Investigation Into Lingering Toxic Chemicals In Buildings Following Ohio Train Derailment

Table of Contents
Types of Toxic Chemicals Released and Their Persistence
The derailment released a cocktail of hazardous substances, with vinyl chloride and butyl acrylate among the most concerning. Vinyl chloride, a known carcinogen [link to EPA information], is a volatile organic compound that can persist in the environment for varying lengths of time, depending on factors like soil type and temperature. Butyl acrylate, another volatile organic compound [link to CDC information], also presents significant health risks.
The persistence of these chemicals is a major concern. They can:
- Remain in the air for extended periods, particularly in enclosed spaces.
- Absorb into porous building materials such as drywall, insulation, and carpeting.
- Leach into soil and groundwater, potentially contaminating nearby structures.
- Accumulate in the bodies of living organisms (bioaccumulation), leading to long-term health problems.
The potential for chemical migration within building structures is significant. HVAC systems, for instance, can inadvertently circulate contaminated air throughout a building, exposing occupants to elevated levels of toxic chemicals.
Methods for Detecting Lingering Toxic Chemicals in Buildings
Detecting lingering toxic chemicals in buildings requires specialized methods and expertise. Several techniques can be employed, each with its own strengths and limitations:
- Air sampling: This method involves collecting air samples at various locations within the building to analyze the concentration of airborne chemicals.
- Surface wipe sampling: This technique involves wiping surfaces with absorbent materials to collect residues of chemicals.
- Soil testing: Analyzing soil samples around the building can help determine the extent of ground contamination and the potential for migration into the structure.
Professional testing is crucial. Certified laboratories employing advanced technologies, such as gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), are essential for accurate and reliable results. Comprehensive testing protocols, considering various matrices (air, surfaces, soil), are vital for a thorough assessment. The use of specialized equipment and experienced personnel is paramount to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the detection process.
Health Impacts of Exposure to Lingering Toxic Chemicals
Exposure to lingering toxic chemicals can have severe consequences for human health. Both short-term and long-term effects are possible, depending on the chemical, concentration, and duration of exposure.
Potential health impacts include:
- Respiratory problems (coughing, shortness of breath, asthma)
- Neurological issues (headaches, dizziness, cognitive impairment)
- Skin irritation and allergic reactions
- Increased cancer risk
Children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing conditions are particularly vulnerable. Immediate medical attention is crucial if any symptoms consistent with chemical exposure arise.
Remediation and Mitigation Strategies for Contaminated Buildings
Remediation of buildings contaminated with lingering toxic chemicals requires a multi-faceted approach. Several strategies can be employed:
- Air filtration: High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration systems can remove airborne contaminants.
- Surface decontamination: Cleaning and decontamination of affected surfaces might be sufficient for less severe cases.
- Building demolition: In cases of severe and widespread contamination, demolition might be the only viable option.
The cost and feasibility of these strategies depend heavily on the extent of contamination and the specific chemicals involved. Proper waste disposal, adhering to all environmental regulations, is paramount. Long-term monitoring after remediation is critical to ensure the effectiveness of the cleanup efforts.
Governmental Response and Regulations
Federal, state, and local agencies, including the EPA and OSHA, play a critical role in responding to contamination events and establishing regulations for cleanup. Legal recourse may be available to affected individuals or communities. Specific agencies involved in overseeing the cleanup efforts and any subsequent legal action need careful monitoring.
Conclusion
The Ohio train derailment highlights the serious threat posed by lingering toxic chemicals in buildings following industrial accidents. Thorough testing, appropriate remediation strategies, and ongoing monitoring are crucial to protect public health and the environment. Continued investigation and stricter regulations are essential to prevent future incidents and mitigate the long-term consequences of such disasters. Learn more about the issue, seek professional help if you suspect contamination in your building, and advocate for stricter regulations to prevent future incidents involving lingering toxic chemicals and other hazardous materials.

