Shared Nuclear Deterrence: France's Proposal For European Security

Table of Contents
The Foundation of France's Proposal
France's proposal for shared nuclear deterrence centers on a more integrated approach to European security, leveraging France's independent nuclear arsenal to bolster the collective defense of willing EU partners. It's not about sharing physical control of nuclear weapons but rather about enhancing strategic cooperation and providing a stronger deterrent against potential adversaries. This involves a deeper level of security cooperation, strategic planning, and potentially joint military exercises, all under the umbrella of a strengthened European defense framework. This differs significantly from simply relying on the US nuclear umbrella and allows for a more autonomous European security posture.
- Enhanced security guarantees for participating EU nations: This offers a more robust defense against potential threats, reducing reliance on a single external power.
- Strengthened transatlantic ties through closer collaboration with NATO: While independent, the proposal doesn't aim to undermine NATO; rather, it seeks to complement and strengthen the alliance through a more cohesive European contribution.
- A more robust and unified European defense posture: Shared nuclear deterrence necessitates closer military and political cooperation, driving integration within the EU's defense capabilities.
- Potential for burden-sharing amongst EU members: This ensures fairer distribution of responsibilities and resources related to maintaining security, enhancing long-term sustainability.
Benefits of Shared Nuclear Deterrence for Europe
The advantages of embracing a framework of shared nuclear deterrence are significant for participating European countries. It offers a unique opportunity to redefine Europe's security architecture and role in the global landscape.
- Deterrence against potential aggressors through a combined nuclear arsenal: The credible threat of a unified response significantly raises the threshold for any potential attack on participating nations. This is a key aspect of nuclear deterrence.
- Reduced reliance on solely US nuclear umbrella: While the transatlantic partnership remains crucial, shared nuclear deterrence reduces Europe’s dependence on US security guarantees, fostering greater strategic autonomy.
- Increased strategic autonomy for Europe: This allows the EU to act more decisively and independently in matters concerning its security, aligning with the broader push for strategic autonomy within the Union.
- Improved crisis management capabilities: Closer security cooperation facilitates more effective response mechanisms to potential crises, improving overall preparedness and coordination.
- Strengthening of EU-NATO cooperation: The initiative aims to strengthen, not weaken, the transatlantic bond by providing a more substantial European contribution to collective security.
Challenges and Obstacles to Implementation
Despite the potential benefits, implementing France's proposal faces several significant hurdles. Addressing these challenges proactively is crucial for its successful adoption.
- Concerns about nuclear proliferation and control: This remains a primary concern. Robust safeguards and transparency mechanisms are necessary to alleviate anxieties about the spread of nuclear weapons.
- Differing opinions on the role of nuclear weapons within the EU: Not all EU members hold the same views on nuclear deterrence, potentially leading to disagreements on the proposal's scope and implementation.
- Potential disagreements on burden-sharing and resource allocation: Fair distribution of financial and military contributions is essential to ensure long-term viability. Disputes over resources could hinder progress.
- Navigating the complexities of existing NATO structures: Integrating the proposal within the existing NATO framework requires careful consideration to avoid duplication or conflict.
- The need for a robust legal and political framework: A comprehensive legal framework is necessary to govern the sharing of information, responsibilities, and resources amongst participating nations.
Addressing the Nuclear Proliferation Concerns
The prospect of nuclear proliferation is a legitimate concern surrounding any discussion of shared nuclear deterrence. However, the French proposal does not advocate for the wider distribution of nuclear weapons. Instead, it emphasizes the strategic use of existing French nuclear capabilities within a tightly controlled framework, subject to strict safeguards and verification mechanisms, similar to existing international agreements. Transparency and stringent protocols are key to addressing these concerns and preventing the uncontrolled spread of nuclear technology.
The Future of European Security and Shared Nuclear Deterrence
Adopting shared nuclear deterrence will significantly impact the future of European security and broader geopolitical relations. Understanding the potential consequences is crucial for informed decision-making.
- Impact on transatlantic relations (EU-US and EU-NATO): The proposal could strengthen the transatlantic partnership by fostering a more capable and responsible European security partner. However, it may also necessitate adjustments in the division of labor and decision-making processes within NATO.
- Influence on Russia's strategic calculations: A more robust European defense capability could alter Russia's strategic calculations, potentially leading to both increased dialogue and potential tensions.
