Analyzing China's Rate Cuts And Increased Bank Lending In Response To Tariffs
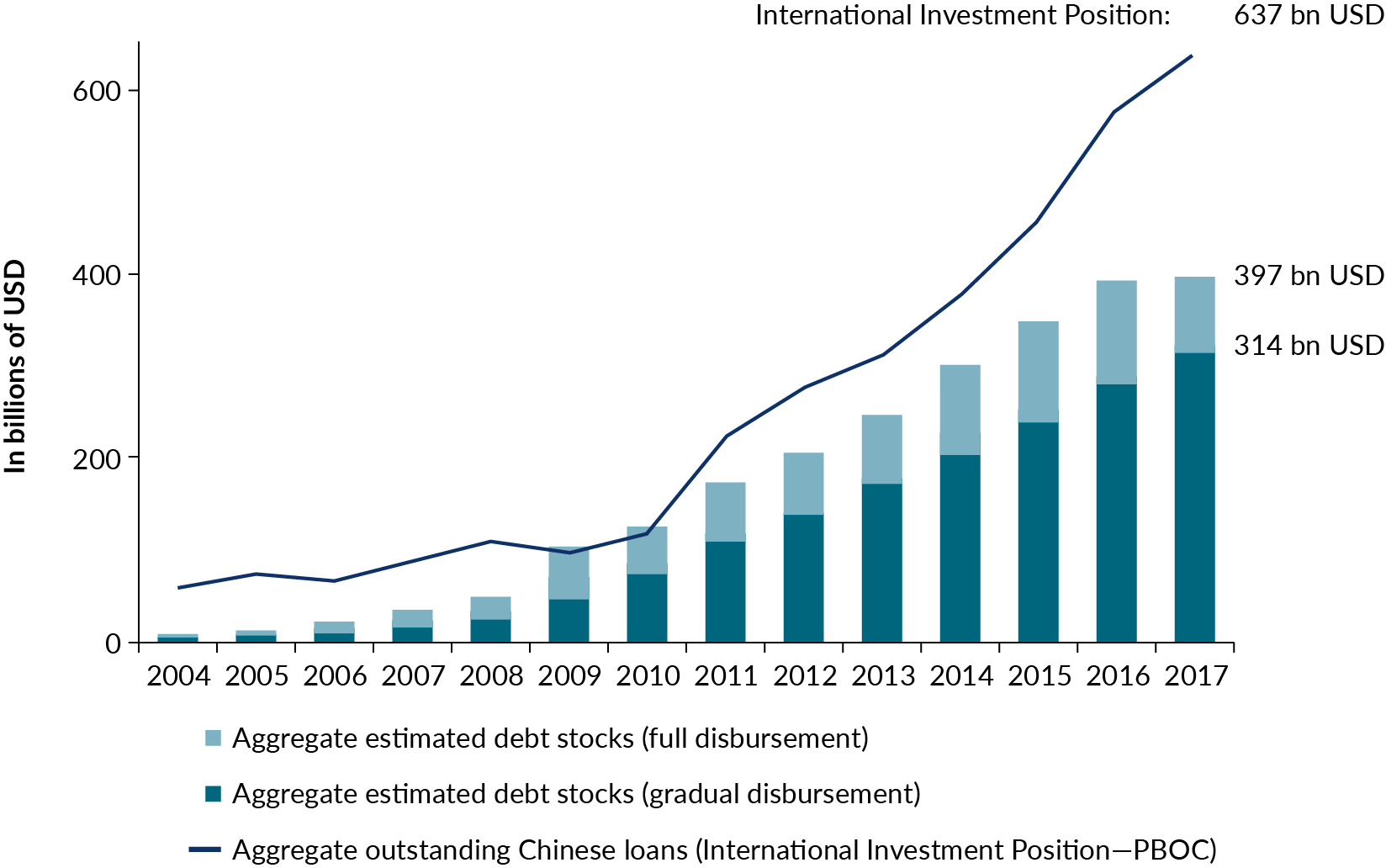
Table of Contents
Interest Rate Cuts as a Stimulus Tool
Interest rate cuts are a classic tool in monetary policy designed to stimulate economic activity. By lowering borrowing costs, central banks aim to encourage businesses and consumers to increase spending and investment. The People's Bank of China (PBOC), China's central bank, implemented several interest rate cuts in response to the escalating trade war. These cuts were strategically timed to coincide with periods of increased tariff pressure, aiming to offset the negative impact on economic growth.
- Specific Dates and Percentages of Rate Cuts: While precise dates vary depending on the specific rate (e.g., the benchmark lending rate, the reserve requirement ratio), a series of cuts were implemented throughout 2018 and 2019. These resulted in a significant reduction in borrowing costs compared to the pre-tariff period.
- Impact on Lending Rates for Businesses (e.g., SMEs): Lower benchmark rates translated into reduced borrowing costs for businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), which often rely heavily on bank loans for operations and expansion. This aimed to stimulate investment and prevent widespread business closures.
- Impact on Consumer Borrowing and Spending: Lower interest rates also made borrowing more attractive for consumers, potentially boosting spending on durable goods and other discretionary items. However, the effectiveness of this aspect was moderated by concerns about overall debt levels.
- Potential for Increased Investment: The lower cost of capital created a more favorable environment for investment in new projects, particularly in infrastructure and other key sectors.
Increased Bank Lending: Facilitating Investment and Consumption
Alongside interest rate cuts, the PBOC actively encouraged increased bank lending to fuel economic growth. This involved various measures, including lowering reserve requirements for banks, allowing them to lend more freely. The intention was to channel this increased credit towards investment projects and consumer spending.
