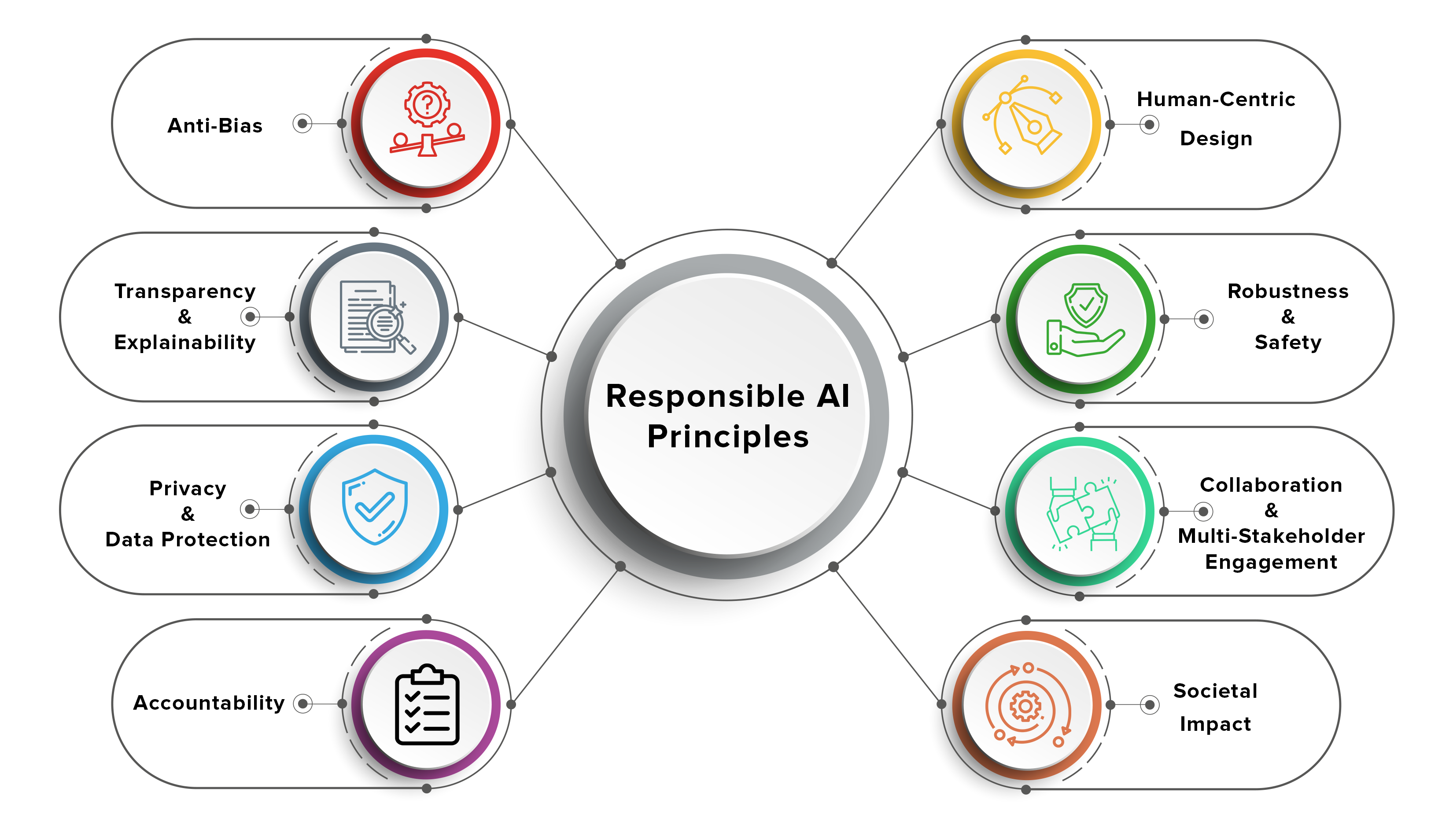
Table of Contents
Understanding the Limitations of Current AI: Beyond Superficial Intelligence
Current AI, despite its impressive feats, operates fundamentally differently than the human brain. While humans learn through genuine understanding and reasoning, AI systems primarily excel at pattern recognition and prediction. This distinction is critical. We often hear about "machine learning" and "deep learning," but these terms describe sophisticated statistical methods, not true comprehension. This distinction between artificial intelligence and human intelligence is often overlooked.
- AI excels at specific tasks but lacks general intelligence: An AI can master chess or translate languages but struggles with tasks outside its narrowly defined training parameters. This is known as "narrow AI," in contrast to the hypothetical "general AI" possessing human-like general intelligence.
