Are We Normalizing Disaster? The Los Angeles Wildfires And The Gambling Culture

Table of Contents
The Increasing Frequency and Severity of Los Angeles Wildfires
The Impact of Climate Change
The dramatic increase in the frequency and severity of Los Angeles wildfires is undeniably linked to climate change. Rising temperatures, prolonged droughts, and increasingly erratic weather patterns create the perfect conditions for devastating wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly. This isn't just about the changing climate; it's about the changing landscape of risk in Los Angeles and how it affects our daily lives and long-term decision-making. Scientific studies consistently demonstrate the correlation between climate change and increased wildfire activity, emphasizing the urgency of addressing this issue. The increasing intensity of wildfires poses a direct threat to lives and property, influencing the overall societal risk tolerance and acceptance of such situations.
The Psychological Impact of Repeated Exposure
Repeated exposure to wildfires, even without direct personal experience of loss, can lead to a dangerous sense of normalization. This desensitization to the risk diminishes preparedness and fosters complacency.
- Increased Complacency: Residents may underestimate the threat, delaying evacuations or neglecting safety precautions.
- Decreased Preparedness: A feeling of inevitability can lead to a lack of planning and investment in wildfire prevention measures, both at the individual and community levels.
- Underestimation of Risk: The repetitive nature of the events can lead to a belief that the risks are less severe than they actually are, contributing to a false sense of security and increased risk tolerance.
Economic Consequences and Their Role in Risk Perception
The substantial economic losses associated with repeated wildfires can ironically influence risk-taking behavior in other areas. The financial strain caused by property damage, insurance claims, and displacement can lead individuals to seek quick financial gains, potentially increasing their involvement in high-risk activities like gambling, as they seek to recover lost funds or escape financial pressure. This creates a complex interplay between economic hardship and increased risk tolerance, feeding into the cycle of disaster normalization and problematic behavior.
The Gambling Culture in Los Angeles
Prevalence of Gambling in the Region
Los Angeles boasts a robust gambling culture, with numerous casinos, card rooms, and readily available lottery options. This widespread access to gambling opportunities, combined with extensive advertising and promotions, creates an environment where gambling is normalized and easily accessible to a broad population. The convenience and readily available nature of gambling activities contributes to the casual approach many individuals take toward this potentially high-risk behavior.
The Psychology of Gambling and Risk
The allure of gambling lies in its inherent uncertainty and the potential for significant rewards. The thrill of risk, the possibility of a life-changing win, and the dopamine rush associated with potential gains all contribute to the addictive nature of gambling. Advertising often plays a significant role in glamorizing gambling, obscuring the significant risks involved. The "big win" narrative frequently overshadows the more common reality of consistent losses.
The Relationship Between Risk-Taking and Disaster Normalization
The normalization of disaster, such as through repeated exposure to wildfires, can correlate with increased risk-taking in gambling. Individuals experiencing a desensitization to risk in one area might exhibit a similar attitude towards risk in others.
- "It's just a game" mentality: The casual approach to seemingly manageable risks, such as wildfires or smaller gambling bets, can translate into a diminished perception of the true consequences of potentially dangerous actions.
- Minimizing Potential Losses: The normalization of significant losses, such as those experienced during wildfires, might lead individuals to underestimate the potential financial devastation of gambling addiction.
- Failure to Acknowledge Personal Vulnerability: The sense of control and predictability often associated with daily life might be challenged by catastrophic events such as wildfires, leading to a compensatory attempt to regain control through gambling.
The Link Between Disaster Normalization and Gambling Addiction
Shared Psychological Mechanisms
Disaster normalization and gambling addiction share crucial psychological underpinnings. Both involve a distorted perception of risk, a reliance on reward systems (the positive reinforcement experienced after a win or the temporary escape from stress), and difficulties with emotional regulation (finding solace in immediate gratification rather than tackling underlying issues).
The Role of Coping Mechanisms
Gambling might serve as a maladaptive coping mechanism for the stress and anxiety associated with living in a region frequently threatened by wildfires. The temporary escape offered by gambling can become a destructive cycle, further exacerbating existing mental health challenges.
The Impact of Societal Messaging
Media portrayals of both wildfires and gambling can unintentionally contribute to a sense of normalization. The repetitive coverage of wildfires, without sufficient emphasis on the long-term risks and the need for preparedness, might contribute to a feeling of inevitability. Similarly, gambling advertisements that highlight the excitement and potential rewards without acknowledging the devastating consequences of addiction normalize risky behavior and contribute to its social acceptance.
