Record-Breaking Global Forest Loss: Wildfires Exacerbate The Crisis
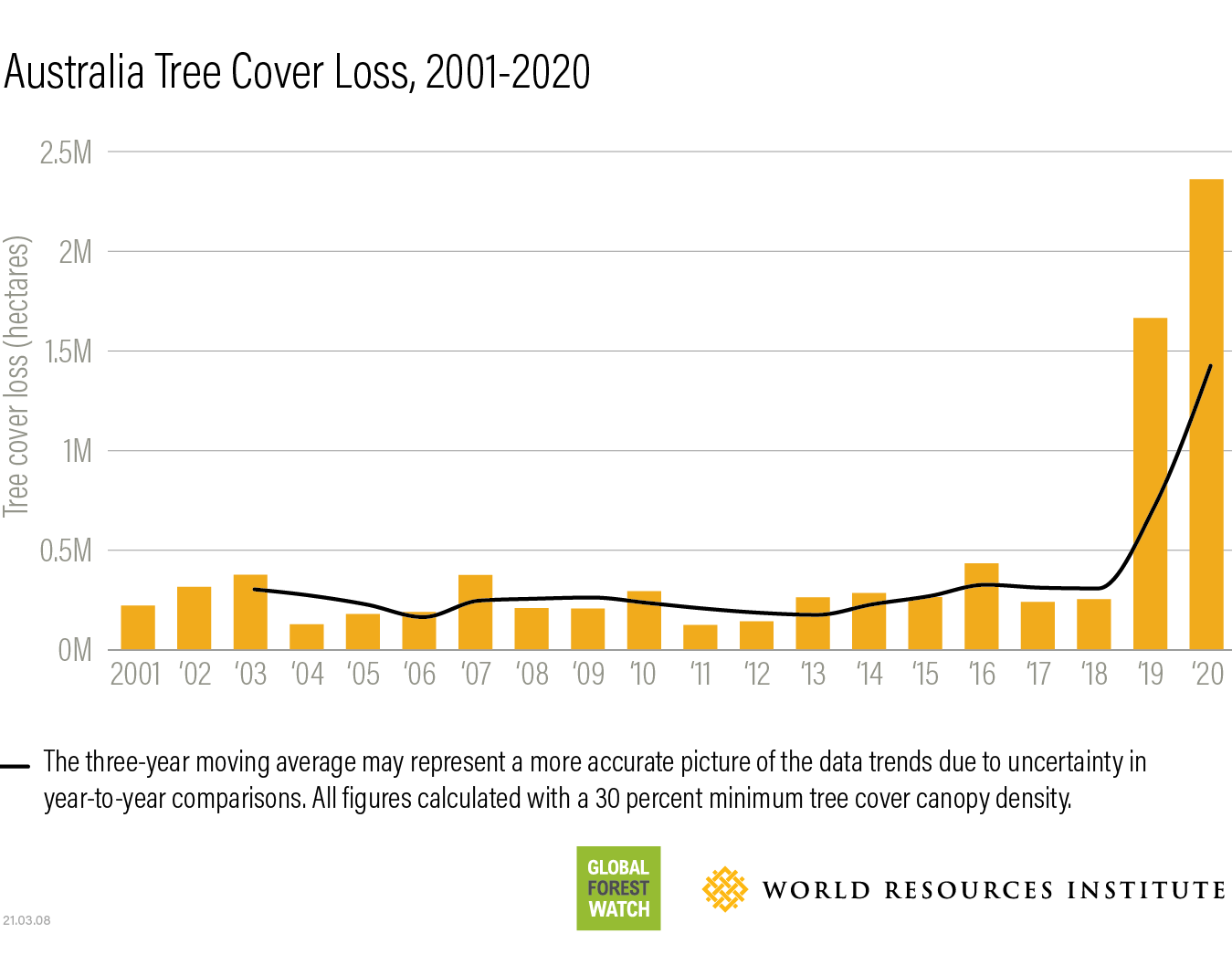
Table of Contents
H2: The Dire Statistics of Global Forest Loss
The extent of deforestation is alarming. Global deforestation rates are accelerating, exceeding previous years' figures by a significant margin. The loss of forest cover is not evenly distributed; key regions like the Amazon rainforest and Borneo are experiencing particularly devastating rates of deforestation.
H3: Extent of Deforestation:
Visualizing this loss is crucial. Charts and graphs illustrating the hectares of forest lost annually would vividly demonstrate the severity of the situation. For instance, the Amazon rainforest, often called the "lungs of the planet," is losing millions of hectares of forest each year, largely due to agricultural expansion, logging, and mining activities. Similarly, Borneo's rainforests, incredibly rich in biodiversity, are facing rapid deforestation driven by palm oil plantations.
- Quantify forest loss: We are losing millions of hectares of forest annually – a figure that continues to climb. Precise numbers, sourced from reputable organizations like the Global Forest Watch, should be included here.
- Contribution of factors: While deforestation is a complex issue, a breakdown of its contributing factors is essential. Logging operations, agricultural expansion (particularly for soy and palm oil), and mining activities are major culprits.
- Comparison to previous years: Comparing current deforestation rates with those from previous decades highlights the dramatic acceleration of this crisis and underscores the urgency for action.
