Rising COVID-19 Cases: Is A New Variant To Blame?
Table of Contents
The Role of New COVID-19 Variants
The emergence of new COVID-19 variants plays a significant role in the fluctuating patterns of infection rates. Understanding their characteristics is key to predicting and managing outbreaks.
Identifying Emerging Variants
Identifying new variants requires robust surveillance systems and advanced laboratory techniques. Genomic sequencing, a process that determines the precise genetic makeup of the virus, is crucial in identifying mutations and classifying new variants. This data is then analyzed to assess the potential impact of these mutations. Global collaborations, such as those coordinated by the World Health Organization (WHO), are essential for rapid variant detection and information sharing.
- Examples of Variants: Recent examples include the Omicron subvariants (e.g., XBB.1.5, EG.5), which have demonstrated increased transmissibility and immune evasion capabilities. These variants, categorized as Variants of Concern (VOC) or Variants of Interest (VOI) by global health organizations, necessitate continuous monitoring and adaptation of public health strategies.
- Increased Transmissibility and Severity: Mutations can alter the virus's ability to bind to human cells, making it more easily transmitted. Some mutations may also affect the severity of the disease, leading to more severe illness in certain populations.
- Immune Evasion: Certain variants may be better at evading the immune response generated by previous infection or vaccination, leading to reinfections and breakthrough cases. This highlights the importance of staying updated with vaccine recommendations and booster shots.
Variant tracking is not merely an academic exercise; it's a critical component of predicting future outbreaks and adapting public health measures. By understanding the characteristics of emerging variants, health officials can better allocate resources, develop effective countermeasures, and inform the public about necessary precautions.
Beyond Variants: Other Factors Contributing to Rising Cases
While new variants are a significant concern, rising COVID-19 cases are rarely solely attributable to them. Several other factors contribute to the complex epidemiological picture.
Seasonal Effects
Seasonal changes significantly influence viral transmission.
- Colder Weather and Indoor Gatherings: The colder months typically see an increase in indoor gatherings, providing ideal conditions for respiratory viruses, including COVID-19, to spread more easily. Reduced ventilation in enclosed spaces also increases transmission risk.
- Relevant Studies: Numerous studies have demonstrated a correlation between seasonal changes and increased respiratory illness transmission. These studies underscore the importance of maintaining vigilance even outside of peak seasons.
Waning Immunity and Booster Shots
Immunity from previous infections or vaccinations wanes over time.
- Booster Shots: Booster shots are essential to maintain high levels of protection against severe illness and hospitalization, particularly against emerging variants.
- Booster Uptake and Impact: Data on booster uptake correlates with levels of severe disease and hospitalizations, demonstrating the importance of maintaining high vaccination rates and encouraging booster shots among eligible populations.
Reduced Public Health Measures
The relaxation of public health measures also plays a crucial role.
- Impact of Relaxed Restrictions: The decreased adherence to mask mandates, social distancing guidelines, and widespread testing can lead to increased community transmission.
- Correlation with Rising Case Numbers: Studies show a strong correlation between reduced public health interventions and subsequent rises in COVID-19 cases.
Data Analysis and Predictions
Accurate data analysis is crucial for effective pandemic management.
Epidemiological Modeling
Scientists employ sophisticated epidemiological modeling techniques to analyze data, predict future trends, and inform public health strategies. These models consider various factors, including variant characteristics, population immunity, and public health measures.
- Limitations of Predictive Models: Predictive models have inherent limitations. Unforeseen events, changes in behavior, and the emergence of new variants can significantly affect the accuracy of projections. Continuous monitoring and model adjustments are crucial.
- Current Predictions: Current predictions vary depending on the model and the assumptions used. However, consistent monitoring of case numbers, hospitalizations, and deaths is essential for accurate real-time assessment.
Importance of Reliable Data
Reliable and timely data collection is paramount for effective public health responses.
- Challenges in Data Collection: Challenges include underreporting of cases (particularly mild or asymptomatic infections), variations in testing practices across regions, and delays in data reporting.
Conclusion
Rising COVID-19 cases are a complex issue influenced by the emergence of new variants, seasonal factors, waning immunity, and the relaxation of public health measures. While new variants pose a significant threat, addressing all contributing factors is essential for effective mitigation. Staying informed about the latest scientific developments and adhering to public health recommendations, such as vaccination, boosters, and testing, remains crucial. Stay up-to-date on the latest information regarding rising COVID-19 cases and new variants to protect yourself and your community.

