Manila Bay's Current State: A Study In Environmental Resilience
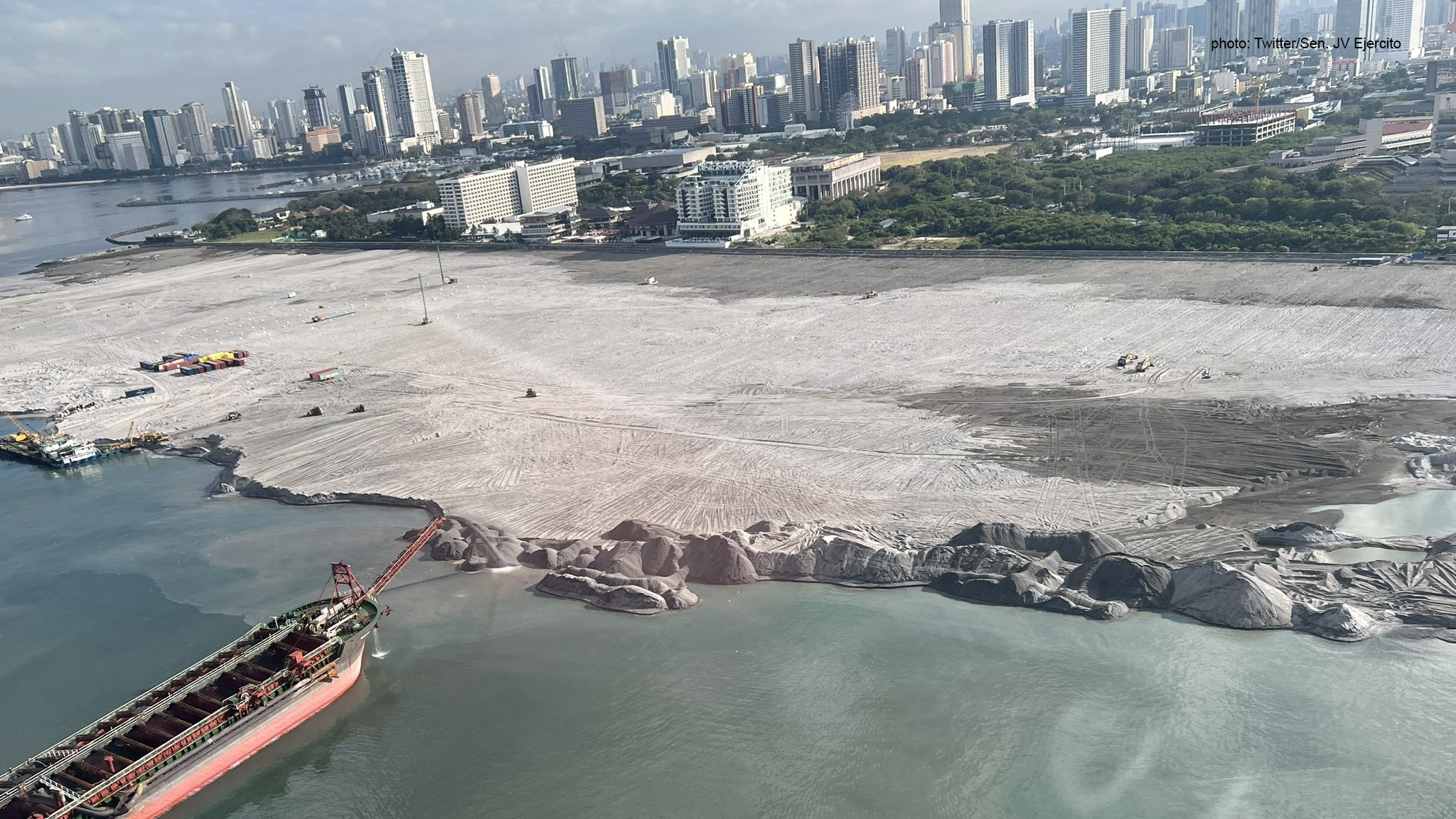

Table of Contents
Manila Bay, a historically significant body of water and a vital part of the Philippines' identity, faces unprecedented environmental challenges. Understanding Manila Bay's current state is crucial for its future. This vibrant bay, once teeming with marine life and a source of livelihood for countless Filipinos, now struggles under the weight of pollution and habitat destruction. This article examines Manila Bay's current state, exploring the extent of environmental degradation, the impact on biodiversity, ongoing restoration efforts, and the prospects for future recovery.
The Extent of Pollution in Manila Bay:
Water Quality Degradation:
The water quality of Manila Bay has significantly deteriorated due to various pollutants. This degradation poses a serious threat to the entire ecosystem.
- Industrial Waste: Untreated or inadequately treated industrial effluents from factories and manufacturing plants release heavy metals (lead, mercury, cadmium), chemicals, and other toxic substances into the bay.
- Sewage: Untreated sewage from densely populated areas significantly contributes to high levels of coliform bacteria and organic pollutants, making the water unsafe for recreation and potentially harmful to human health.
- Agricultural Runoff: Fertilizers and pesticides used in agriculture run off into the bay, causing eutrophication (excessive nutrient enrichment) and algal blooms that deplete oxygen levels.
Studies by the Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR) and other agencies consistently reveal alarmingly high levels of coliform bacteria, exceeding safe limits for recreational use. Dissolved oxygen levels are often dangerously low, indicating a stressed ecosystem.
Sediment Contamination:
Sediment contamination is another major concern in Manila Bay. Heavy metal accumulation in the sediment poses a long-term threat to the entire food chain.