- AI systems are trained on data; biases in the data lead to biased outcomes: AI algorithms learn from the data they are fed. If this data reflects societal biases (e.g., gender, racial, or socioeconomic), the AI system will inevitably perpetuate and even amplify those biases.
- AI's "learning" is based on statistical correlations, not true comprehension: AI identifies patterns and makes predictions based on statistical probabilities. It doesn't "understand" the underlying meaning or context in the same way a human does.
- The "black box" problem: Many complex AI systems, particularly deep learning models, operate as "black boxes." Their decision-making processes are opaque, making it difficult to understand how they arrive at specific conclusions. This lack of transparency poses significant ethical challenges.
Addressing Bias and Ensuring Fairness in AI Systems
The presence of bias in AI systems is a major ethical concern. Algorithmic bias can lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes in various domains.
- Examples of AI bias: Facial recognition systems have demonstrated higher error rates for people of color, loan applications have been unfairly denied based on biased algorithms, and AI-driven criminal justice tools have been shown to perpetuate existing inequalities.
- Techniques for detecting and mitigating bias: Researchers are developing methods to identify and mitigate bias in algorithms, including techniques for data pre-processing, algorithm design, and post-processing adjustments.
- The role of human oversight: Human oversight is crucial to ensure fairness and accountability. Experts must carefully monitor AI systems, identify potential biases, and intervene when necessary.
- The need for transparency: Transparency in AI development and deployment is vital to building trust and ensuring accountability. Clear explanations of how AI systems work and the data used to train them are essential.
The Importance of Transparency and Explainability in AI
Understanding how AI systems make decisions is critical, especially in high-stakes scenarios. The "black box" nature of some AI models raises significant ethical concerns.
- Challenges in interpreting AI decision-making: The complexity of deep learning models makes it difficult to interpret their internal processes and understand the reasoning behind their outputs.
- Explainable AI (XAI): The field of explainable AI is developing techniques to make AI systems more transparent and understandable. These methods aim to provide insights into the decision-making process of complex AI models.
- Ethical implications of "black box" AI: Using opaque AI systems in high-stakes decisions, such as loan approvals or medical diagnoses, raises significant ethical concerns.
- Regulations and standards for transparency: Governments and regulatory bodies are beginning to develop standards and regulations for transparency in AI to ensure accountability and promote responsible innovation.
Responsible Data Handling and Privacy in the Age of AI
AI systems rely heavily on data, raising crucial ethical concerns about data collection, storage, and use.
- Data privacy regulations: Regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) are designed to protect individuals' data privacy. These regulations have significant implications for the development and deployment of AI systems.
- Informed consent and data security: Obtaining informed consent from individuals before collecting and using their data is paramount. Robust data security measures are necessary to prevent data breaches and misuse.
- Potential for misuse of personal data: AI systems can be used to infer sensitive information about individuals, raising concerns about privacy violations and potential discrimination.
- Ethical considerations for data anonymization and de-identification: Techniques for anonymizing and de-identifying data are crucial to protecting individual privacy while still allowing the use of data for AI development.
Conclusion: Guiding the Future of AI: Ethical Considerations for Responsible Development
The illusion of learning in AI highlights the critical need for ethical considerations in its development and deployment. We've seen that current AI systems, while powerful, are limited in their understanding and prone to bias. Addressing these limitations requires a concerted effort towards fairness, transparency, and responsible data handling. Understanding the inherent limitations of AI, actively mitigating bias, ensuring transparency through explainable AI (XAI) techniques, and prioritizing ethical data handling are not merely optional; they are essential for building a future where AI benefits all of humanity. Engage in discussions about responsible AI development, advocate for policies that promote fairness, and continue exploring the complexities of "AI and the illusion of learning." The future of AI depends on our commitment to ethical development.

Featured Posts
-
 The Limitations Of Ai Learning A Guide To Ethical And Effective Application
May 31, 2025
The Limitations Of Ai Learning A Guide To Ethical And Effective Application
May 31, 2025 -
 Sopa Aragonesa En 20 Minutos Receta Casera Facil Sin Cebolla Ni Sobres
May 31, 2025
Sopa Aragonesa En 20 Minutos Receta Casera Facil Sin Cebolla Ni Sobres
May 31, 2025 -
 The Jn 1 Covid 19 Variant Everything You Need To Know About Symptoms And Prevention
May 31, 2025
The Jn 1 Covid 19 Variant Everything You Need To Know About Symptoms And Prevention
May 31, 2025 -
 Monte Carlo Defeat For Thompson
May 31, 2025
Monte Carlo Defeat For Thompson
May 31, 2025 -
 River Thames Rescue Police Search For Missing Child 11
May 31, 2025
River Thames Rescue Police Search For Missing Child 11
May 31, 2025
