Understanding Food Startup Failure: Insights And Strategies For Success
Table of Contents
Common Causes of Food Startup Failure
Many factors contribute to the high rate of food startup failure. Let's examine some of the most prevalent pitfalls:
Inadequate Market Research
Insufficient market research is a primary driver of food startup failure. Before investing time and resources, a deep understanding of your target market is paramount. This includes:
- Insufficient understanding of target customer needs and preferences: Failing to identify your ideal customer's demographics, dietary restrictions, purchasing habits, and price sensitivity can lead to a product that simply doesn't resonate.
- Failure to analyze competitor landscape and identify unique selling propositions (USPs): Ignoring the competition or failing to differentiate your offering can result in a lack of market share and ultimately, failure. A strong USP is vital.
- Neglecting market trends and evolving consumer demands: The food industry is dynamic. Ignoring shifts in consumer preferences (e.g., towards healthier options, sustainable sourcing, or specific dietary needs) can lead to irrelevance.
Specific examples of inadequate market research leading to food startup failure:
- Poor product-market fit: Developing a product that doesn't meet the needs or desires of the target market.
- Underestimating competition: Failing to account for existing competitors and their market share.
- Misjudging pricing strategies: Setting prices too high or too low, resulting in either low profitability or insufficient revenue.
Poor Financial Management
Robust financial planning is essential to avoid food startup failure. Many food businesses fail due to mismanagement of funds:
- Underestimating startup costs and ongoing operational expenses: Unexpected expenses are common in the food industry (e.g., ingredient price fluctuations, equipment repairs). Thorough budgeting is crucial.
- Ineffective cash flow management and insufficient funding: Maintaining sufficient cash reserves to cover operational costs during lean periods is vital. Securing adequate funding through loans, investors, or bootstrapping is also critical.
- Lack of a robust financial plan and budgeting process: A detailed financial plan, including projected revenue, expenses, and profitability, is essential for securing funding and tracking performance.
Examples of poor financial management leading to food startup failure:
- Cost overruns: Unexpected expenses exceeding the initial budget.
- Neglecting to secure sufficient funding: Running out of cash before achieving profitability.
- Poor inventory management: Holding excessive inventory leading to spoilage and waste, or running out of key ingredients.
Operational Inefficiencies
Efficient operations are critical for success. Inefficiencies can significantly impact profitability and contribute to food startup failure:
- Ineffective supply chain management and logistical challenges: Reliable and efficient sourcing of ingredients is crucial for consistent product quality and timely delivery.
- Difficulties in scaling production to meet demand: The ability to increase production efficiently as demand grows is vital for growth.
- Poor quality control and product consistency issues: Maintaining consistent product quality is essential for customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
Examples of operational inefficiencies leading to food startup failure:
- Issues with sourcing ingredients: Supplier unreliability or inconsistent ingredient quality.
- Production bottlenecks: Inefficient production processes causing delays and impacting output.
- Inconsistent product quality: Leading to customer dissatisfaction and negative reviews.
Lack of Marketing and Branding
Effective marketing and branding are crucial for attracting customers and building a successful food business. Neglecting these areas often leads to food startup failure:
- Inadequate brand building and customer engagement strategies: Creating a compelling brand identity and engaging with customers through various channels is essential.
- Ineffective marketing campaigns and limited reach to target audience: Poorly targeted marketing campaigns fail to reach the right customers, resulting in wasted resources.
- Failure to establish a strong online presence and build brand awareness: A strong online presence (website, social media) is crucial in today's digital world.
Examples of poor marketing leading to food startup failure:
- Weak social media strategy: Failing to utilize social media effectively to engage with customers and build brand awareness.
- Poor website design: A poorly designed website can deter potential customers.
- Ineffective advertising campaigns: Wasting resources on advertising campaigns that do not generate a return on investment.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Issues
Navigating the regulatory landscape is critical to avoid food startup failure. Non-compliance can result in significant penalties and legal issues:
- Failure to comply with food safety regulations and licensing requirements: Food safety regulations are stringent and vary by location. Non-compliance can lead to closures and legal action.
- Legal issues related to intellectual property, contracts, and liability: Protecting intellectual property and ensuring legally sound contracts are essential.
Examples of legal issues leading to food startup failure:
- Food safety violations: Leading to fines, closures, and reputational damage.
- Contract disputes: Disagreements with suppliers, distributors, or other partners.
