Trump's China Tariffs: Higher Prices And Empty Shelves? The Impact On The US Economy
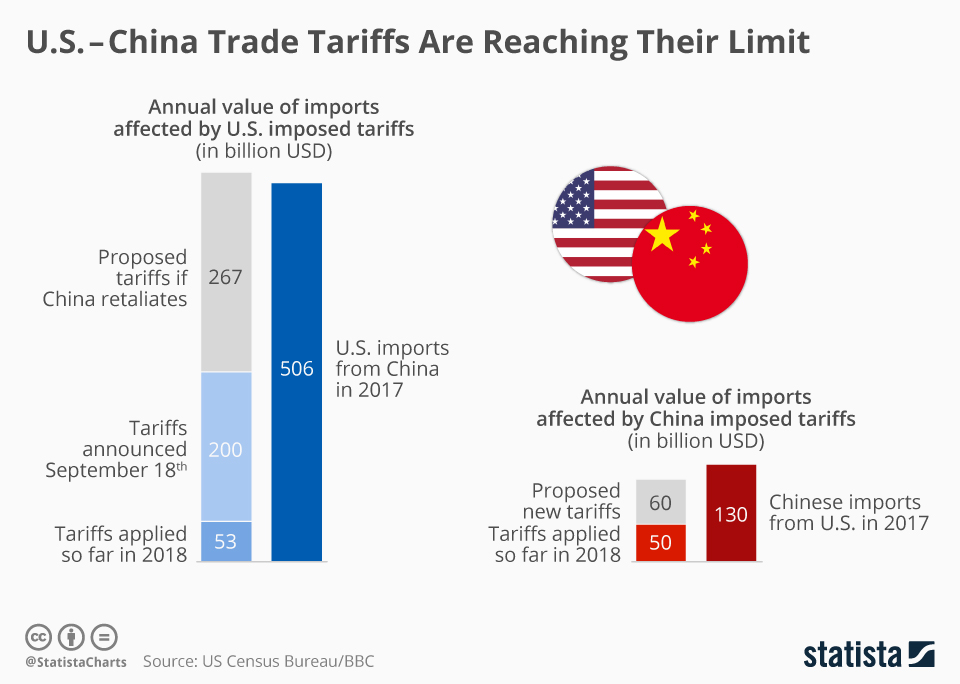
Table of Contents
The Direct Impact on Consumer Prices
Increased Costs of Imported Goods
Tariffs directly increased the price of goods imported from China. These duties, essentially taxes on imports, were levied on a wide range of products.
- Examples: Electronics (smartphones, laptops), furniture, clothing, toys, and household goods all experienced price increases due to the tariffs. Even seemingly small increases on individual items added up significantly for consumers.
- Data points: While pinpointing the exact amount added to each product is difficult, studies from organizations like the Peterson Institute for International Economics estimated substantial price increases on various tariffed goods. These increases were often passed on to consumers through higher retail prices.
- Analysis: The mechanism is straightforward: The tariff is added to the cost of the imported good, increasing the price the importer pays. This increased cost is then largely passed on to wholesalers and retailers, ultimately reaching the consumer.
Inflationary Pressures
The increased prices of imported goods contributed to overall inflation in the US economy. This inflationary pressure added to the cost of living for many Americans.
- Data points: Analyzing inflation rates before, during, and after the tariff period reveals a complex picture. While some studies suggest a modest inflationary impact from the tariffs, others argue the effect was limited or even offset by other economic factors.
- Analysis: The relationship between tariffs and inflation is not always straightforward. Other economic factors can mask or amplify the effect of tariffs on prices. The impact also varied depending on the specific goods affected and the overall state of the economy.
- Counterarguments: Some argue that the impact on inflation was minimal, pointing to other contributing factors like energy prices and supply chain disruptions unrelated to tariffs. However, the added cost of imported goods undoubtedly played some role in overall inflationary pressures.
Disruptions to the US Supply Chain
Reduced Trade Volume
The tariffs significantly reduced the volume of trade between the US and China. This reduction had ripple effects throughout the global economy.
- Data points: Statistics from the US Census Bureau clearly show a decline in both US imports from and exports to China during the tariff period.
- Analysis: Reduced trade disrupted established supply chains. Businesses that relied on timely imports from China faced delays and increased costs, impacting their ability to meet consumer demand.
Increased Production Costs for Businesses
Businesses faced higher input costs due to the tariffs, leading to price increases or reduced output. This impacted profitability and competitiveness.
- Examples: Manufacturers reliant on Chinese-made components, like those in the electronics and automotive industries, experienced significant cost increases.
- Case studies: Many businesses publicly documented the challenges they faced due to the increased cost of imports. Some were forced to raise prices, while others absorbed the costs, reducing profit margins.