- Heavy Metals: The accumulation of heavy metals in the sediments acts as a reservoir of pollution, impacting benthic organisms and bioaccumulating in the tissues of fish and shellfish.
- Plastic Pollution: Manila Bay suffers from significant plastic pollution, with plastic debris accumulating in the sediments. This plastic breaks down into microplastics, which enter the food chain and harm marine life.
Research studies, such as those published by the University of the Philippines Marine Science Institute (UP MSI), highlight the severe impact of this contamination on the benthic community and the overall health of the bay. Visual representations of the contaminated sediment are readily available online, showcasing the extent of this environmental problem.
The Impact on Biodiversity and Marine Life:
Decline in Fish Stocks:
Pollution and habitat destruction have led to a drastic decline in fish stocks in Manila Bay. This has severe consequences for the local fishing industry and the food security of coastal communities.
- Overfishing: Unsustainable fishing practices exacerbate the decline in fish populations.
- Habitat Loss: The destruction of mangrove forests and seagrass beds, vital habitats for many fish species, further contributes to the decline.
Several species of fish, once abundant in Manila Bay, are now considered endangered or threatened.
Damage to Coral Reefs:
Manila Bay's coral reefs, once thriving ecosystems, are now severely degraded due to pollution, destructive fishing practices, and sedimentation.
- Coral Bleaching: Increased water temperatures and pollution contribute to coral bleaching events, leading to the death of coral colonies.
- Physical Damage: Destructive fishing practices, such as dynamite fishing, cause direct physical damage to coral reefs.
Conservation efforts, including coral reef rehabilitation projects, are underway, but significant challenges remain.
Impact on other marine life:
The degradation of Manila Bay affects various other marine species.
- Seabirds: Many seabirds rely on Manila Bay for food; pollution threatens their survival.
- Marine Mammals: Marine mammals, including dolphins and dugongs, are affected by pollution and habitat loss.
- Invertebrates: Benthic invertebrates, crucial components of the marine food web, are heavily impacted by sediment contamination.
Government Initiatives and Environmental Restoration Efforts:
Clean-up Campaigns and Rehabilitation Projects:
The Philippine government, through the DENR and other agencies, has launched several clean-up campaigns and rehabilitation projects in Manila Bay.
- "Manila Baywalk Project": This project aims to rehabilitate the Manila Baywalk area and improve its aesthetic appeal.
- Wastewater Treatment Plants: The construction and improvement of wastewater treatment plants are crucial for reducing sewage pollution.
- Mangrove Reforestation: Planting mangroves helps restore coastal ecosystems and protect against erosion.
Private sector involvement in these initiatives is increasingly important for successful implementation.
Policy and Legislation:
Several laws and policies aim to protect Manila Bay's environment.
- Clean Water Act: This act sets water quality standards and regulates pollution discharge.
- Philippine Fisheries Code: This code regulates fishing practices to promote sustainable fisheries.
The effectiveness of these policies relies on strict enforcement and community participation.
Community Involvement and Sustainability:
Community involvement is vital for the long-term success of Manila Bay's restoration.
- Coastal Clean-up Drives: Regular coastal clean-up drives organized by communities and NGOs help remove debris and raise awareness.
- Sustainable Fishing Practices: Promoting sustainable fishing practices helps ensure the long-term viability of fish stocks.
- Education and Awareness Campaigns: Educating communities about the importance of protecting Manila Bay is crucial for long-term sustainability.
Signs of Resilience and Future Outlook for Manila Bay:
Positive Indicators of Recovery:
Despite the significant challenges, there are some positive signs:
- Improved water quality in some areas due to clean-up efforts.
- Increased awareness among communities about environmental protection.
- Successful mangrove reforestation projects.
These positive indicators suggest that with continued effort, the bay's ecosystem can recover.
Challenges and Future Strategies:
Significant challenges remain in restoring Manila Bay's ecosystem. Long-term success requires sustained commitment.
- Continued government funding and support for rehabilitation projects.
- Stricter enforcement of environmental laws.
- Increased community participation and awareness.
- Adoption of sustainable practices in all sectors.
Conclusion:
Manila Bay's current state is a complex picture of environmental degradation and ongoing restoration efforts. While pollution and habitat destruction pose significant challenges, there are also signs of resilience. The success of future restoration efforts depends on sustained government support, effective policy implementation, increased community involvement, and the adoption of sustainable practices. Protecting Manila Bay's future requires a collective commitment from all stakeholders. Contribute to the restoration of Manila Bay and learn more about the current state of Manila Bay. Let's work together to revitalize this historically significant and ecologically vital body of water.

Featured Posts
-
 Elections Municipales Metz 2026 L Avenir Politique De Laurent Jacobelli
May 30, 2025
Elections Municipales Metz 2026 L Avenir Politique De Laurent Jacobelli
May 30, 2025 -
 Increased Us Tariffs On Solar Imports Hanwha And Ocis Market Share Play
May 30, 2025
Increased Us Tariffs On Solar Imports Hanwha And Ocis Market Share Play
May 30, 2025 -
 Roland Garros Day 1 Djokovics Strong Start Gauff And Andreevas Wins
May 30, 2025
Roland Garros Day 1 Djokovics Strong Start Gauff And Andreevas Wins
May 30, 2025 -
 Projet A69 Un Recours Pour Tenter De Relancer La Construction Apres Annulation
May 30, 2025
Projet A69 Un Recours Pour Tenter De Relancer La Construction Apres Annulation
May 30, 2025 -
 The Canadian Economy Under Trumps Trade War 8 Indicators To Watch
May 30, 2025
The Canadian Economy Under Trumps Trade War 8 Indicators To Watch
May 30, 2025
