How Tariffs Threaten China's Export-Led Growth Model
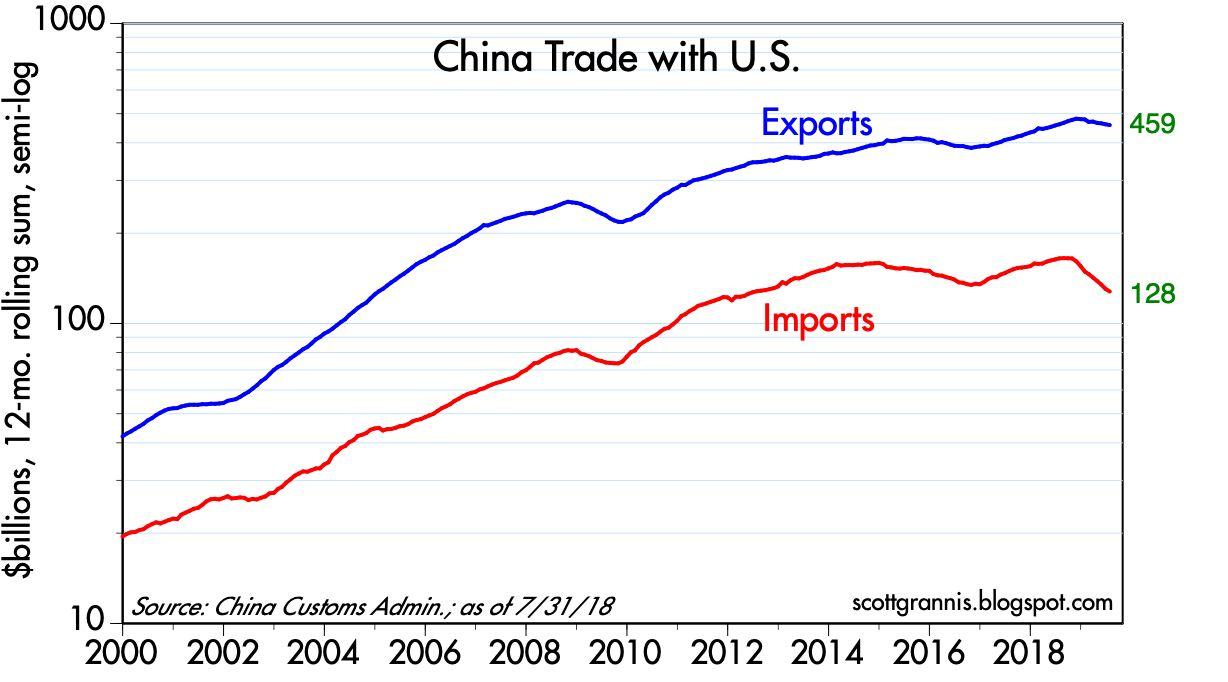
Table of Contents
The Impact of Tariffs on Chinese Exports
Tariffs, essentially taxes on imported goods, significantly reduce the competitiveness of Chinese products in international markets. This directly translates to decreased global demand for Chinese exports, jeopardizing the very foundation of China's economic strategy.
Reduced Global Demand
- Tariffs on Chinese electronics, a cornerstone of its export sector, have led to reduced demand in key markets like the US and Europe.
- Similarly, tariffs on textiles and clothing have impacted Chinese manufacturers, leading to decreased export volumes.
- Data from the World Trade Organization shows a marked decline in the value of Chinese exports following the implementation of several rounds of tariffs. This decline is particularly noticeable in industries heavily reliant on export markets, resulting in job losses and reduced economic activity in specific regions, especially those concentrated in manufacturing.
Increased Production Costs
Tariffs also increase the cost of imported raw materials and intermediate goods crucial for Chinese manufacturing. This leads to higher production costs and, consequently, less competitive export prices in the global market.
- Increased tariffs on essential raw materials, such as steel and rare earth minerals, directly impact the cost of production for a wide array of Chinese goods.
- These added costs force Chinese manufacturers to either absorb the increased expenses, reducing profit margins, or pass them on to consumers, making their products less attractive compared to competitors.
- This pressure is driving some businesses to relocate their production facilities to countries with lower tariffs, further weakening China's manufacturing base.
