England's Heatwave Death Toll Reaches 311: Lessons Learned And Future Preparations

Table of Contents
The Devastating Impact of the Heatwave
High Mortality Rates and Vulnerable Groups
The England heatwave disproportionately impacted vulnerable populations, leading to significantly higher mortality rates. The elderly, those with pre-existing health conditions, and socially isolated individuals were particularly at risk.
- Statistics on age-related deaths: Preliminary data suggests a significant increase in deaths among individuals aged 65 and older during the heatwave, accounting for a large proportion of the overall heatwave mortality rate.
- Impact on specific health conditions: Individuals with cardiovascular disease, respiratory illnesses, and chronic kidney disease experienced exacerbated symptoms and increased mortality risks due to the extreme heat. The heatwave vulnerability of these groups necessitates targeted support.
- The role of social isolation and lack of access to cooling: Social isolation played a crucial role, leaving many vulnerable individuals without access to support or cooling facilities. This highlights the need for community initiatives to reach and protect those most at risk from heatwave vulnerability. Lack of access to adequate cooling exacerbated the situation, contributing significantly to excess deaths.
Strain on Healthcare Services
The intense heat placed immense strain on England's healthcare system. Hospitals and emergency services faced unprecedented pressure, struggling to cope with the surge in patients.
- Increased hospital admissions: Admissions for heat-related illnesses, such as heatstroke and dehydration, dramatically increased, overwhelming hospital capacity.
- Ambulance callouts: Emergency services reported a significant rise in ambulance callouts, further stretching already limited resources. The NHS heatwave response was tested to its limits.
- Strain on NHS resources: The increased demand for medical services resulted in staff shortages and delays in treatment, impacting the overall quality of care. This emphasizes the need to improve healthcare capacity and plan for future heatwaves.
Lessons Learned from the 2023 Heatwave
Failures in Early Warning Systems
Shortcomings in the heatwave warning system and public communication contributed to the high death toll. Improvements are crucial to ensure timely and effective warnings.
- Ineffective messaging: Heatwave alerts often lacked clarity and urgency, failing to effectively communicate the severity of the risk.
- Lack of reach to vulnerable groups: Many vulnerable individuals, especially those socially isolated or with limited access to information, did not receive timely warnings.
- Delayed warnings: In some instances, warnings were issued too late to allow for adequate preventative measures. This resulted in increased heatwave vulnerability for those affected.
- Lack of clear action plans: The messaging often lacked concrete advice on how individuals and communities should respond to the extreme heat.
Insufficient Community Support and Resources
A lack of adequate resources and support systems for vulnerable populations during the heatwave exacerbated the situation.
- Lack of access to cooling centers: Insufficient numbers of cooling centers meant many vulnerable individuals lacked access to safe and comfortable spaces to escape the heat.
- Insufficient support for home-bound individuals: Many homebound individuals lacked the necessary support to stay safe and hydrated during the heatwave.
- Inadequate provision of water and essential supplies: Access to clean drinking water and other essential supplies remained limited in some areas, hindering the ability of vulnerable individuals to cope with the extreme heat.
Improving Future Heatwave Preparations
Enhancing Early Warning and Communication Strategies
Significant improvements are needed to ensure timely and effective communication of heatwave warnings, reducing heatwave mortality.
- Targeted communication to vulnerable groups: Warnings must be tailored to reach vulnerable groups through diverse channels and languages.
- Multilingual resources: Information needs to be readily available in multiple languages to cater to diverse communities.
- Proactive community outreach: Active community engagement is crucial to raise public awareness and ensure that information reaches those most at risk.
- Use of multiple communication channels: Employing a range of communication channels, such as social media, local media, and community networks, is essential to reach a broader audience.
Strengthening Community Support and Infrastructure
Bolstering community resources and support systems will be vital to mitigate the impact of future heatwaves.
- Increased funding for cooling centers: A significant increase in funding is needed to establish more cooling centers and expand their capacity.
- Community-based support programs: Develop and implement community-based support programs specifically designed to assist vulnerable individuals during heatwaves.
- Partnerships with voluntary organizations: Collaboration with voluntary and community organizations is crucial to enhance outreach and support efforts.
- Improved access to water and essential supplies: Ensuring access to clean drinking water and essential supplies is vital for vulnerable populations.
Investing in Climate Change Adaptation
Long-term strategies to mitigate the effects of climate change and the increasing frequency of heatwaves are crucial.
- Building regulations incorporating heat resilience: Update building regulations to incorporate measures that improve heat resilience in new constructions.
- Urban planning strategies to promote cooling: Implement urban planning strategies that prioritize green spaces, shade, and natural ventilation to mitigate the urban heat island effect.
- Investment in green infrastructure: Invest in green infrastructure, such as trees and green roofs, to reduce temperatures and improve air quality.
Conclusion
The tragic loss of life during England's recent heatwave underscores the urgent need for improved heatwave preparedness. This requires a multi-pronged approach encompassing better early warning systems, strengthened community support, and long-term investment in climate change adaptation. We must learn from this devastating event and implement effective strategies to protect vulnerable populations and minimize the impact of future heatwaves. Failure to act decisively risks repeating this tragedy. Let's work together to create a more resilient England, better prepared for the challenges of extreme heat. Invest in better England heatwave preparedness today, and save lives tomorrow.