- Effect on the broader global security landscape: The implementation could reshape the global balance of power, impacting relationships with other major players and potentially influencing arms control negotiations.
- Potential for further European integration on defense and security matters: Shared nuclear deterrence could serve as a catalyst for deeper European integration in the realm of defense, leading to greater cooperation and harmonization of military capabilities.
Conclusion:
France's proposal for shared nuclear deterrence presents a complex but potentially transformative vision for European security. While challenges related to implementation and nuclear proliferation are undeniable, the potential benefits of enhanced deterrence, strategic autonomy, and stronger transatlantic ties warrant serious consideration. A thorough cost-benefit analysis is crucial to weigh the risks and rewards. Continued dialogue and collaboration among EU member states, coupled with transparent engagement with NATO and other international partners, are vital to explore the viability and implications of this innovative approach to ensuring European security through effective shared nuclear deterrence. Further research and discussion on shared nuclear deterrence, including alternative models and mitigating strategies, are essential to navigate the complexities and opportunities it presents.

Featured Posts
-
 Punjab Launches Technical Training Programme For Transgender Individuals
May 10, 2025
Punjab Launches Technical Training Programme For Transgender Individuals
May 10, 2025 -
 Arkema Premiere Ligue Le Psg Brise La Serie De Dijon
May 10, 2025
Arkema Premiere Ligue Le Psg Brise La Serie De Dijon
May 10, 2025 -
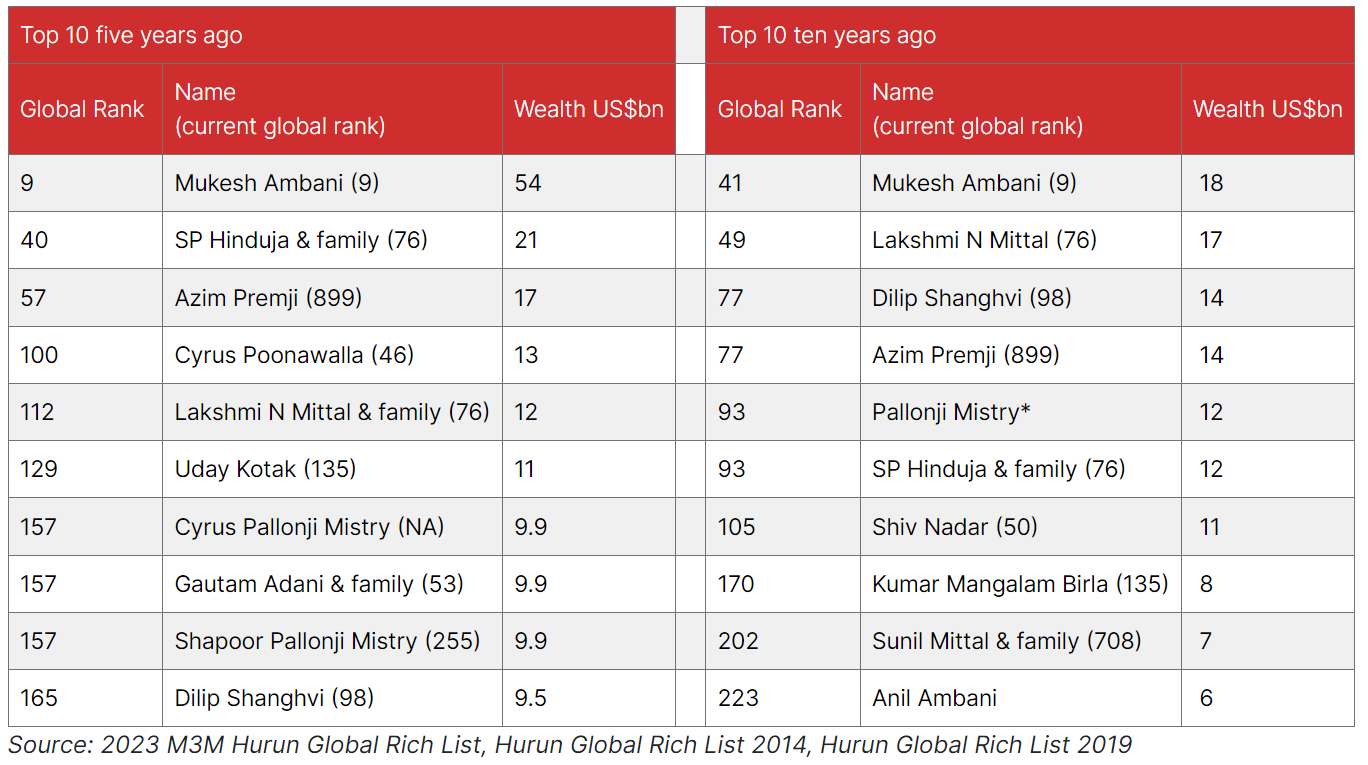 Hurun Global Rich List 2025 Elon Musks Net Worth Takes A Hit Still Worlds Richest
May 10, 2025
Hurun Global Rich List 2025 Elon Musks Net Worth Takes A Hit Still Worlds Richest
May 10, 2025 -
 Examining Transgender Equality Issues As Highlighted By The Bangkok Post
May 10, 2025
Examining Transgender Equality Issues As Highlighted By The Bangkok Post
May 10, 2025 -
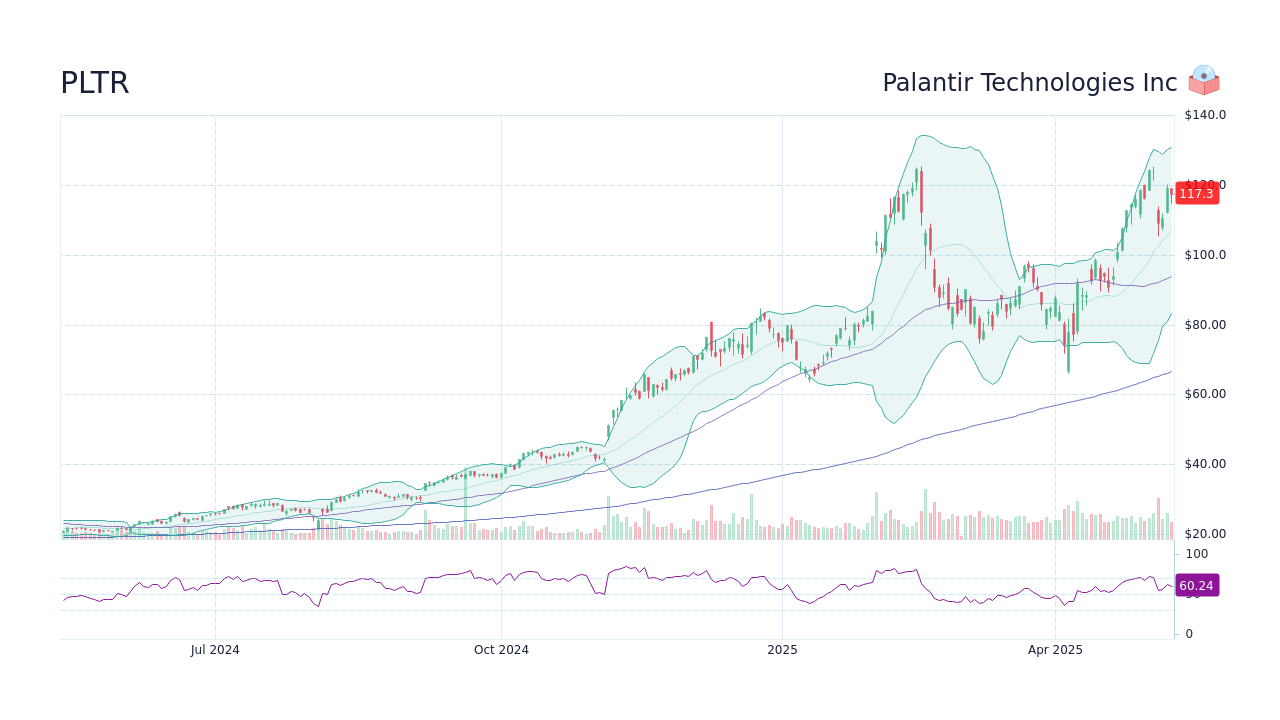 Palantir Stock Prediction Should You Buy Before May 5th
May 10, 2025
Palantir Stock Prediction Should You Buy Before May 5th
May 10, 2025
