China's Next Giant Leap: A Supercomputer In Space
Table of Contents
The Need for a Space-Based Supercomputer
The limitations of current Earth-bound supercomputers are significant, hindering progress in several critical areas. A space-based supercomputer offers a compelling solution to these limitations, paving the way for unprecedented scientific advancements.
Limitations of Earth-Bound Systems
Earth-based supercomputers, despite their immense processing power, face inherent constraints:
- Limited processing power for certain tasks: Extremely complex simulations, such as those required for detailed climate modeling or advanced astrophysical research, often exceed the capacity of even the most powerful terrestrial systems.
- Susceptibility to natural disasters: Earthquakes, floods, and other natural events can severely damage or destroy these expensive and delicate facilities, causing significant disruptions to research.
- High energy costs: The enormous energy consumption of supercomputers translates to significant operational costs and a substantial carbon footprint.
- Geographical limitations affecting access and collaboration: The physical location of supercomputers can restrict access for researchers in different parts of the world, hindering international collaboration.
Advantages of a Space-Based Environment
Placing a supercomputer in space offers several significant advantages:
- Reduced gravity impact on components: The absence of significant gravitational forces minimizes stress on sensitive components, potentially improving their lifespan and performance.
- Improved signal reception and transmission for deep space exploration: A space-based supercomputer would enjoy unparalleled access to data from deep space probes and telescopes, enabling faster and more comprehensive analysis.
- Potential for increased processing speed and efficiency due to environmental factors: The unique environmental conditions of space could potentially lead to increased processing speed and energy efficiency compared to terrestrial systems.
- Unique opportunities for astronomical observation and data analysis: A space-based supercomputer can be directly integrated with space telescopes and observatories, providing real-time analysis of astronomical phenomena.
Technological Challenges and Innovations
Developing and deploying a space-based supercomputer presents formidable technological challenges. Overcoming these hurdles requires significant advancements in miniaturization, power efficiency, and radiation hardening.
Miniaturization and Power Efficiency
Miniaturizing a supercomputer for space while maintaining its computational power requires groundbreaking innovations:
- Development of new, smaller, and more efficient processors: New processor architectures and materials are needed to achieve the necessary miniaturization and power efficiency.
- Advanced cooling systems for space: Innovative cooling systems are crucial to dissipate heat generated by the supercomputer in the vacuum of space.
- Sustainable power sources for prolonged operation: Reliable and long-lasting power sources are essential for the continuous operation of the space-based supercomputer.
Radiation Hardening and Space Qualification
Protecting the supercomputer from the harsh space environment is crucial:
- Shielding against cosmic rays and solar flares: Robust shielding is required to protect sensitive components from high-energy particles and radiation.
- Rigorous testing procedures to ensure system reliability: Extensive testing is necessary to validate the supercomputer’s ability to withstand the extreme conditions of space.
- Fault-tolerant design for mission criticality: The system needs to be designed to tolerate failures and continue operating even with component malfunctions.
Potential Applications and Scientific Breakthroughs
A space-based supercomputer has the potential to revolutionize various scientific fields:
Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Faster processing of astronomical data: Enabling rapid analysis of vast datasets from space telescopes like the James Webb Space Telescope.
- Real-time analysis of events like supernovae: Allowing for immediate responses to transient astronomical events.
- Improved accuracy in cosmological simulations: Leading to a more profound understanding of the universe's origin and evolution.
- Potential discoveries in dark matter and dark energy research: Facilitating new research avenues in these enigmatic areas of cosmology.
Materials Science and Drug Discovery
- Advanced simulations to design new materials with specific properties: Accelerating the development of advanced materials for various applications.
- Faster drug discovery through efficient molecular modeling: Enabling the faster identification and development of new drugs and therapies.
- Personalized medicine advances through improved genetic analysis: Leading to more tailored and effective medical treatments.
Climate Modeling and Earth Observation
- Enhanced climate change prediction models: Providing more accurate and reliable predictions of future climate scenarios.
- Improved weather forecasting: Leading to more accurate and timely weather forecasts.
- Better monitoring of environmental changes through satellite data analysis: Enabling better understanding and management of environmental resources.
- Support for sustainable resource management: Facilitating data-driven decisions for sustainable resource utilization.
International Collaboration and Competition
China's space-based supercomputer initiative has significant global implications:
Global Implications
- Increased competition in space technology: Stimulating advancements in space technology globally.
- Potential for international partnerships in scientific research: Creating opportunities for collaboration on large-scale scientific projects.
- Implications for data sharing and access: Raising questions about data ownership and accessibility.
- Advancements in space-based infrastructure: Driving the development of advanced space-based infrastructure.
Conclusion
China's ambitious plan to launch a supercomputer into space represents a significant leap forward in scientific and technological innovation. This initiative holds immense potential to revolutionize various scientific fields, accelerating breakthroughs in astronomy, materials science, and climate modeling, among others. The technological challenges are substantial, but the potential rewards justify the investment. The successful deployment of a space-based supercomputer will not only solidify China's position as a global leader in technological advancement but also pave the way for unprecedented scientific discoveries. Stay informed about the progress of this game-changing project and the future of China's space-based supercomputer.

Featured Posts
-
 Analyzing Liverpool Arne Slot And Luis Enriques Views On Luck And Alisson
May 21, 2025
Analyzing Liverpool Arne Slot And Luis Enriques Views On Luck And Alisson
May 21, 2025 -
 Understanding And Addressing The Increase In Femicide
May 21, 2025
Understanding And Addressing The Increase In Femicide
May 21, 2025 -
 Adios Enfermedades Cronicas El Superalimento Que Necesitas Para Una Vida Larga Y Saludable
May 21, 2025
Adios Enfermedades Cronicas El Superalimento Que Necesitas Para Una Vida Larga Y Saludable
May 21, 2025 -
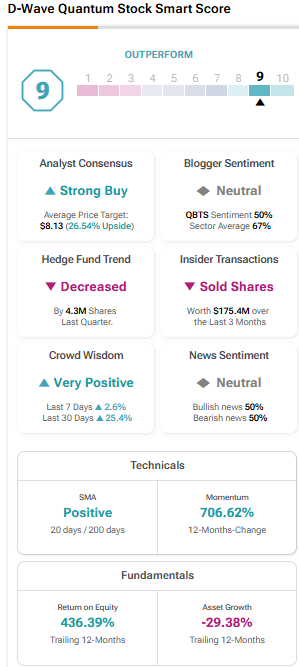 The D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Market Crash On Monday Causes And Effects
May 21, 2025
The D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Market Crash On Monday Causes And Effects
May 21, 2025 -
 D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Jump On Monday Analysis Of The Market Movement
May 21, 2025
D Wave Quantum Qbts Stock Jump On Monday Analysis Of The Market Movement
May 21, 2025