Featured Posts
-
 Amysha Ptyl Ky Hamlgy Ky Khbryn Tsawyr Ne Mdahwn Myn Khbrwn Ka Twfan Le Aya
May 30, 2025
Amysha Ptyl Ky Hamlgy Ky Khbryn Tsawyr Ne Mdahwn Myn Khbrwn Ka Twfan Le Aya
May 30, 2025 -
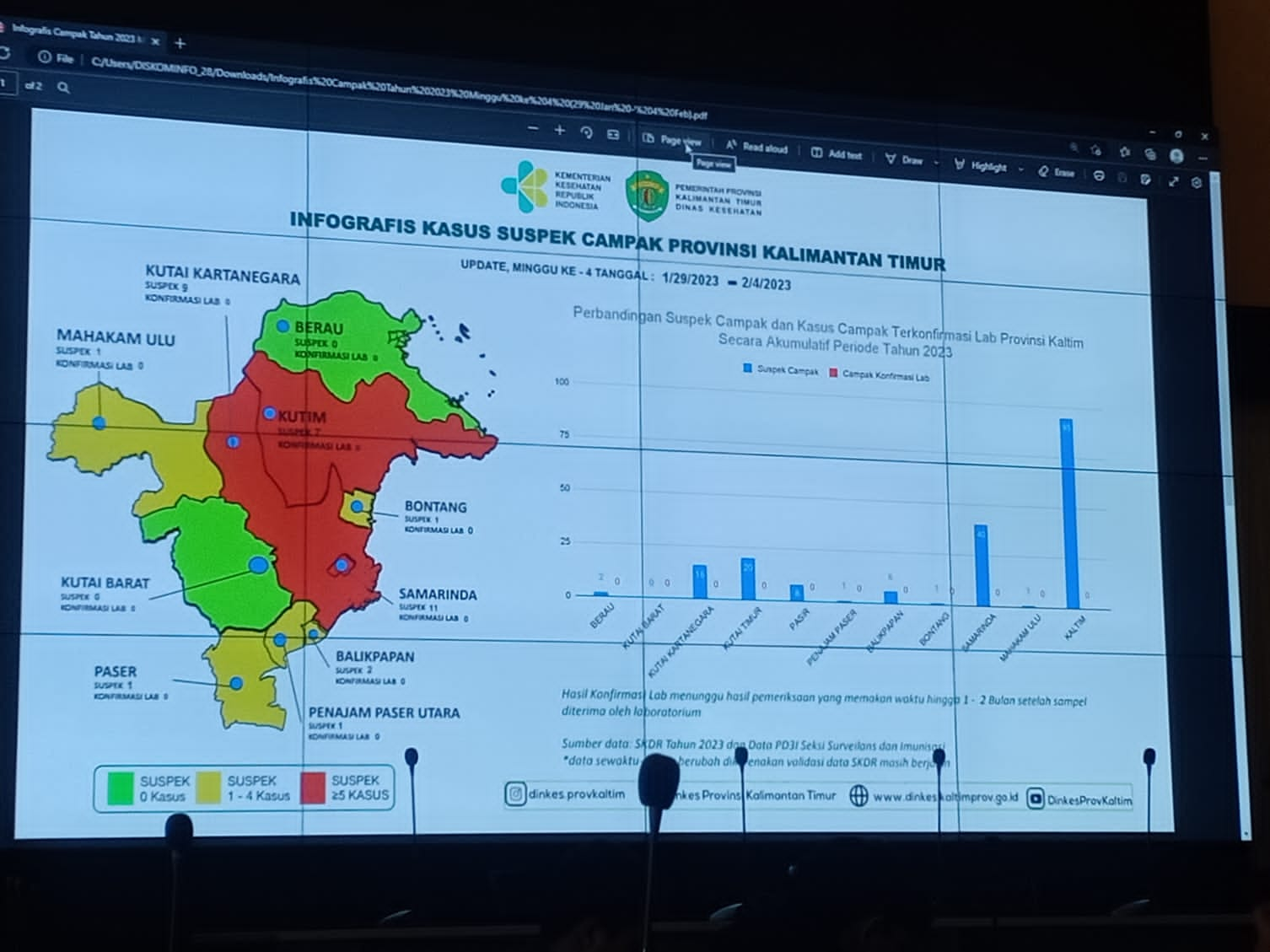 Imunisasi Anak Rendah Kasus Suspek Campak Di Pohuwato Melonjak Peringatan Dinkes Gorontalo
May 30, 2025
Imunisasi Anak Rendah Kasus Suspek Campak Di Pohuwato Melonjak Peringatan Dinkes Gorontalo
May 30, 2025 -
 Maitriser Les Droits De Douane Tout Ce Que Vous Devez Savoir
May 30, 2025
Maitriser Les Droits De Douane Tout Ce Que Vous Devez Savoir
May 30, 2025 -
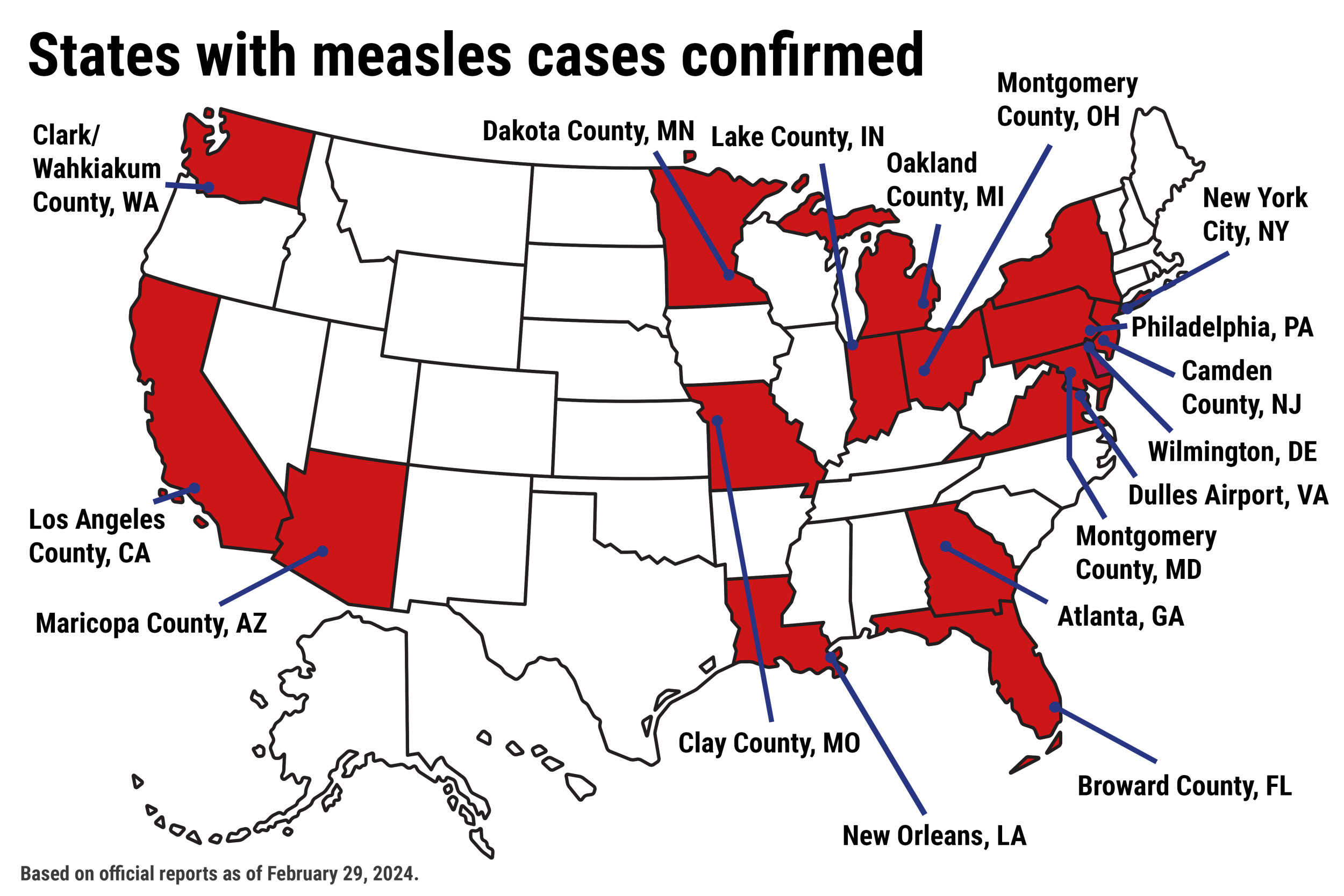 The Return Of Measles Examining The Kansas Outbreak
May 30, 2025
The Return Of Measles Examining The Kansas Outbreak
May 30, 2025 -
 Fridays Market Outlook Further Losses Expected For Live Music Stocks
May 30, 2025
Fridays Market Outlook Further Losses Expected For Live Music Stocks
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Donald Trump And His Friend Separating Fact From Fiction In The Viral Story
May 31, 2025
Donald Trump And His Friend Separating Fact From Fiction In The Viral Story
May 31, 2025 -
 Rolan Garos 2024 Kontuziyata Na Grigor Dimitrov Analiz I Prognozi
May 31, 2025
Rolan Garos 2024 Kontuziyata Na Grigor Dimitrov Analiz I Prognozi
May 31, 2025 -
 15 Godini Rolan Garos Za Grigor Dimitrov
May 31, 2025
15 Godini Rolan Garos Za Grigor Dimitrov
May 31, 2025 -
 Elon Musk Dogecoin And The Trump Administration A Retrospective Analysis
May 31, 2025
Elon Musk Dogecoin And The Trump Administration A Retrospective Analysis
May 31, 2025 -
 Rolan Garos 2024 Grigor Dimitrov Se Zavrscha
May 31, 2025
Rolan Garos 2024 Grigor Dimitrov Se Zavrscha
May 31, 2025
