Nuclear Power Plant Construction: Trump's Plans For Faster Development

Table of Contents
Regulatory Reforms Under Trump's Administration
The Trump administration aimed to significantly reduce the time and complexity involved in building new nuclear power plants. This involved substantial regulatory reforms focused on two key areas: streamlining the approval process and addressing environmental impact assessments.
Streamlining the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) Approval Process
A central element of Trump's plan was to expedite the licensing and permitting stages overseen by the Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC). This involved several key reforms:
- Reduced Review Times: The NRC implemented initiatives to shorten the review period for applications, aiming to significantly cut down the time from application to license approval.
- Simplified Application Processes: Efforts were made to simplify the application process, reducing bureaucratic hurdles and making it easier for companies to submit complete and accurate documentation.
- Increased Staff Resources: The administration prioritized allocating more staff and resources to the NRC's nuclear power plant licensing division to expedite review processes.
These changes had a tangible impact on several projects. For example, [insert example of a nuclear power project that benefited from faster NRC approval]. The overall effect was a demonstrable reduction in the time needed for licensing, potentially shaving years off the overall construction timeline for new plants. However, the extent of this impact is debated, with some arguing that the streamlining efforts were insufficient to truly overcome long-standing challenges.
Addressing Environmental Impact Assessments
Environmental impact assessments (EIS) are a critical part of the nuclear power plant construction process. The Trump administration sought to expedite these reviews while maintaining compliance with environmental regulations. This approach involved:
- Streamlined EIS Procedures: The administration attempted to streamline the EIS process, aiming to reduce unnecessary delays without compromising environmental protection.
- Prioritized Review of Nuclear Projects: Some argue that the administration prioritized the review of nuclear projects, potentially leading to faster approvals compared to other energy projects.
However, this approach faced criticism. Environmental groups raised concerns about potential compromises in environmental protection due to the accelerated review process. Specific projects like [insert example of a project facing environmental challenges] faced significant delays and opposition despite the administration's efforts.
Financial Incentives and Investment Strategies
The Trump administration also focused on providing financial incentives and employing investment strategies to attract private sector participation in nuclear power plant construction.
Tax Credits and Subsidies
To encourage investment, the Trump administration considered or implemented (depending on actual policy) various tax breaks and subsidies for new nuclear power plant construction. These incentives aimed to:
- Reduce upfront costs: Tax credits could lessen the initial financial burden on developers, encouraging them to undertake projects that would otherwise be too risky.
- Increase profitability: Subsidies could increase the long-term profitability of nuclear power plants, making them more attractive to investors.
Data on investment levels in nuclear energy before and after the introduction of these potential incentives would be crucial to evaluate their effectiveness. The impact of these policies on private sector investment remains a subject of ongoing debate and requires further analysis.
Government Loan Guarantees
Government loan guarantees played a significant role in reducing the financial risk associated with the substantial investment required for nuclear power plant construction. These guarantees aimed to:
- Reduce investor risk: Loan guarantees from the government would reduce the risk for lenders and investors, making it easier to secure financing for large-scale nuclear projects.
- Attract private capital: By mitigating financial risk, loan guarantees can help attract private sector participation, which is essential for large-scale infrastructure projects.
[Insert an example of a project that leveraged government loan guarantees]. The success of this strategy in attracting investment needs further evaluation and analysis of the projects that received these guarantees.
Technological Advancements and Standardized Designs
The Trump administration also recognized the potential of advanced reactor designs to accelerate nuclear power plant construction.
Small Modular Reactors (SMRs)
The administration expressed support for the development and deployment of Small Modular Reactors (SMRs). These reactors offer potential advantages in terms of construction speed:
- Factory fabrication: Many components of SMRs are factory-fabricated, reducing on-site construction time and complexity.
- Standardized designs: Standardized designs streamline the engineering and licensing processes.
- Modular construction: The modular nature of SMRs allows for phased construction and deployment, potentially reducing overall project timelines.
However, the deployment of SMRs also faces challenges, such as the need for new manufacturing facilities and regulatory frameworks adapted to these novel technologies.
Advanced Reactor Designs
Beyond SMRs, the administration explored other advanced reactor designs that might offer quicker construction timelines. These could include things like:
- Passive safety systems: Reactors with passive safety systems may require less complex and time-consuming safety-related engineering and construction.
- Improved materials and manufacturing techniques: Advanced materials and manufacturing processes could speed up the construction of reactor components.
The successful deployment of these advanced reactor designs hinges on overcoming technological and regulatory challenges and ensuring their cost-effectiveness compared to traditional reactors.
Conclusion: The Future of Nuclear Power Plant Construction
Trump's administration implemented several strategies to accelerate nuclear power plant construction, including regulatory reforms, financial incentives, and a focus on advanced reactor technologies. While some successes were achieved in streamlining the approval process, challenges remained, particularly concerning environmental reviews and the overall cost of nuclear power. The long-term impact of these policies on the future of nuclear energy development in the U.S. remains to be seen and requires further study. Nuclear power remains vital for meeting rising energy demands and reducing carbon emissions, making it crucial to continue exploring and improving strategies for accelerating nuclear power plant construction. Further research and discussion are needed to determine the effectiveness of policies designed to expedite nuclear power plant projects and to explore innovative approaches for streamlining nuclear power plant development. Let's continue the conversation on how we can efficiently and safely implement expediting nuclear power plant projects.

Featured Posts
-
 Grand Slam Action The Jamaica Observers View
May 11, 2025
Grand Slam Action The Jamaica Observers View
May 11, 2025 -
 Two Celtics Players Unexpectedly Score 40 Points Each In One Game
May 11, 2025
Two Celtics Players Unexpectedly Score 40 Points Each In One Game
May 11, 2025 -
 Pentagons Book Review Impact On Military Academy Curricula
May 11, 2025
Pentagons Book Review Impact On Military Academy Curricula
May 11, 2025 -
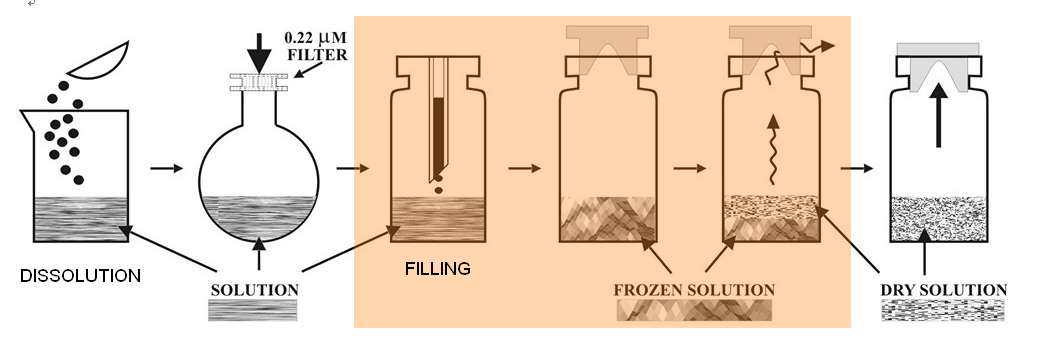 Improving The Accuracy Of Automated Visual Inspection For Lyophilized Vials
May 11, 2025
Improving The Accuracy Of Automated Visual Inspection For Lyophilized Vials
May 11, 2025 -
 Criticism Mounts Against Faber For Rejecting Coa Volunteer Honours
May 11, 2025
Criticism Mounts Against Faber For Rejecting Coa Volunteer Honours
May 11, 2025
