Tesla's Optimus Robot: China's Rare Earth Restrictions Cause Delays
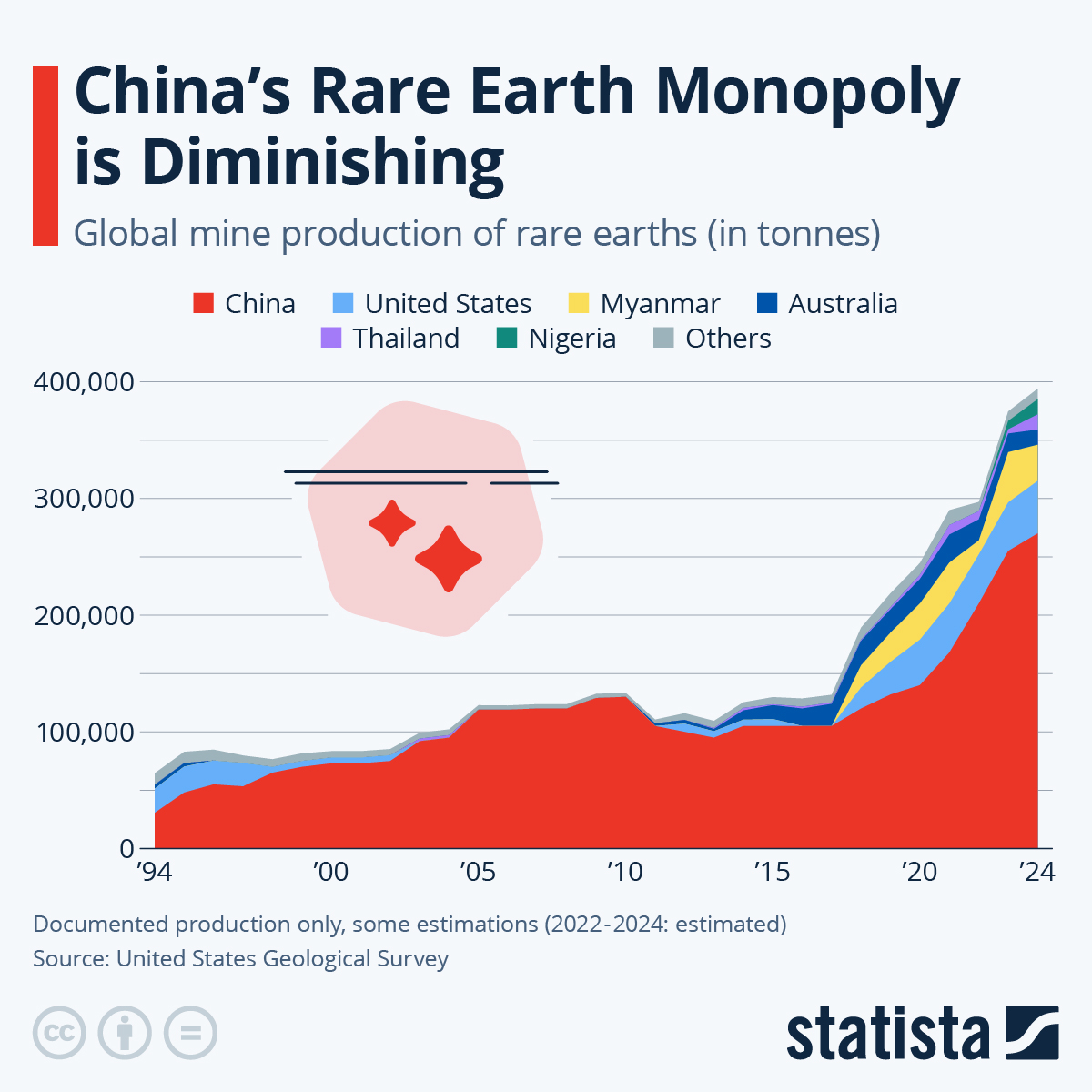
Table of Contents
Tesla's ambitious Optimus robot project, aiming to revolutionize automation and manufacturing, faces significant hurdles due to China's tightening control over rare earth element exports. This article explores the crucial role of these materials in Optimus's development and how restricted access is impacting Tesla's timeline and broader implications for the robotics industry. The future of this groundbreaking technology may depend on overcoming these complex supply chain challenges.
The Critical Role of Rare Earth Elements in Robotics
Neodymium Magnets – The Heart of Robotics
Neodymium magnets, powerful permanent magnets containing rare earth elements, are indispensable components in the motors and actuators that power robots like Optimus. Their high power-to-weight ratio is crucial for achieving the precise movements and dexterity required for sophisticated robotic tasks. Without these magnets, the smooth, efficient operation of Optimus would be severely compromised.
- High power-to-weight ratio: Allows for compact and lightweight motor designs, essential for a mobile robot like Optimus.
- Essential for precise movements: Enables the robot's arms and legs to perform complex actions with accuracy and control.
- Crucial for robot dexterity and efficiency: Facilitates the intricate movements needed for tasks such as assembly, manipulation, and navigation.
- Currently dominated by Chinese production: China holds a near-monopoly on the processing and refining of neodymium, creating a significant reliance for manufacturers.
