ECB: Lingering Pandemic Fiscal Support Fuels Inflation
Table of Contents
Government Spending and Pandemic Recovery Funds
The COVID-19 pandemic triggered unprecedented government intervention across the Eurozone. Massive fiscal stimulus packages were implemented to cushion the economic blow, aiming to prevent a deeper recession and support businesses and households. This involved:
- Furlough schemes: Governments paid a significant portion of employee salaries to keep people employed.
- Business loans and grants: Financial assistance was provided to businesses to help them weather the storm.
- Stimulus checks: Direct payments were made to individuals to boost spending.
The scale of this spending was enormous, injecting vast sums of money into the Eurozone economy. This significantly increased aggregate demand. While intended to prevent a collapse, this surge in disposable income, coupled with supply chain constraints (discussed below), created significant inflationary pressures. The increased purchasing power outstripped the ability of the economy to produce goods and services, driving up prices.
The ECB's Monetary Policy Response
The ECB responded to the pandemic with a range of monetary policy measures designed to stimulate the economy and prevent a credit crunch. These included:
- Quantitative easing (QE): The ECB purchased large quantities of government bonds and other assets, injecting liquidity into the financial system.
- Near-zero interest rates: Interest rates were kept extremely low to encourage borrowing and investment.
These actions were successful in preventing a major economic collapse. However, the increased money supply, a consequence of QE, also contributed to inflationary pressures. The ECB faced a difficult balancing act: stimulating the economy to avoid a recession while simultaneously controlling inflation. This delicate balancing act is further complicated by the lingering effects of the fiscal stimulus.
Supply Chain Disruptions and Inflationary Pressures
The pandemic caused widespread supply chain disruptions, exacerbating inflationary pressures. Lockdowns, port congestion, and labor shortages created bottlenecks, leading to shortages of goods and increased prices. These supply-side constraints interacted negatively with the increased demand fueled by the fiscal stimulus. The result was a perfect storm for inflation: high demand colliding with constrained supply. This manifested in higher prices for a wide range of goods, from energy to consumer durables.
- Increased shipping costs: Global shipping costs skyrocketed due to port congestion and container shortages.
- Shortages of raw materials: Manufacturing was disrupted due to shortages of key components and raw materials.
- Labor shortages: Lockdowns and illness led to labor shortages in various sectors, further constricting supply.
The Lagging Effects of Pandemic Fiscal Support
The impact of fiscal support measures on inflation isn't immediate; there's a significant time lag. Even as the immediate health crisis of the pandemic subsides, the effects of the vast sums of money injected into the economy continue to reverberate. This poses a significant challenge for the ECB, which must now manage inflation stemming from policies implemented earlier. The ECB's challenge is amplified by the continued uncertainty surrounding global supply chains and the potential for further economic shocks. A strategic exit from these expansive fiscal policies is crucial to prevent further inflationary pressures.
Conclusion: Addressing the ECB's Inflation Challenge
The evidence strongly suggests that lingering pandemic fiscal support has played a significant role in fueling inflation within the Eurozone. The ECB faces a complex challenge: balancing the need to support economic recovery with the imperative to control inflation. Understanding the interplay between government spending, monetary policy, supply chain disruptions, and the lagging effects of pandemic-related measures is critical. We must closely follow the ECB's policy decisions and their impact on inflation. Further research into the long-term economic consequences of these unprecedented fiscal interventions is essential. Understanding the ECB's response to this complex situation, and the ongoing impact of pandemic fiscal support on ECB inflation, is crucial for navigating the current economic climate. Visit the ECB website for more information on their current monetary policy and related publications.

Featured Posts
-
 Tech Stock Losses Seven Giants Down 2 5 Trillion This Year
Apr 29, 2025
Tech Stock Losses Seven Giants Down 2 5 Trillion This Year
Apr 29, 2025 -
 The Impact Of Tariff Uncertainty On U S Corporate Cost Cutting
Apr 29, 2025
The Impact Of Tariff Uncertainty On U S Corporate Cost Cutting
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Strong Reliance Results Potential Uplift For Indias Large Cap Index
Apr 29, 2025
Strong Reliance Results Potential Uplift For Indias Large Cap Index
Apr 29, 2025 -
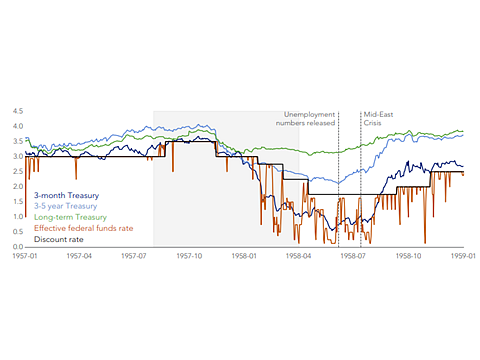 April 8th Treasury Market Update Lessons Learned
Apr 29, 2025
April 8th Treasury Market Update Lessons Learned
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Israel Under Scrutiny For Gaza Aid Blockade As Resources Deplete
Apr 29, 2025
Israel Under Scrutiny For Gaza Aid Blockade As Resources Deplete
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Petition To Remove Pete Rose From Ineligible List Mlbs Decision
Apr 29, 2025
Petition To Remove Pete Rose From Ineligible List Mlbs Decision
Apr 29, 2025 -
 The Pete Rose Pardon Examining Trumps Rationale And Potential Impact
Apr 29, 2025
The Pete Rose Pardon Examining Trumps Rationale And Potential Impact
Apr 29, 2025 -
 The Pete Rose Pardon Examining Trumps Potential Action And Its Fallout
Apr 29, 2025
The Pete Rose Pardon Examining Trumps Potential Action And Its Fallout
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Rose Ban Trump Promises Posthumous Pardon Attacks Mlb
Apr 29, 2025
Rose Ban Trump Promises Posthumous Pardon Attacks Mlb
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Will Trump Pardon Pete Rose A Call For Hall Of Fame Consideration
Apr 29, 2025
Will Trump Pardon Pete Rose A Call For Hall Of Fame Consideration
Apr 29, 2025
