Indonesia Reserve Drop: Rupiah Depreciation Impacts Foreign Exchange Holdings

Table of Contents
Factors Contributing to the Decline in Indonesia's Foreign Exchange Reserves
Several factors have contributed to the recent decline in Indonesia's foreign exchange reserves. These factors are intricately linked and often exacerbate each other's effects.
Impact of Global Economic Slowdown
The global economic slowdown significantly impacts Indonesia's reserves. A weaker global economy translates into reduced demand for Indonesian exports, a crucial source of foreign currency inflows. This decreased export revenue directly affects the country's ability to replenish its foreign currency reserves.
- Reduced Exports: Lower global demand leads to a decline in export earnings, reducing the supply of foreign currency entering the Indonesian economy.
- Decreased Foreign Investment (FDI): Uncertainty in the global economy discourages foreign direct investment, further limiting the inflow of foreign currency. Data from the World Bank shows a [Insert Data: Percentage change in FDI in Indonesia in the last year/quarter].
- Capital Flight: Investors may withdraw their funds from Indonesia in search of safer havens, leading to a rapid outflow of capital and depletion of foreign exchange reserves.
Rupiah Depreciation and its Role
The weakening of the Indonesian Rupiah (IDR) against major currencies like the US dollar (USD) plays a direct role in the decline of foreign exchange reserves. The central bank, Bank Indonesia (BI), often intervenes in the forex market to stabilize the Rupiah's value. These interventions involve using reserves to buy Rupiah, thus supporting its value. However, sustained intervention depletes the reserves.
- BI Intervention to Stabilize the Rupiah: Bank Indonesia's continuous intervention in the forex market to manage the Rupiah's exchange rate directly consumes foreign exchange reserves.
- Depletion of Reserves Due to Interventions: The more the Rupiah depreciates, the more BI needs to intervene, leading to a faster depletion of its reserves. [Insert Chart illustrating Rupiah exchange rate fluctuations against major currencies (USD, EUR, JPY) over the last year/quarter].
Increased Import Costs and Current Account Deficit
A weaker Rupiah increases the cost of imports, widening the current account deficit. This is because Indonesia needs more Rupiah to buy the same amount of foreign goods and services. A larger deficit necessitates more foreign currency to finance the gap, putting further pressure on reserves.
- Rising Import Prices: A weaker Rupiah makes imported goods more expensive, increasing inflation and impacting the purchasing power of consumers.
- Widening Current Account Deficit: The increase in import costs coupled with potentially lower export earnings leads to a larger current account deficit. [Insert Data: Indonesia's trade balance and current account deficit figures for the last year/quarter].
- Pressure on Reserves: The need to finance this widening deficit puts substantial pressure on the country's foreign exchange reserves.
The Ripple Effect: Impacts of Reduced Foreign Exchange Reserves
The dwindling foreign exchange reserves have a ripple effect across Indonesia's economy.
Impact on Indonesia's Credit Rating and Borrowing Costs
Lower reserves can negatively affect investor confidence, leading to potential downgrades in Indonesia's credit rating. This, in turn, increases borrowing costs for the government and businesses, making it more expensive to finance public spending and private investment.
- Potential Downgrades: Credit rating agencies may downgrade Indonesia's sovereign credit rating, making it riskier for international investors.
- Increased Borrowing Costs for the Government: Higher borrowing costs limit the government's ability to invest in crucial infrastructure and social programs.
- Higher Interest Rates: To attract foreign investment and stabilize the Rupiah, interest rates might rise, impacting borrowing costs for businesses and individuals.
Implications for Inflation and Purchasing Power
A weaker Rupiah fuels inflation by increasing the price of imported goods. This reduces the purchasing power of consumers, affecting their living standards.
- Increased Import Prices Leading to Higher Consumer Prices: The rising cost of imported goods is passed on to consumers, contributing to inflation.
- Reduced Real Incomes: Inflation erodes the real value of incomes, especially for low-income households, impacting their purchasing power.
Vulnerability to External Shocks
Reduced foreign exchange reserves leave Indonesia more vulnerable to future economic crises and external shocks. The country's ability to respond effectively to economic challenges is diminished.