Sourcing Alternatives and Reshoring
Businesses began exploring sourcing goods from alternative countries or reshoring (bringing production back to the US).
- Analysis: While some companies successfully diversified their sourcing, this process was often expensive and time-consuming. Reshoring also presented challenges, including higher labor costs and potentially longer lead times. The overall effectiveness of these strategies varied significantly depending on the industry and the specific business.
The Impact on Specific Industries
Agriculture
The tariffs negatively impacted US agricultural exports to China. China retaliated with its own tariffs on US agricultural products.
- Examples: Soybean and pork farmers faced significant losses due to reduced exports to China.
- Data points: Quantifying the economic losses in the agricultural sector due to the trade war requires considering both reduced exports and increased domestic prices.
Manufacturing
US manufacturing was also affected, though the impact was complex and varied across sectors.
- Examples: Some sectors, like electronics manufacturing, experienced increased costs due to tariffed components. Others might have benefited from increased domestic demand due to the tariffs.
- Data points: Data on job losses and gains related to the tariffs is complex, with varying conclusions depending on the methodology used.
Retail
Retailers faced higher prices for imported goods, forcing them to either absorb the increased costs or pass them on to consumers.
- Examples: Many retailers saw increased costs for clothing, household goods, and electronics.
- Data points: Data on consumer spending patterns during this period shows a mixed picture, with some sectors experiencing reduced sales due to price increases.
The Overall Economic Impact
GDP Growth
The effect of the tariffs on US GDP growth is debated. Some economists argue the tariffs hampered growth, while others suggest the impact was minimal or even positive in certain aspects.
- Data points: GDP growth rates during and after the tariff period need to be analyzed in conjunction with other macroeconomic factors to assess the specific impact of the tariffs.
- Analysis: Determining the precise impact of the tariffs on GDP growth is difficult due to other economic forces at play at the time.
Job Creation/Loss
The net effect of the tariffs on employment is uncertain and complex.
- Data points: Studies offer varying conclusions on the impact of the tariffs on job creation and loss, emphasizing the need for nuanced analysis.
- Analysis: It is difficult to isolate the employment impact of the tariffs from other factors affecting the labor market.
Long-Term Consequences
The long-term consequences of Trump's China tariffs are still unfolding. They created uncertainty for businesses, impacted supply chains, and affected consumer prices. The shifts in global trade patterns and sourcing strategies initiated during this period are likely to have lasting effects.
Conclusion
Trump's China tariffs had a multifaceted impact on the US economy. While they did lead to increased prices for some imported goods, the extent to which this resulted in widespread "empty shelves" is debatable. The tariffs created significant disruptions to supply chains, impacting various industries differentially. The overall economic impact remains a topic of ongoing debate, with economists presenting differing perspectives on the net effect on GDP growth and employment. Understanding the complexities of Trump's China tariffs and their lingering impact is crucial. Continue exploring this issue to form your own informed opinion on trade policy and its effects on the US economy.

Featured Posts
-
 Nyt Strands February 25 2025 Solutions And Spangram
Apr 29, 2025
Nyt Strands February 25 2025 Solutions And Spangram
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Ohio Doctors Murder Conviction Sons Emotional Journey Before Parole Decision
Apr 29, 2025
Ohio Doctors Murder Conviction Sons Emotional Journey Before Parole Decision
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Harvard Faces Trump Administration In Court Over Funding Cuts
Apr 29, 2025
Harvard Faces Trump Administration In Court Over Funding Cuts
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Sag Aftra Joins Wga On Strike What This Means For Hollywood
Apr 29, 2025
Sag Aftra Joins Wga On Strike What This Means For Hollywood
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Dysprosiums Critical Role In Electric Vehicle Motors And Its Supply Chain Challenges
Apr 29, 2025
Dysprosiums Critical Role In Electric Vehicle Motors And Its Supply Chain Challenges
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 February 26th Nyt Spelling Bee 360 Hints Solutions And Strategies
Apr 29, 2025
February 26th Nyt Spelling Bee 360 Hints Solutions And Strategies
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Nyt Spelling Bee February 28 2025 Solutions And Spangram
Apr 29, 2025
Nyt Spelling Bee February 28 2025 Solutions And Spangram
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Nyt Spelling Bee Answers For February 25 2025 Find The Pangram
Apr 29, 2025
Nyt Spelling Bee Answers For February 25 2025 Find The Pangram
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Todays Nyt Spelling Bee Hints And Answers For Puzzle 360 Feb 26th
Apr 29, 2025
Todays Nyt Spelling Bee Hints And Answers For Puzzle 360 Feb 26th
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Solving The Nyt Spelling Bee February 25 2025 Puzzle And Spangram
Apr 29, 2025
Solving The Nyt Spelling Bee February 25 2025 Puzzle And Spangram
Apr 29, 2025