Featured Posts
-
 Depakine Sanofi Mis En Examen Pour Rejets Toxiques A Mourenx
May 31, 2025
Depakine Sanofi Mis En Examen Pour Rejets Toxiques A Mourenx
May 31, 2025 -
 Zverevs Comeback Victory Sends Him To Munich Semifinals
May 31, 2025
Zverevs Comeback Victory Sends Him To Munich Semifinals
May 31, 2025 -
 Miley Cyrus Dan Busananya Sebuah Studi Gaya
May 31, 2025
Miley Cyrus Dan Busananya Sebuah Studi Gaya
May 31, 2025 -
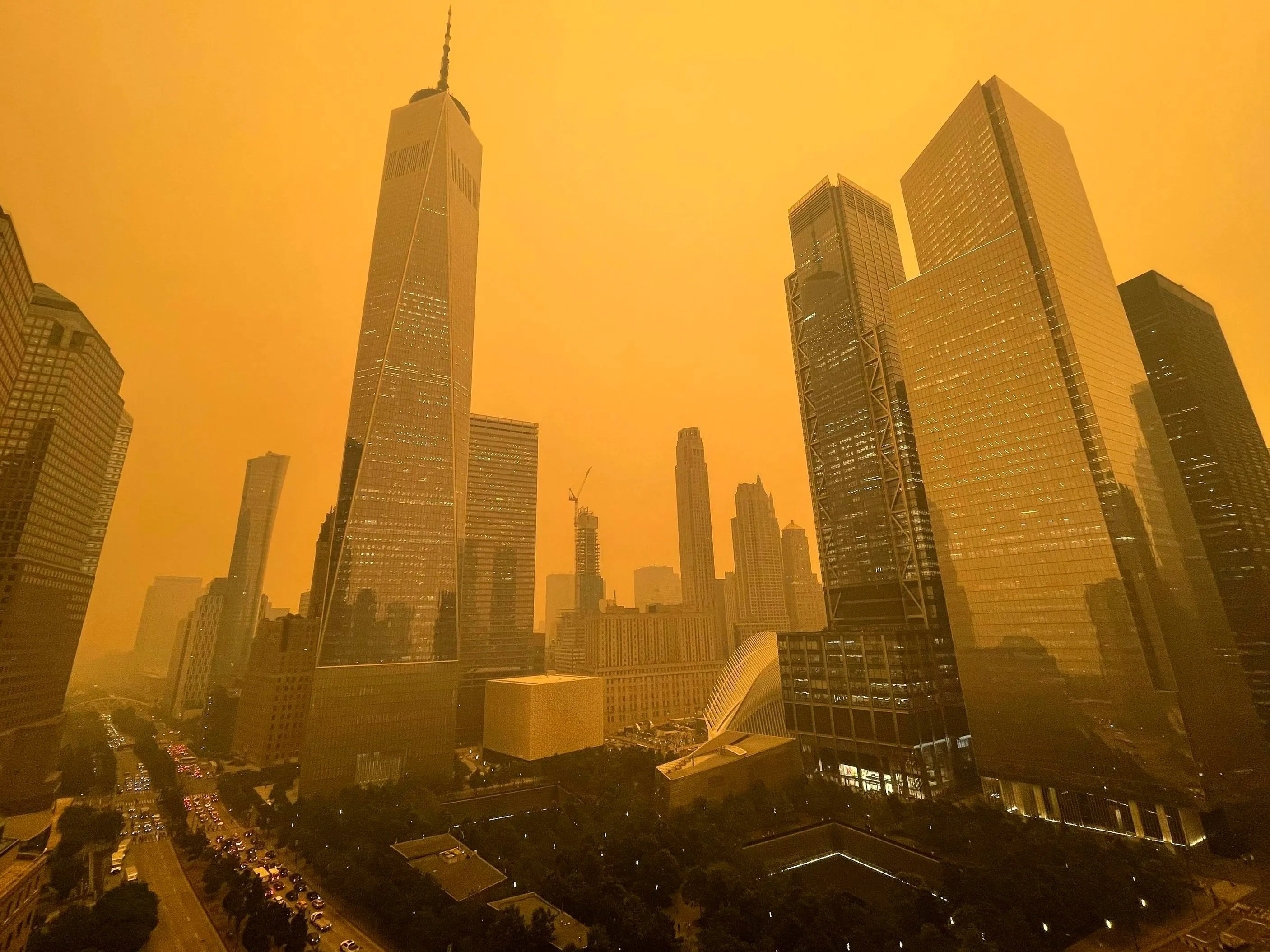 Canadian Wildfires 3 C New York Temperature Drop And Air Toxicant Trapping
May 31, 2025
Canadian Wildfires 3 C New York Temperature Drop And Air Toxicant Trapping
May 31, 2025 -
 Seattle Weather Soggy Skies Continue Into The Weekend
May 31, 2025
Seattle Weather Soggy Skies Continue Into The Weekend
May 31, 2025