Retaliatory Tariffs and Trade Wars
China's response to imposed tariffs often involves retaliatory measures, further complicating the situation and harming its own export sector. These trade wars create a negative feedback loop, damaging global economic growth and exacerbating the challenges faced by Chinese exporters.
- Retaliatory tariffs on agricultural products from the US and other countries have disrupted supply chains and impacted Chinese consumers and businesses.
- The resulting trade tensions have created uncertainty in the global market, making it more difficult for Chinese businesses to plan for the future and hindering investment.
- The broader consequences of these trade wars extend beyond China, impacting global economic growth and potentially destabilizing the international trading system.
Alternative Growth Strategies for China
Faced with these challenges, China needs to diversify its economic model and reduce its over-reliance on exports. This requires a strategic shift toward alternative growth strategies.
Focus on Domestic Consumption
Stimulating domestic consumption can significantly reduce dependence on exports. The Chinese government is actively pursuing policies aimed at boosting domestic demand, including measures to increase disposable income and improve infrastructure.
- Initiatives focused on expanding social security systems and improving access to healthcare aim to boost consumer confidence and spending.
- Significant investments in infrastructure, particularly in transportation and urban development, aim to create economic opportunities and stimulate consumption.
- However, challenges remain, including addressing income inequality and fostering greater consumer confidence.
Technological Innovation and Upgrading
Moving up the value chain through technological innovation is critical for long-term sustainable growth. This involves investing in research and development (R&D) and fostering the growth of high-tech industries.
- Chinese companies are increasingly becoming global leaders in areas like renewable energy, telecommunications, and artificial intelligence.
- Government investment in R&D and supportive policies aimed at nurturing innovation are crucial for this transition.
- However, competition with established tech giants in the global market presents a significant challenge.
Investment in Services and High-Value Industries
Diversifying beyond manufacturing by focusing on the service sector and high-value industries is crucial. This includes developing sectors like finance, tourism, and technology services.
- The Chinese service sector is already a significant contributor to the economy and shows substantial growth potential.
- Government efforts to attract foreign investment in these sectors aim to promote innovation and technological advancement.
- This diversification can create a more resilient and balanced economy, less vulnerable to external shocks like tariffs.
Long-Term Implications for China's Economic Growth
The continued imposition of tariffs poses significant risks to China's economic growth, with potentially far-reaching consequences.
Potential for Economic Slowdown
The combination of reduced export demand, increased production costs, and trade wars could lead to a significant slowdown in China's economic growth.
- This slowdown would likely result in job losses and reduced income levels, potentially creating social and political instability.
- Maintaining stable economic growth is crucial for ensuring social harmony and political stability.
Geopolitical Consequences
China's economic challenges have broader geopolitical implications, affecting its relationships with other countries and the global economic order.
- Increased international tensions due to trade disputes could lead to further instability in the global economic system.
- The future of global trade and the international economic order will significantly be influenced by how China navigates these economic challenges.
Conclusion: Navigating the Threat of Tariffs to China's Export-Led Growth Model
Tariffs present a significant threat to China's export-led growth model, with potentially severe long-term economic and geopolitical consequences. The country's continued economic prosperity depends on successfully adapting to these new realities and embracing alternative growth strategies. Further research and policy discussions are essential to ensure China's continued economic prosperity and its ability to navigate the complexities of the global trading environment in the face of increasing protectionism and trade wars. Understanding the impact of tariffs on China's export-led growth model is crucial for navigating the complexities of the global economy.

Featured Posts
-
 The Looming Threat Of Googles Breakup Examining The Antitrust Concerns
Apr 22, 2025
The Looming Threat Of Googles Breakup Examining The Antitrust Concerns
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Signal Chat Leak Hegseths Military Plans Exposed Family Members Included
Apr 22, 2025
Signal Chat Leak Hegseths Military Plans Exposed Family Members Included
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Understanding High Stock Valuations Bof As Insights For Investors
Apr 22, 2025
Understanding High Stock Valuations Bof As Insights For Investors
Apr 22, 2025 -
 1 Billion Funding Cut Exclusive Look At Trumps Harvard Dispute
Apr 22, 2025
1 Billion Funding Cut Exclusive Look At Trumps Harvard Dispute
Apr 22, 2025 -
 Anchor Brewing Company To Shutter A Legacy Ends
Apr 22, 2025
Anchor Brewing Company To Shutter A Legacy Ends
Apr 22, 2025