Within the Optimus robot's design, neodymium magnets are likely integral to the actuators in its arms and legs, enabling the powerful and precise movements necessary for its intended functions. Their presence in the motors controlling the robot's joints is also critical for efficient and smooth operation.
Other Rare Earth Elements in Optimus
Beyond neodymium, other rare earth elements likely play crucial roles in Optimus's sophisticated technology. These materials offer unique properties that enhance various robot components and functionalities.
- Dysprosium: Often used in neodymium magnets to improve their high-temperature performance and resistance to demagnetization, ensuring reliable operation even under stress.
- Terbium: Used in certain types of sensors and actuators to enhance their sensitivity and responsiveness.
- Other elements: Various other rare earth elements might be used in specialized sensors, control systems, and other components, adding to the complexity of sourcing these materials.
Sourcing these elements presents a significant logistical challenge due to their dispersed geographic distribution and complex refining processes, a challenge amplified by China's dominant position in the global supply chain.
China's Dominance in Rare Earth Mining and Processing
Geopolitical Implications
China's near-monopoly in rare earth mining and processing has profound geopolitical implications for global supply chains. This dominance grants China significant leverage over industries reliant on these critical materials, including the robotics sector.
- China's control over the supply chain: Gives China considerable influence over prices and availability of rare earth elements.
- Potential for export restrictions and price manipulation: Creates uncertainty and risks for companies relying on these materials for manufacturing.
- Impact on global robotics companies: Forces companies to depend on a single major supplier, increasing their vulnerability to supply disruptions.
Export Restrictions and Their Impact on Tesla
China has implemented various export restrictions, including quotas and tariffs, affecting the availability and cost of rare earth elements. These restrictions directly impact Tesla's ability to procure the necessary materials for Optimus production.
- Specific restrictions: Quotas on certain rare earth elements limit the quantity available for export. Tariffs increase the cost of importing these vital materials.
- Impact on Tesla's timeline and production costs: Delays production schedules and increases manufacturing costs, potentially affecting profitability.
- Alternative sourcing strategies: Tesla is likely exploring alternative sources and potentially investing in alternative technologies to mitigate these risks, but this represents a significant undertaking.
Potential Solutions and Future Outlook for Tesla's Optimus Robot
Diversification of Supply Chains
To mitigate future supply chain risks, Tesla and other robotics companies are actively pursuing strategies to diversify their sources of rare earth elements.
- Investment in mining and processing outside China: Developing new mines and processing facilities in other countries to reduce reliance on China.
- Partnerships with other companies: Collaborating with companies involved in rare earth mining and processing to secure stable supply chains.
- Research into alternative materials: Exploring the use of alternative materials that can replace rare earth elements in certain applications.
Technological Innovation and Material Substitution
Technological advancements offer a potential path to reduce reliance on rare earth elements in robotics.
- Development of new magnet materials: Researching and developing alternative magnet materials that do not rely on rare earth elements.
- Improved motor designs: Optimizing motor designs to require less rare earth material while maintaining performance.
- Exploring alternative technologies for actuators: Developing new actuator technologies that don't depend on rare earth magnets.
The Long-Term Implications for the Robotics Industry
China's dominance over rare earth elements poses significant challenges for the long-term growth and development of the robotics industry globally.
- Increased production costs: The scarcity and geopolitical complexities surrounding rare earth elements will likely lead to increased production costs for robots.
- Potential for technological bottlenecks: Dependence on a single supplier can create technological bottlenecks, hindering innovation and competitiveness.
- Implications for national security and technological independence: The dependence on China for crucial materials raises concerns about national security and technological sovereignty for various countries.
Conclusion
Tesla's Optimus robot project, a significant advancement in robotics, is facing substantial delays due to China's control over crucial rare earth elements. The reliance on neodymium magnets and other rare earth materials highlights the vulnerability of advanced manufacturing to geopolitical factors. While Tesla is likely exploring alternative sourcing and technological solutions, the challenges underscore the need for diversified supply chains and innovative material science in the robotics sector. The future of the Optimus robot, and indeed the broader robotics industry, hinges on successfully navigating these complexities. Stay informed on the latest developments regarding the Tesla Optimus robot and its ongoing struggle with rare earth supply chain disruptions. Understanding the rare earth elements challenge is crucial for anyone following the progress of this revolutionary technology.

Featured Posts
-
 Powell Job Secure Stock Futures React Positively To Trumps Remarks
Apr 24, 2025
Powell Job Secure Stock Futures React Positively To Trumps Remarks
Apr 24, 2025 -
 World Economic Forum New Probe Into Klaus Schwabs Leadership
Apr 24, 2025
World Economic Forum New Probe Into Klaus Schwabs Leadership
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Instagram Aims To Rival Tik Tok With New Video Editing App
Apr 24, 2025
Instagram Aims To Rival Tik Tok With New Video Editing App
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Understanding The Bitcoin Btc Increase Trumps Role And Market Reaction
Apr 24, 2025
Understanding The Bitcoin Btc Increase Trumps Role And Market Reaction
Apr 24, 2025 -
 Eus Planned Phaseout Of Russian Gas Spot Market In Focus
Apr 24, 2025
Eus Planned Phaseout Of Russian Gas Spot Market In Focus
Apr 24, 2025