- Quantitative Measures of Increased Lending: Significant increases in total bank lending were observed during this period, reflecting the PBOC's efforts to stimulate the economy. Specific figures can be sourced from official PBOC data and financial reports.
- Sectors Receiving the Most Credit (e.g., Infrastructure, Manufacturing): While lending expanded across various sectors, a significant portion targeted infrastructure projects and manufacturing, viewed as crucial for maintaining economic stability.
- Potential Risks of Non-Performing Loans: Rapid credit expansion always carries risks. The rapid increase in lending raised concerns about a potential surge in non-performing loans (NPLs) if borrowers struggle to repay due to economic slowdowns.
- Impact on Overall Debt Levels in China: The increased lending contributed to a further rise in China's overall debt levels, a long-term concern for the stability of the Chinese financial system.
Effectiveness of the Policy Response
Assessing the effectiveness of China's policy response requires a comprehensive analysis of macroeconomic indicators. While the rate cuts and increased lending undoubtedly injected liquidity into the economy, their success in fully mitigating the negative effects of tariffs remains debatable.
- Evidence of Increased Investment or Consumer Spending: While some evidence suggests increased investment in certain sectors and a modest rise in consumer spending, the impact was less dramatic than initially hoped.
- Analysis of GDP Growth Before and After Policy Implementation: Comparing GDP growth rates before and after the policy implementation provides insights into its effectiveness. While the growth rate might have been lower without the stimulus, it didn't fully return to pre-tariff levels.
- Discussion of Limitations of the Monetary Policy Response: Monetary policy alone has limitations. Structural reforms, fiscal stimulus, and trade negotiations are also necessary for sustainable economic growth.
- Mention of Other Government Policies Implemented Alongside Monetary Policy: China implemented other policies, such as fiscal stimulus measures, alongside monetary policy to support its economy.
Global Implications of China's Response
China's economic response to tariffs had significant global implications. The massive increase in bank lending and its impact on commodity demand influenced global markets, while the resulting economic slowdown in China had ripple effects on global supply chains.
- Impact on Global Commodity Prices: Increased demand for certain commodities driven by China's infrastructure projects affected their global prices.
- Effects on Global Supply Chains: China's economic slowdown impacted global supply chains, creating disruptions and uncertainties for businesses worldwide.
- Influence on International Capital Flows: China's economic policies influenced international capital flows, affecting investment decisions in other countries.
- Potential for Trade Tensions to Escalate Further: China's response, while aimed at mitigating the impact of tariffs, could also be viewed as a defensive measure that might further escalate trade tensions.
Conclusion: Assessing the Long-Term Impact of China's Rate Cuts and Lending on Economic Growth
China's response to US tariffs, involving interest rate cuts and increased bank lending, aimed to stimulate economic growth and counter the negative impact of trade tensions. While these measures injected liquidity into the economy, their effectiveness in fully offsetting the impact of tariffs remains a subject of ongoing debate. The substantial increase in debt levels poses a long-term risk to financial stability. Further analysis of China's interest rate cuts and bank lending, combined with a study of other government policies, is crucial for a complete understanding of this complex economic situation. Stay informed about future developments in China's monetary policy and its broader economic strategy to fully grasp the long-term impacts. Understanding China's response to tariffs requires ongoing monitoring of macroeconomic indicators and policy announcements.

Featured Posts
-
 Lahore Schools Adjust Timings For Psl Matches
May 08, 2025
Lahore Schools Adjust Timings For Psl Matches
May 08, 2025 -
 Brookfield Capitalizes On Market Dislocation With Opportunistic Investments
May 08, 2025
Brookfield Capitalizes On Market Dislocation With Opportunistic Investments
May 08, 2025 -
 Okc Thunders Unprecedented Double Performance Records
May 08, 2025
Okc Thunders Unprecedented Double Performance Records
May 08, 2025 -
 Recent Political Developments And The Xrp Price A Correlation Analysis
May 08, 2025
Recent Political Developments And The Xrp Price A Correlation Analysis
May 08, 2025 -
 Fundi I Eres Se Pese Yjeve Te Psg Nen Luis Enriquen
May 08, 2025
Fundi I Eres Se Pese Yjeve Te Psg Nen Luis Enriquen
May 08, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Aj Aym Aym Ealm Ky 12 Wyn Brsy Pakstan Bhr Myn Khraj Eqydt
May 08, 2025
Aj Aym Aym Ealm Ky 12 Wyn Brsy Pakstan Bhr Myn Khraj Eqydt
May 08, 2025 -
 2025 Ptt Personel Alim Tarihleri Kpss Li Ve Kpss Siz Pozisyonlar
May 08, 2025
2025 Ptt Personel Alim Tarihleri Kpss Li Ve Kpss Siz Pozisyonlar
May 08, 2025 -
 Qwmy Hyrw Aym Aym Ealm Ky 12 Wyn Brsy Yadgar Tqaryb Ka Aneqad
May 08, 2025
Qwmy Hyrw Aym Aym Ealm Ky 12 Wyn Brsy Yadgar Tqaryb Ka Aneqad
May 08, 2025 -
 Postane Alimlari 2025 Kpss Ile Personel Secimi Ve Basvuru Tarihleri
May 08, 2025
Postane Alimlari 2025 Kpss Ile Personel Secimi Ve Basvuru Tarihleri
May 08, 2025 -
 Ptt Personel Alimi 2025 Basvuru Tarihleri Ve Kpss Sartlari
May 08, 2025
Ptt Personel Alimi 2025 Basvuru Tarihleri Ve Kpss Sartlari
May 08, 2025
