China's Export-Led Growth: A Rising Tide Of Tariff Risks

Table of Contents
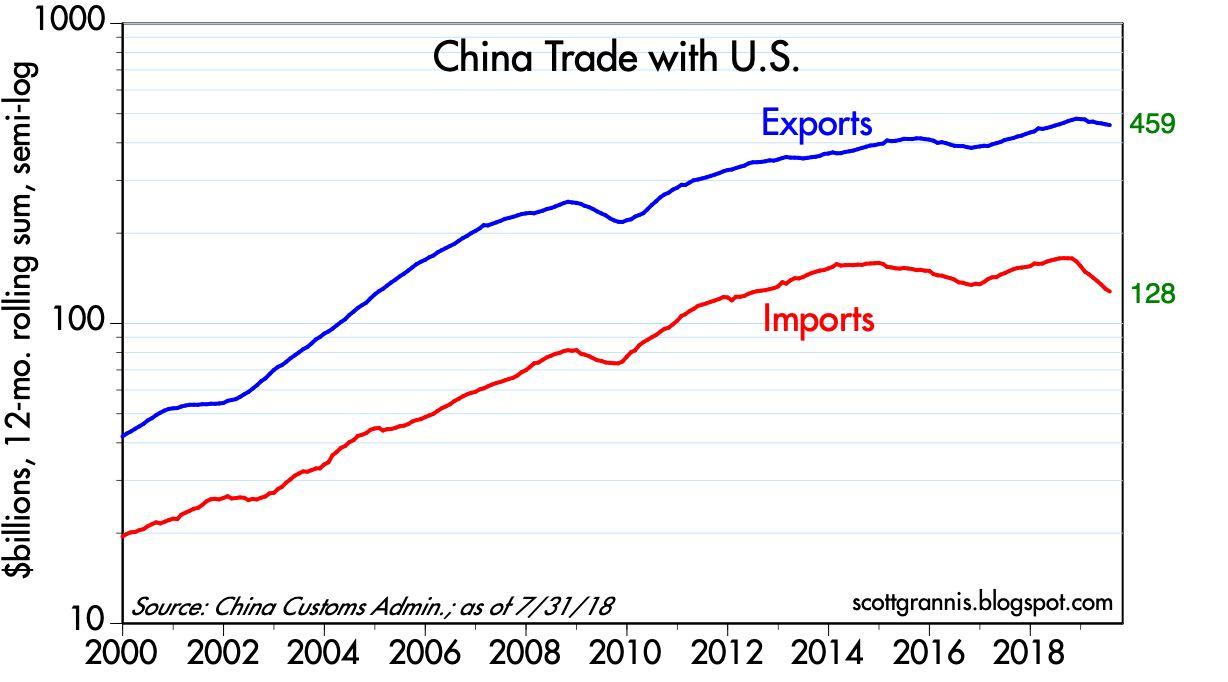
China's Export Dependence: A Double-Edged Sword
China's export-led growth strategy centers on producing goods for international markets, using this external demand to drive domestic economic expansion. Historically, this model has been incredibly effective. The country's integration into the global trading system propelled its economic miracle, lifting millions out of poverty.
- Historical Significance: China's accession to the World Trade Organization (WTO) in 2001 significantly accelerated its export growth, unlocking access to vast new markets.
- Benefits: Increased foreign exchange reserves, job creation, technological advancement through exposure to international competition, and rapid GDP growth.
- Drawbacks: Over-reliance on external demand makes the economy vulnerable to global economic downturns and protectionist policies. It can also lead to imbalances in economic development, neglecting domestic consumption.
Key Export Sectors Driving China's GDP:
- Electronics (smartphones, computers, etc.)
- Textiles and apparel
- Machinery and equipment
- Household goods
- Automotive parts
Illustrative Statistics (Note: Replace with up-to-date statistics):
- China's share of global export volume: [Insert statistic]
- Contribution of exports to China's GDP: [Insert statistic]
- Growth rate of key export sectors: [Insert statistics]
The Rising Tide of Trade Wars and Tariffs
The harmonious global trading environment that facilitated China's export boom is increasingly disrupted by escalating trade tensions. Trade disputes, particularly with the United States and the European Union, have led to the imposition of significant tariffs on numerous Chinese products.
