The Impact Of Reduced Chinese Enrollment On American Higher Education Finances

Table of Contents
The decline in Chinese student enrollment in US universities is a significant concern, with some estimates suggesting a drop of over 30% in recent years. This represents a substantial shift in the landscape of international education and carries significant financial implications for American higher education institutions. Chinese students have historically been a major source of tuition revenue, contributing billions of dollars annually to the US economy. This article will analyze the impact of this decline on the financial health of US colleges and universities, exploring the contributing factors and potential mitigation strategies. Keywords: Chinese student enrollment, American higher education, international students, tuition revenue, university finances, financial impact.
H2: The Magnitude of Chinese Student Contribution to US University Revenue
Chinese students have long been a cornerstone of international enrollment in American universities, contributing significantly to their financial stability. Their substantial tuition fees, coupled with living expenses and other spending, inject millions of dollars into the US economy annually. Universities, particularly those with strong STEM programs, have become heavily reliant on this influx of revenue.
- Percentage of international student population comprised of Chinese students: Before the recent decline, Chinese students constituted a significant portion (often the largest) of the international student population at many leading US universities.
- Average tuition fees paid by Chinese students: Chinese students typically pay full tuition, often exceeding domestic tuition rates, significantly boosting university revenue.
- Estimated annual spending by Chinese students in the US: Beyond tuition, Chinese students contribute substantially to local economies through living expenses, accommodation, and other consumer spending.
- Examples of universities with high Chinese student enrollment: Universities like the University of Southern California, New York University, and the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, historically relied heavily on Chinese student enrollment for a significant portion of their revenue.
H2: Factors Contributing to the Decline in Chinese Enrollment
The decrease in Chinese student enrollment is a multifaceted issue stemming from various interconnected factors.
-
Geopolitical factors: Strained US-China relations, increased political tensions, and shifting geopolitical landscapes have created uncertainty and apprehension among prospective Chinese students.
-
Impact of changing visa policies and immigration procedures: Stricter visa processing times and increased scrutiny have made the application process more challenging and discouraging for some Chinese students.
-
Rise of domestic educational opportunities in China: The rapid development of high-quality universities and educational programs within China provides a compelling alternative for many students, reducing the perceived need to study abroad.
-
Influence of the COVID-19 pandemic and travel restrictions: The pandemic significantly disrupted international travel, causing lengthy delays and uncertainties for students planning to study in the US.
-
Specific examples of changes in US visa policies: Changes in visa application procedures and stricter requirements have contributed to the slowdown in Chinese student applications.
-
Growth in the quality and availability of higher education in China: The rise of world-class universities in China has made studying domestically a more attractive option.
-
Impact of travel restrictions on student mobility: The pandemic-related travel restrictions significantly hampered the ability of Chinese students to reach US universities.
H2: The Financial Implications for American Universities
The decline in Chinese student enrollment is translating into substantial budget shortfalls for many American universities.
-
Budget shortfalls resulting from reduced Chinese enrollment: The decrease in tuition revenue directly impacts university budgets, forcing institutions to make difficult financial decisions.
-
Potential cost-cutting measures adopted by universities: Universities are resorting to various cost-cutting measures, including staff reductions, program cuts, and increased tuition for domestic students.
-
Impact on financial aid programs and scholarships: Reduced revenue may necessitate cuts to financial aid, making higher education less accessible for domestic students.
-
Alternative strategies for increasing revenue and international enrollment: Universities are actively seeking alternative strategies to attract students from other countries and diversify their international student body.
-
Examples of universities implementing budget cuts: Many universities have already announced budget cuts and program eliminations due to the revenue shortfall.
-
Potential changes to financial aid programs: Reduced funding may lead to reduced financial aid for deserving students.
-
Strategies for attracting students from other countries: Universities are increasingly targeting students from other countries to mitigate the loss of Chinese students.
-
Exploration of alternative funding sources for universities: Universities are exploring alternative funding sources, including increased fundraising and private donations.
H2: Long-Term Projections and Strategies for Mitigation
The long-term consequences of this trend could be significant, potentially impacting research funding and the overall diversity of the student body.
-
Potential impact on research funding: Reduced tuition revenue may impact research funding, hindering innovation and academic progress.
-
Strategies for diversifying the international student body: Universities must actively diversify their international recruitment strategies, targeting students from other regions with strong academic potential.
-
Potential for increased online programs to attract international students: Expanding online programs can make education more accessible to international students who may face visa or travel challenges.