- Reduced Ability to Manage External Debt: Lower reserves make it harder to manage and repay external debts.
- Decreased Capacity to Intervene in Forex Markets: The central bank's ability to stabilize the Rupiah through intervention is compromised.
Potential Mitigation Strategies and Policy Responses
Addressing the challenges posed by the decline in foreign exchange reserves requires a multi-pronged approach.
Strengthening the Rupiah through Monetary Policy
Bank Indonesia (BI) can use monetary policy tools to strengthen the Rupiah and manage inflation.
- Interest Rate Adjustments: Increasing interest rates can attract foreign investment, boosting demand for the Rupiah.
- Managing Liquidity in the Money Market: BI can control money supply to influence the exchange rate.
Promoting Exports and Diversifying the Economy
Boosting exports and reducing reliance on imports are crucial to improving the current account balance and strengthening the Rupiah.
- Export Diversification: Developing a wider range of export products reduces vulnerability to shocks in specific sectors.
- Attracting Foreign Investment in Export-Oriented Industries: FDI in export sectors can generate foreign currency inflows.
Fiscal Prudence and Debt Management
Sound fiscal management is essential to maintain investor confidence and ensure sustainable economic growth.
- Efficient Government Spending: Careful allocation of government resources is crucial to avoid unnecessary debt accumulation.
- Sustainable Debt Levels: Managing debt responsibly limits the risk of a debt crisis.
Conclusion
The decline in Indonesia's foreign exchange reserves, driven by Rupiah depreciation and global economic headwinds, presents serious challenges. Addressing these challenges requires a coordinated approach involving monetary policy adjustments, export promotion, fiscal prudence, and diversification strategies. Continuously monitoring the situation and understanding the implications of Indonesia's foreign exchange reserves is vital for navigating these complexities. By proactively implementing these measures, Indonesia can mitigate the risks and build a more resilient and stable economy. Staying informed about the dynamics of Indonesia foreign exchange reserves and Rupiah depreciation is crucial for investors and policymakers alike.

Featured Posts
-
 High Potentials Impressive Season Finale What Abc Must Have Thought
May 10, 2025
High Potentials Impressive Season Finale What Abc Must Have Thought
May 10, 2025 -
 Analysis Factors Behind Elon Musks Net Worth Drop Below 300 Billion
May 10, 2025
Analysis Factors Behind Elon Musks Net Worth Drop Below 300 Billion
May 10, 2025 -
 Metas 168 Million Payment In Whats App Spyware Case A Turning Point
May 10, 2025
Metas 168 Million Payment In Whats App Spyware Case A Turning Point
May 10, 2025 -
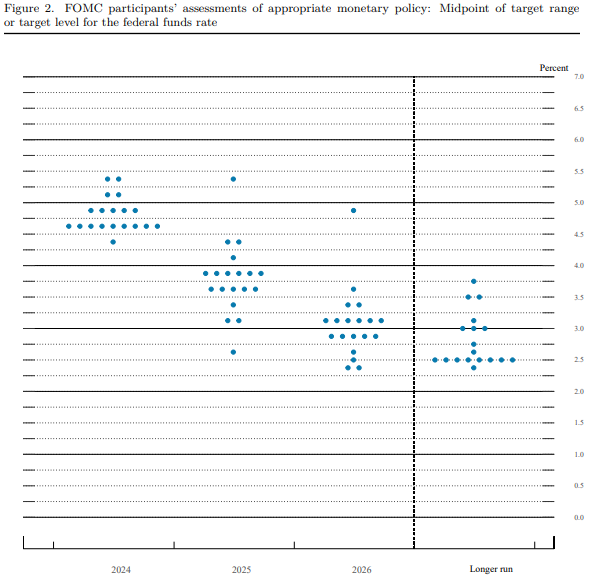 U S Federal Reserve Maintains Rates Inflation Unemployment Weigh Heavily
May 10, 2025
U S Federal Reserve Maintains Rates Inflation Unemployment Weigh Heavily
May 10, 2025 -
 Revealing Elizabeth Hurleys Daring Cleavage Photos And Fashion Choices
May 10, 2025
Revealing Elizabeth Hurleys Daring Cleavage Photos And Fashion Choices
May 10, 2025