- Intellectual property infringement: Using copyrighted materials or trademarks without permission.
Strategies for Food Startup Success
By avoiding the pitfalls discussed above, you can significantly improve your chances of success. Here are some key strategies:
Thorough Market Research & Validation
Conduct extensive market research before launching. Utilize:
- Surveys and focus groups: Gather direct feedback from your target audience.
- Competitive analysis: Identify your competitors' strengths and weaknesses.
- Minimum Viable Product (MVP) development and testing: Launch a scaled-down version of your product to test market response before a full launch.
Robust Financial Planning & Funding
Develop a detailed business plan with realistic financial projections. Explore funding options like:
- Bootstrapping: Self-funding your business.
- Angel investors: Seeking funding from individual investors.
- Venture capital: Seeking funding from venture capital firms.
- Small business loans: Securing loans from financial institutions.
- Implement effective cash flow management techniques, such as budgeting, forecasting, and tracking expenses.
Efficient Operations & Scalability
Establish strong relationships with reliable suppliers. Implement efficient production processes and quality control measures, and develop a scalable business model to adapt to increasing demand.
Effective Marketing & Branding
Build a strong brand identity that reflects your values and resonates with your target audience. Implement a multi-channel marketing strategy including:
- Social media marketing: Engage with your audience on relevant platforms.
- Email marketing: Build an email list and nurture leads.
- Content marketing: Create valuable content to attract and engage potential customers.
- Public relations: Build relationships with media outlets and influencers.
- Focus on building a loyal customer base through excellent customer service and creating a positive brand experience.
Regulatory Compliance & Legal Frameworks
Understand and comply with all relevant food safety regulations and licensing requirements. Seek legal advice to protect intellectual property and address potential legal issues.