- Trade Disputes: The US-China trade war, initiated in 2018, exemplifies the challenges. Tariff increases targeted various sectors, impacting export volumes and profitability. Similar tensions exist with the EU and other countries.
- Types of Tariffs and their Impact: Anti-dumping tariffs aim to counteract unfairly low pricing, while countervailing duties address government subsidies. These tariffs raise the cost of Chinese goods in target markets, reducing competitiveness.
- Impact on Specific Sectors: The electronics sector, for example, faced significant challenges due to tariffs on components and finished products. Similarly, textile and apparel exports have been affected.
Key Events Impacting China's Export Sector:
- [Insert specific dates and details of major trade disputes or tariff announcements.]
China's Response Strategies to Tariff Risks
Facing the threat of sustained trade wars, the Chinese government has adopted a multi-pronged approach to mitigate the negative impacts on its export-led growth.
- Diversification of Export Markets: Reducing dependence on any single market by actively pursuing new trade partnerships with countries in Africa, Latin America, and Asia.
- Stimulating Domestic Consumption: Government initiatives to boost domestic demand through measures like infrastructure investment and income support programs.
- Technological Upgrades: Investing in research and development to enhance competitiveness and move towards higher-value manufacturing.
- Policy Changes: Adjusting trade policies to address specific challenges and promoting greater self-reliance.
Key Government Initiatives:
- The Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), aimed at expanding infrastructure and trade links across Eurasia.
- Made in China 2025, a strategic plan to upgrade manufacturing capabilities.
- Various stimulus packages aimed at boosting domestic consumption.
Global Implications of China's Export Slowdown
A significant slowdown in China's export-led growth would have far-reaching global consequences, given its central role in global supply chains and international trade.
- Impact on Supply Chains: Many global companies rely on China for manufacturing and components. Disruptions would impact production schedules and potentially increase costs.
- Global Trade Impact: A decline in Chinese exports would affect global trade volumes and potentially trigger a domino effect on other economies.
- Economic Interdependence: The interconnectedness of the global economy means that a significant slowdown in China could trigger wider economic instability.
Key Dependent Industries and Regions:
- Technology companies reliant on Chinese manufacturing.
- Retailers dependent on Chinese-made goods.
- Countries with strong trade ties to China.
Conclusion: Charting a Course Through China's Export-Led Growth Challenges
China's export-led growth model faces significant headwinds due to escalating tariff risks. While this model has driven remarkable economic expansion, its vulnerability to protectionist measures necessitates diversification and adaptation. Understanding the complexities of this model and its global implications is crucial. China’s ability to successfully navigate these challenges, through initiatives like the BRI and a focus on domestic consumption, will significantly impact not only its own future but also the stability of the global economy. Further research into China's evolving trade strategies and the effectiveness of its responses to tariff risks is essential. Consider exploring related topics such as the long-term effects of the Belt and Road Initiative or the progress of China's efforts to cultivate a robust domestic consumer market to gain a fuller understanding of the future of China's export-led growth.

Featured Posts
-
 How Tariffs Threaten Chinas Export Led Growth Model
Apr 22, 2025
How Tariffs Threaten Chinas Export Led Growth Model
Apr 22, 2025 -
 China And Indonesia Deepen Security Ties Through High Level Talks
Apr 22, 2025
China And Indonesia Deepen Security Ties Through High Level Talks
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Revolutionizing Voice Assistant Creation Open Ais 2024 Innovation
Apr 22, 2025
Revolutionizing Voice Assistant Creation Open Ais 2024 Innovation
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Googles Monopoly The Growing Call For A Breakup
Apr 22, 2025
Googles Monopoly The Growing Call For A Breakup
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Chinas Economy Assessing The Risks Of Rising Tariffs On Exports
Apr 22, 2025
Chinas Economy Assessing The Risks Of Rising Tariffs On Exports
Apr 22, 2025
