Reactor Power Uprate: A Guide To The NRC Approval Process
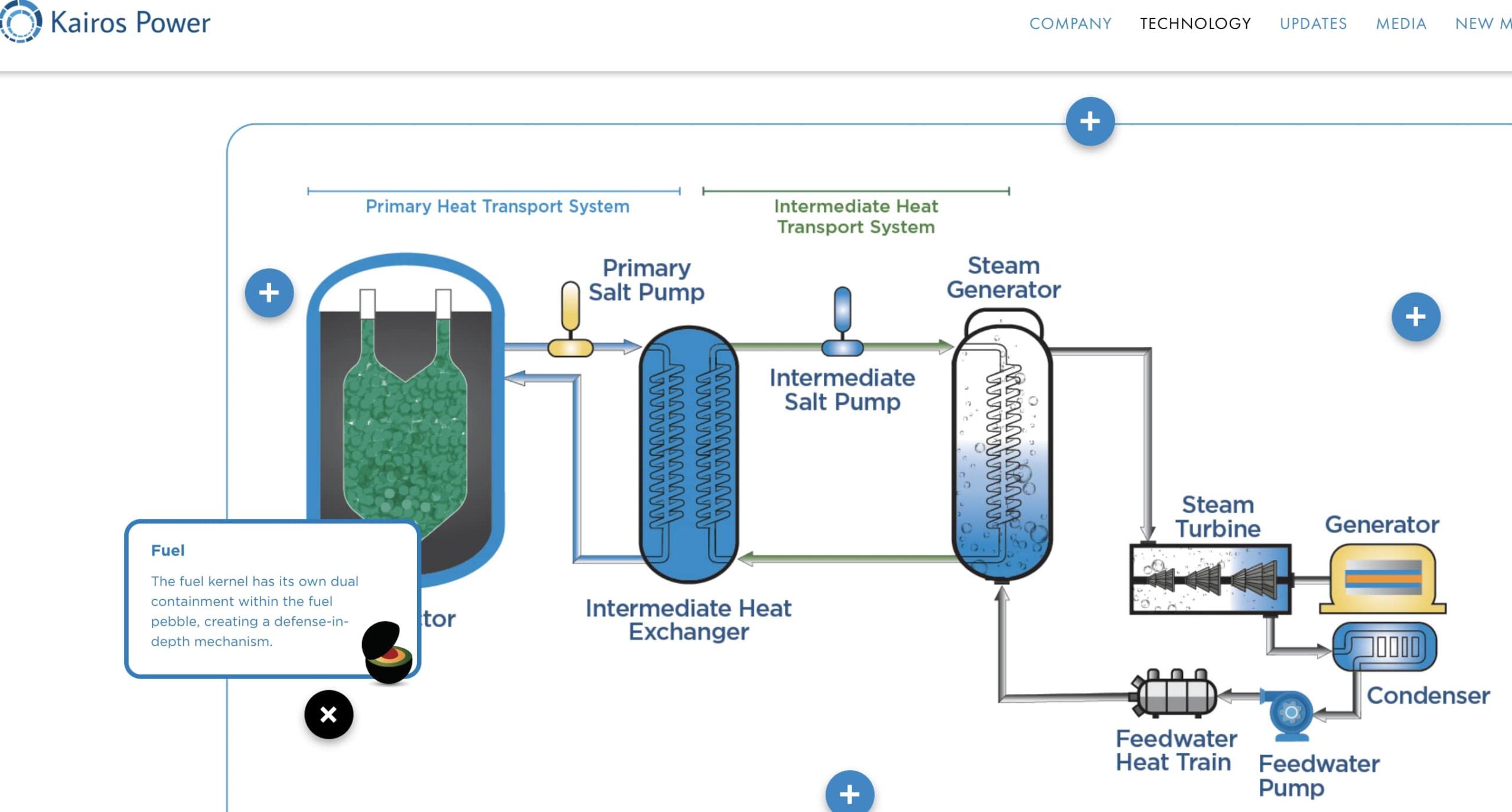
Table of Contents
Understanding the Benefits of Reactor Power Uprate
A reactor power uprate represents a substantial opportunity for nuclear power plant operators. The increased power output directly translates into several key advantages:
-
Increased energy production: A higher power output directly leads to a greater amount of electricity generated. This increased capacity can significantly contribute to meeting growing energy demands and bolstering grid stability. For example, a 10% power uprate can result in a substantial increase in annual energy production, reducing reliance on other, potentially less sustainable energy sources.
-
Improved economic efficiency: Higher power output leads to lower production costs per unit of energy. This is because the fixed operational costs are spread across a larger energy output, resulting in a reduced levelized cost of electricity (LCOE). This improved economic efficiency enhances the plant's profitability and strengthens its long-term viability.
-
Extended plant life: In some cases, a well-executed reactor power uprate can contribute to extending the operational lifespan of the reactor. This is achieved by optimizing plant operations and potentially delaying some of the maintenance activities that are normally associated with aging infrastructure.