Conclusion: Avoiding Food Startup Failure – A Path to Success
The key takeaways from this article highlight the critical importance of thorough market research, robust financial planning, efficient operations, effective marketing, and stringent regulatory compliance. The high failure rate of food startups underscores the critical need for a well-defined strategy. By understanding the common causes of food startup failure and implementing the strategies discussed, you can significantly increase your chances of building a thriving and sustainable food business. Start planning your success today!

Featured Posts
-
 Perselisihan Nft Nike Gugatan Rp 84 Miliar Dari Seorang Pembeli
May 29, 2025
Perselisihan Nft Nike Gugatan Rp 84 Miliar Dari Seorang Pembeli
May 29, 2025 -
 Dem Alastqlal Mswwlyt Jmaeyt
May 29, 2025
Dem Alastqlal Mswwlyt Jmaeyt
May 29, 2025 -
 Nieuw Statendams Invergordon Visit A Boost For Easter Ross Tourism
May 29, 2025
Nieuw Statendams Invergordon Visit A Boost For Easter Ross Tourism
May 29, 2025 -
 Understanding The Netherlands Eurovision 2025 Choice C Est La Vie Lyrics And Odds
May 29, 2025
Understanding The Netherlands Eurovision 2025 Choice C Est La Vie Lyrics And Odds
May 29, 2025 -
 Koeln C O Pop Festival Tickets Lineup And Infos
May 29, 2025
Koeln C O Pop Festival Tickets Lineup And Infos
May 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Episodio De Run Bts Jin De Bts Protagoniza Una Pelicula De Accion
May 30, 2025
Episodio De Run Bts Jin De Bts Protagoniza Una Pelicula De Accion
May 30, 2025 -
 Fewer Excessive Heat Warnings Whats Changed And Why
May 30, 2025
Fewer Excessive Heat Warnings Whats Changed And Why
May 30, 2025 -
 Jin De Bts Accion Explosiva En El Nuevo Episodio De Run Bts
May 30, 2025
Jin De Bts Accion Explosiva En El Nuevo Episodio De Run Bts
May 30, 2025 -
 Jins Coldplay Seoul Concert Appearance Promises A Soon Comeback For Bts
May 30, 2025
Jins Coldplay Seoul Concert Appearance Promises A Soon Comeback For Bts
May 30, 2025 -
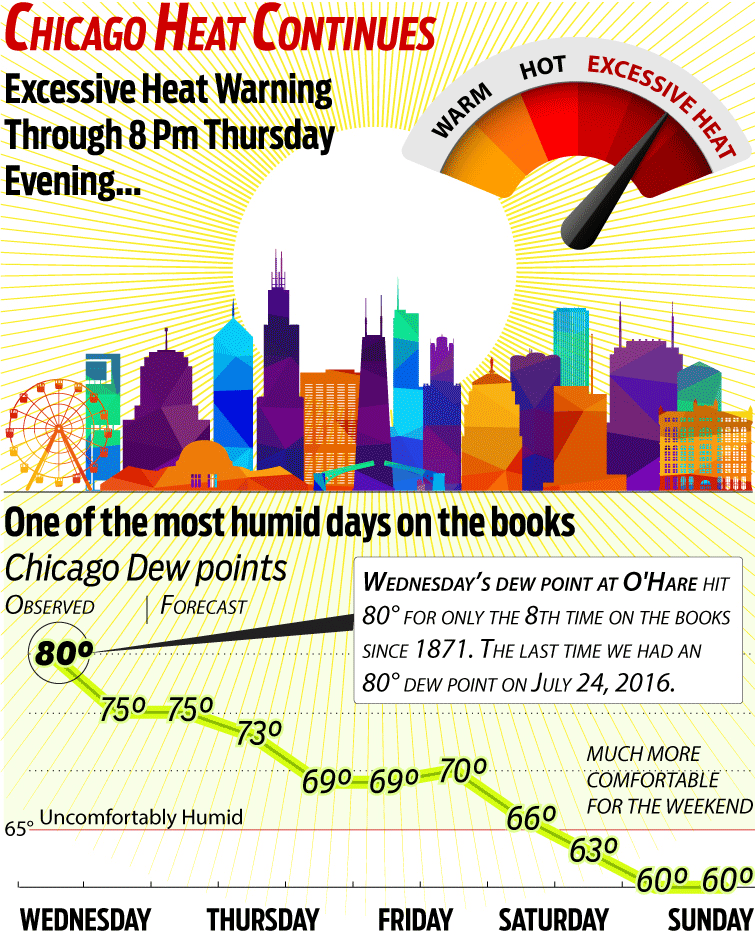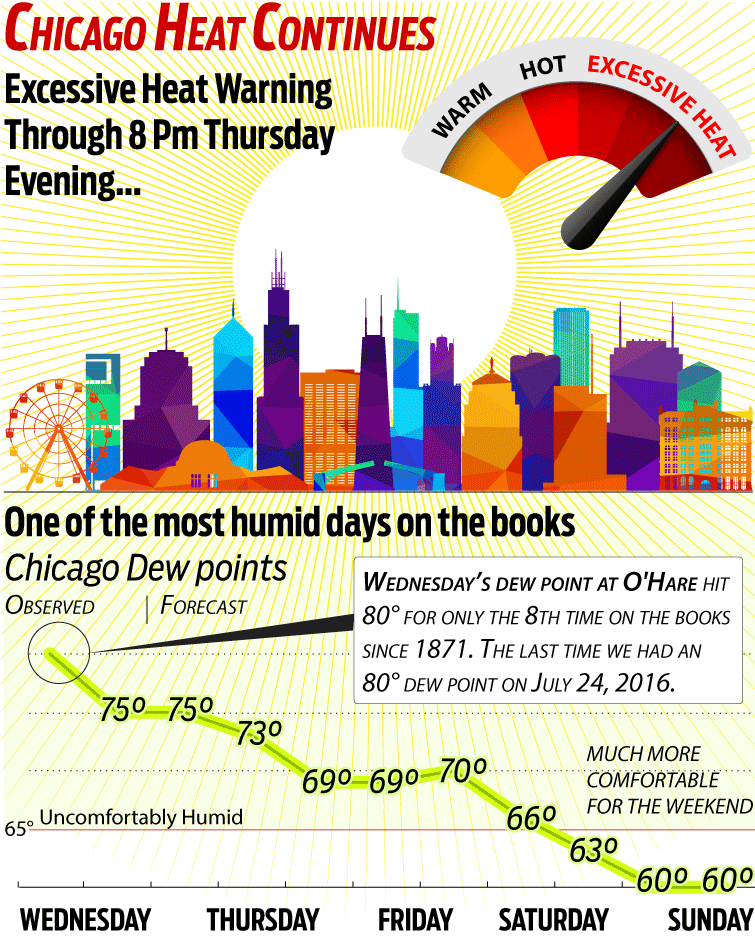 Why Excessive Heat Warnings Are Often Missing From Weather Forecasts
May 30, 2025
Why Excessive Heat Warnings Are Often Missing From Weather Forecasts
May 30, 2025