Keywords: deforestation rates, global deforestation, Amazon deforestation, forest cover loss, land conversion
H2: Wildfires: A Major Driver of Forest Loss
Wildfires are now a major driver of global forest loss, significantly amplifying the impact of deforestation. The escalating frequency and intensity of these fires are inextricably linked to climate change.
H3: The Role of Climate Change in Wildfire Severity:
Climate change is creating a perfect storm for devastating wildfires. Rising global temperatures lead to prolonged periods of drought, creating tinder-dry conditions in forests. This makes them significantly more susceptible to ignition, whether from human activities or natural causes. The resulting fires burn hotter and spread faster, consuming vast areas of forest in record time.
- Drier conditions: Climate change is creating a feedback loop. Warmer temperatures and reduced rainfall result in drier vegetation and soil, making forests more vulnerable to ignition and increasing the intensity of fires.
- Devastating wildfires: Examples of recent, devastating wildfires, such as those in Australia, California, and Siberia, should be cited, highlighting their impact on forest areas and the associated loss of biodiversity.
- Changing wildfire seasons: The length and intensity of wildfire seasons are also changing, extending well beyond traditional periods, posing a greater threat to forests for longer durations.
Keywords: climate change impacts, wildfire intensity, drought conditions, extreme weather events, fire season
H2: Consequences of Record-Breaking Forest Loss
The consequences of this record-breaking forest loss are far-reaching and devastating. The impact on biodiversity and the climate is particularly concerning.
H3: Biodiversity Loss and Habitat Destruction:
The destruction of forests leads to catastrophic biodiversity loss. Countless animal and plant species, including numerous endangered ones, lose their habitats, leading to population declines and even extinctions. The disruption of complex ecological processes further exacerbates this crisis.
- Loss of habitat: The sheer scale of deforestation directly translates into widespread habitat loss for millions of species.
- Extinction risk: Specific examples of endangered species affected by deforestation and habitat loss should be included.
- Disruption of ecological processes: The intricate balance of ecosystems is easily disrupted, triggering cascading effects that can destabilize entire regions.
H3: Impact on Climate Change:
Forests act as crucial carbon sinks, absorbing significant amounts of atmospheric carbon dioxide. Deforestation and wildfires release this stored carbon back into the atmosphere, significantly contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and accelerating global warming. This creates a vicious cycle where climate change fuels more intense wildfires, leading to further deforestation and increased carbon emissions.
- Forests as carbon sinks: The role of forests in carbon sequestration should be clearly explained.
- Release of CO2: The massive release of CO2 during wildfires and deforestation should be quantified.
- Contribution to global warming: The connection between forest loss, increased greenhouse gas emissions, and accelerated global warming should be explicitly stated.
Keywords: biodiversity loss, habitat destruction, endangered species, carbon sink, greenhouse gas emissions, climate feedback loop
H2: Mitigating the Crisis: Solutions and Actions
Addressing this crisis requires immediate and concerted action on multiple fronts. Combating deforestation and improving wildfire prevention and management are critical.
H3: Combating Deforestation:
Effective strategies to reduce deforestation involve a multi-pronged approach:
- Sustainable forestry practices: Promoting sustainable logging practices that ensure forest regeneration is crucial.
- Stronger regulations: Enacting and enforcing stronger laws against illegal logging and land grabbing is vital.
- Community involvement: Engaging local communities in forest conservation efforts is key to long-term success.
H3: Wildfire Prevention and Management:
Investing in wildfire prevention and management is crucial:
- Early warning systems: Developing and implementing sophisticated early warning systems for wildfires is essential.
- Improved forest management: Implementing proactive forest management practices to reduce wildfire risk is vital.
- Better firefighting resources: Investing in better firefighting resources and technologies is crucial for effective fire suppression.
Keywords: sustainable forestry, reforestation, forest management, wildfire prevention, fire suppression, conservation efforts
3. Conclusion
Record-breaking global forest loss, significantly worsened by increasingly intense wildfires fueled by climate change, poses a dire threat to biodiversity and climate stability. The consequences are far-reaching, impacting ecosystems, species, and human populations alike. To mitigate this crisis, we need urgent and comprehensive action. We must combat deforestation through sustainable practices and strong regulations, while simultaneously investing in robust wildfire prevention and management strategies. Learn more about global forest loss and get involved in conservation efforts. Support organizations dedicated to fighting deforestation and tackling the wildfire crisis. Together, we can make a difference in reducing global forest loss and protecting our planet's invaluable forests.

Featured Posts
-
 Amundi Djia Ucits Etf A Deep Dive Into Net Asset Value Nav
May 24, 2025
Amundi Djia Ucits Etf A Deep Dive Into Net Asset Value Nav
May 24, 2025 -
 Amerikaanse Beurs Onrustig Aex Blijft Positief Wat Betekent Dit Voor Beleggers
May 24, 2025
Amerikaanse Beurs Onrustig Aex Blijft Positief Wat Betekent Dit Voor Beleggers
May 24, 2025 -
 Prime Videos Picture This A Full Guide To The Movies Music
May 24, 2025
Prime Videos Picture This A Full Guide To The Movies Music
May 24, 2025 -
 Florida Store Hours Memorial Day 2025 Publix And More
May 24, 2025
Florida Store Hours Memorial Day 2025 Publix And More
May 24, 2025 -
 The Jonas Brothers Joe Jonas His Response To A Marital Dispute
May 24, 2025
The Jonas Brothers Joe Jonas His Response To A Marital Dispute
May 24, 2025