-
Role of government policies in supporting international education: Government policies play a crucial role in fostering a welcoming environment for international students and ensuring the continued success of international education initiatives.
-
Potential impact on research funding: The decline in international student enrollment could lead to a reduction in research funding.
-
Strategies for attracting students from other countries: Universities need to explore new markets and develop targeted recruitment strategies.
-
Examples of successful online international education programs: Successful examples of online programs can serve as models for other institutions.
-
Policy recommendations for supporting international education: Governments can play a vital role in creating a supportive environment for international students.
Conclusion: Navigating the Financial Landscape: The Future of Chinese Enrollment and American Higher Education
The reduction in Chinese student enrollment presents significant financial challenges for American higher education. The loss of substantial tuition revenue necessitates immediate and long-term strategies to ensure financial stability. Diversification of the international student body, adaptation to evolving geopolitical factors, and exploration of alternative funding models are crucial for navigating this new landscape. Universities must proactively address the challenges presented by managing reduced Chinese student enrollment, adapting to shifting international student demographics, and securing financial stability in higher education. Further research into the impact of specific government policies on international student recruitment and the effectiveness of various diversification strategies is essential. Institutions need to develop comprehensive strategies to ensure the long-term health and sustainability of American higher education.

Featured Posts
-
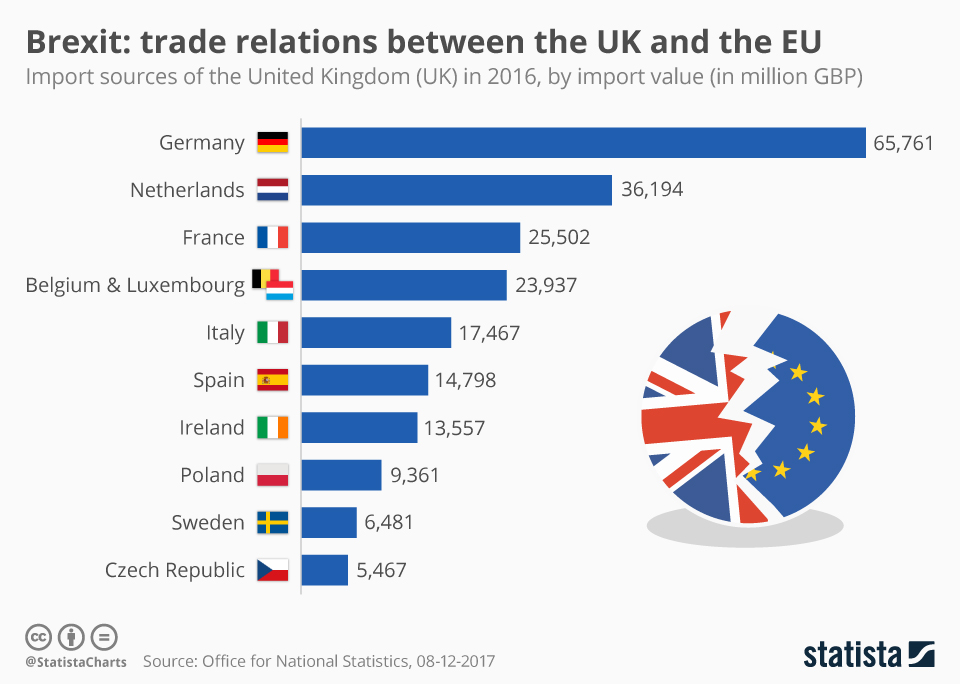 Brexit Damage Boes Bailey Advocates For Enhanced Eu Trade Relations
May 31, 2025
Brexit Damage Boes Bailey Advocates For Enhanced Eu Trade Relations
May 31, 2025 -
 Samsung Galaxy Tab Undercuts I Pad 101 Bargain
May 31, 2025
Samsung Galaxy Tab Undercuts I Pad 101 Bargain
May 31, 2025 -
 New Covid 19 Variant Surge In Cases Explained
May 31, 2025
New Covid 19 Variant Surge In Cases Explained
May 31, 2025 -
 Find Your New Home Two Weeks Of Free Accommodation In A German City
May 31, 2025
Find Your New Home Two Weeks Of Free Accommodation In A German City
May 31, 2025 -
 Former Nyc Mayor Giuliani Honors Bernie Keriks Legacy
May 31, 2025
Former Nyc Mayor Giuliani Honors Bernie Keriks Legacy
May 31, 2025