Conclusion
The increasing frequency of devastating Los Angeles wildfires has the potential to foster a sense of disaster normalization, which, in turn, can influence risk tolerance and potentially contribute to problematic gambling behaviors. The shared psychological mechanisms, the role of coping mechanisms, and the impact of societal messaging all contribute to this complex interplay. It's crucial to acknowledge the potential link between these seemingly disparate phenomena.
Call to Action: Be mindful of the potential link between disaster normalization and problematic gambling. Practice responsible gambling habits, and seek help if needed. Resources are available: [Link to Gambling Addiction Support]. Prepare for wildfires: [Link to Wildfire Preparedness Information]. By understanding the connection between the normalization of disaster and the prevalence of risk-taking behavior, we can work towards building more resilient communities, both physically and mentally. The normalization of disaster like the Los Angeles wildfires shouldn't lead to the normalization of risky behavior like gambling addiction. Let's break the cycle.

Featured Posts
-
 Solve The Nyt Crossword Strands April 12 2025 Hints And Answers
May 10, 2025
Solve The Nyt Crossword Strands April 12 2025 Hints And Answers
May 10, 2025 -
 Le Cas Epicure La Ville De Dijon Et La Cite De La Gastronomie
May 10, 2025
Le Cas Epicure La Ville De Dijon Et La Cite De La Gastronomie
May 10, 2025 -
 The Trump Administrations First 100 Days And Elon Musks Net Worth
May 10, 2025
The Trump Administrations First 100 Days And Elon Musks Net Worth
May 10, 2025 -
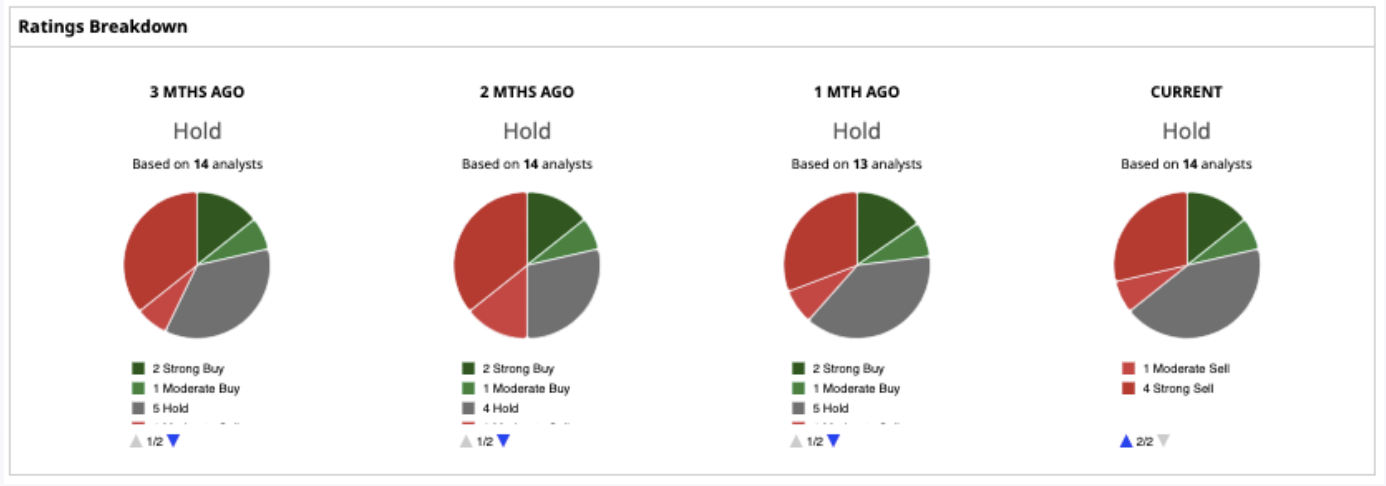 Up 40 In 2025 Evaluating The Investment Opportunity In Palantir Stock
May 10, 2025
Up 40 In 2025 Evaluating The Investment Opportunity In Palantir Stock
May 10, 2025 -
 The Lived Experiences Of Transgender People Navigating The Landscape Shaped By Trumps Policies
May 10, 2025
The Lived Experiences Of Transgender People Navigating The Landscape Shaped By Trumps Policies
May 10, 2025