Bullet Points:
- Reduced levelized cost of electricity (LCOE)
- Enhanced return on investment (ROI)
- Improved grid stability and reliability
- Increased competitiveness in the energy market
The NRC Approval Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
The NRC approval process for a reactor power uprate is rigorous and demanding. It's crucial to understand each phase to ensure a successful outcome. The process generally unfolds in these key stages:
Pre-Application Phase
This initial phase involves extensive preparation and lays the groundwork for the formal application. Key activities include:
- Gathering necessary data: Collecting comprehensive information on the reactor's current performance, safety systems, and operational history.
- Scoping the project: Defining the proposed power uprate level, identifying necessary modifications, and outlining the project timeline.
- Initial consultations with the NRC: Engaging with the NRC early in the process to discuss the proposed uprate and obtain preliminary feedback on the project's feasibility.
Formal Application Submission
Once the pre-application phase is complete, a comprehensive and detailed application must be submitted to the NRC. This includes:
- Detailed safety analysis report: A thorough assessment of the safety implications of the proposed power uprate, addressing all potential risks and mitigation strategies.
- Technical specifications: Detailed documentation outlining the proposed modifications to the reactor and its associated systems.
- Environmental impact statement: A comprehensive evaluation of the potential environmental impacts of the power uprate, addressing potential effects on air and water quality. This often includes consideration of environmental justice concerns.
NRC Review and Evaluation
The NRC conducts a thorough review of the submitted application, which includes:
- Detailed technical review: A rigorous evaluation of the safety analysis report, technical specifications, and other supporting documentation.
- Public comment period: An opportunity for the public to provide feedback and raise any concerns regarding the proposed power uprate. Addressing these public concerns effectively is crucial for a positive outcome.
- Safety evaluations: A comprehensive assessment of the safety implications of the proposed uprate, focusing on the potential for accidents and their consequences.
- Inspections: On-site inspections may be conducted to verify the accuracy of the information provided in the application and assess the plant's readiness for the power uprate.
Licensing and Implementation
Upon successful completion of the NRC's review and evaluation, a license amendment will be issued, authorizing the power uprate. The final phase involves:
- Implementing approved modifications: Making the necessary modifications to the reactor and its associated systems according to the approved plans.
- Rigorous testing procedures: Conducting extensive testing to verify the safety and performance of the modified systems before increasing power levels.
- Ongoing monitoring and compliance: Continuous monitoring of the reactor's performance and adherence to all NRC regulations and safety standards post-uprate.
Key Considerations for a Successful Reactor Power Uprate
Several critical factors contribute to the success of a reactor power uprate project:
- Safety: Safety must be the paramount concern throughout the entire process. A robust safety culture and rigorous adherence to safety protocols are essential.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meticulous adherence to all NRC regulations and guidelines is crucial for obtaining and maintaining approval. Any deviation from these requirements can result in delays or rejection of the application.
- Technical Expertise: A team of experienced engineers and specialists is necessary to manage the technical complexities of the project, especially given the specialized nature of nuclear reactor technology.
- Financial Planning: A comprehensive financial plan, including cost estimations and secure funding sources, is essential to ensure the project's financial viability.
- Public Engagement: Engaging with local communities and stakeholders is important for building trust and addressing any potential concerns. Open communication fosters a positive environment and contributes to smooth regulatory approvals.
Bullet Points:
- Thorough risk assessments and mitigation strategies.
- Development of comprehensive safety plans and emergency preparedness procedures.
- Effective communication and collaboration with the NRC throughout the process.
Conclusion
Successfully completing a reactor power uprate requires a thorough understanding of the NRC approval process and meticulous attention to detail. This guide has provided a comprehensive overview of the key steps involved, from initial planning to final implementation. By carefully considering the benefits, navigating the regulatory requirements, and prioritizing safety, nuclear power plant operators can effectively leverage reactor power uprates to enhance energy production and improve overall plant efficiency. To learn more about navigating the complexities of the reactor power uprate process and ensuring a smooth and successful outcome, contact our expert consultants today.

Featured Posts
-
 Ups Exploring Humanoid Robots With Figure Ai
May 01, 2025
Ups Exploring Humanoid Robots With Figure Ai
May 01, 2025 -
 Successfully Navigating The Nrc For Reactor Power Uprates
May 01, 2025
Successfully Navigating The Nrc For Reactor Power Uprates
May 01, 2025 -
 Obituary Priscilla Pointer Mother Of Amy Irving Passes Away At 100
May 01, 2025
Obituary Priscilla Pointer Mother Of Amy Irving Passes Away At 100
May 01, 2025 -
 How Healthy Is Asparagus Unveiling The Nutritional Benefits
May 01, 2025
How Healthy Is Asparagus Unveiling The Nutritional Benefits
May 01, 2025 -
 Dragon Den Shock Businessman Rejects Top Investors Accepts Risky Deal
May 01, 2025
Dragon Den Shock Businessman Rejects Top Investors Accepts Risky Deal
May 01, 2025
