The Construction Of China's Orbital Supercomputer: Technological Advancements
Table of Contents
The Driving Force Behind Orbital Supercomputing in China
The impetus behind China's pursuit of an orbital supercomputer is multifaceted, driven by a confluence of national security interests, scientific ambitions, and economic goals.
National Security and Strategic Advantage
The military and national security apparatus are significant driving forces behind this initiative. An orbital supercomputer would provide China with a substantial strategic advantage in several key areas:
- Improved satellite communication: Enhanced communication networks for military and civilian applications.
- Enhanced surveillance capabilities: Advanced real-time monitoring and analysis of global events.
- Advanced weather prediction models: More accurate and timely weather forecasting for both military operations and civilian preparedness.
- Development of autonomous weapons systems: Enabling the development and deployment of sophisticated AI-driven weaponry.
Scientific Research and Technological Leadership
Beyond national security, the project promises significant advancements in various scientific fields:
- Faster processing speeds for complex simulations: Enabling breakthroughs in materials science, drug discovery, and fusion energy research.
- Access to vast datasets: Facilitating the analysis of large-scale datasets from Earth observation satellites and other sources.
- Improved collaboration among researchers globally: Providing a platform for international scientific collaboration on large-scale research projects.
Economic Benefits and Global Competitiveness
The economic implications of China's Orbital Supercomputer are substantial:
- Job creation: Stimulating growth in the aerospace, computing, and related industries.
- Attracting foreign investment: Drawing international investment in cutting-edge technological development.
- Boosting technological innovation: Accelerating the pace of innovation in artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and space-based industries.
Key Technological Advancements Required for Construction
Constructing China's Orbital Supercomputer requires breakthroughs in several key technological areas:
Advanced Computing Architecture
The project necessitates the development of advanced computing architectures specifically designed for the harsh environment of space:
- Radiation-hardened components: Protecting the computer from the damaging effects of cosmic rays and solar flares.
- Efficient power management systems: Minimizing energy consumption in the space environment.
- Thermal control mechanisms: Maintaining optimal operating temperatures for the sensitive computing components. The adoption of quantum computing, neuromorphic computing, or other novel approaches could be crucial for achieving the desired computational power.
Space-Based Communication and Data Transfer
High-bandwidth, low-latency communication between the orbital supercomputer and ground stations is essential:
- Laser communication systems: Enabling high-speed data transfer over long distances.
- Advanced satellite networks: Creating a robust and reliable communication infrastructure.
- Data compression techniques: Optimizing data transmission to minimize bandwidth requirements.
Power Generation and Resource Management in Orbit
Sustainably powering a supercomputer in orbit poses significant challenges:
- Solar power technology: Utilizing advanced solar panels to harness solar energy.
- Nuclear fission reactors (if applicable): Providing a reliable and long-lasting power source (though this aspect raises significant safety and environmental concerns).
- Efficient power distribution: Minimizing energy loss during transmission and distribution.
Challenges and Potential Hurdles in the Project
Despite the ambitious goals, several challenges hinder the project's success:
Technological Complexity and Development Costs
The sheer scale and technological complexity of building an orbital supercomputer are immense, with astronomical development costs.
International Collaboration and Competition
International collaboration could be beneficial, but fierce competition from other nations pursuing similar goals also poses a challenge.
Ethical and Security Concerns
Data privacy and the potential misuse of the supercomputer's immense processing power raise significant ethical and security concerns.
Conclusion
The construction of China's Orbital Supercomputer represents a significant leap forward in high-performance computing. The project's success hinges on overcoming substantial technological hurdles and addressing crucial ethical considerations. Its potential impact on national security, scientific research, and the global economy is undeniable. Continued investigation into its progress and implications is crucial to understanding the future of space-based computing and the broader implications of this transformative technology. Further research and discussion on the ethical implications and technological challenges surrounding China's Orbital Supercomputer are essential for navigating this rapidly evolving landscape.
Featured Posts
-
 Former Munster Player James Cronin Takes Highfield Coaching Role
May 20, 2025
Former Munster Player James Cronin Takes Highfield Coaching Role
May 20, 2025 -
 Fremantles Q1 Revenue Falls 5 6 Amidst Buyer Budget Constraints
May 20, 2025
Fremantles Q1 Revenue Falls 5 6 Amidst Buyer Budget Constraints
May 20, 2025 -
 Leeds Uniteds Championship Return Tottenham Loanee Shines
May 20, 2025
Leeds Uniteds Championship Return Tottenham Loanee Shines
May 20, 2025 -
 Aghatha Krysty Tewd Llhyat Kyf Aead Aldhkae Alastnaey Ihyae Aemalha
May 20, 2025
Aghatha Krysty Tewd Llhyat Kyf Aead Aldhkae Alastnaey Ihyae Aemalha
May 20, 2025 -
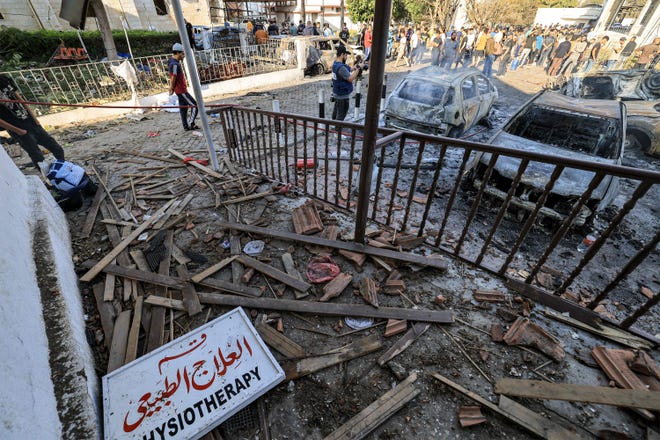 Femicide In Focus Colombian Models Death And Mexican Influencers Killing Spark Global Condemnation
May 20, 2025
Femicide In Focus Colombian Models Death And Mexican Influencers Killing Spark Global Condemnation
May 20, 2025