Featured Posts
-
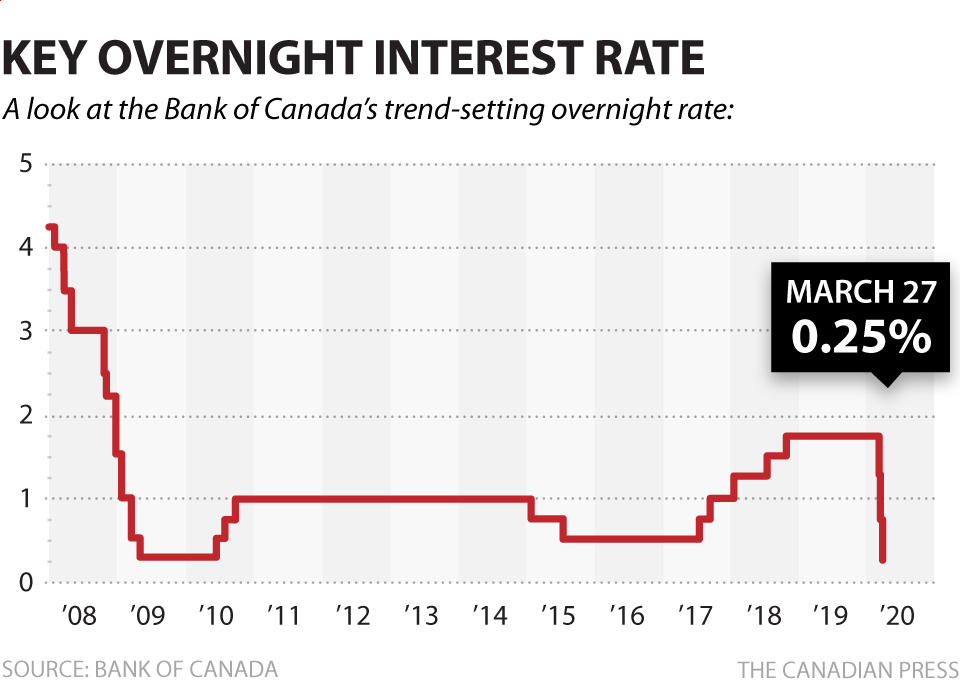 Falling Retail Sales A Sign Of Impending Bank Of Canada Rate Cuts
Apr 28, 2025
Falling Retail Sales A Sign Of Impending Bank Of Canada Rate Cuts
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Market Downturn A Case Study Of Professional Selling And Individual Purchasing
Apr 28, 2025
Market Downturn A Case Study Of Professional Selling And Individual Purchasing
Apr 28, 2025 -
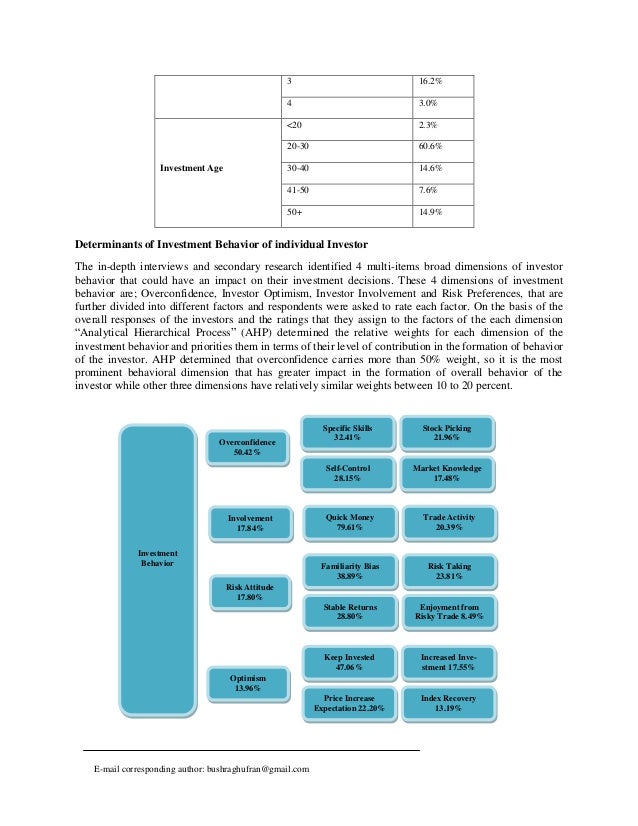 Analyzing The Recent Market Dip Professional Vs Individual Investor Behavior
Apr 28, 2025
Analyzing The Recent Market Dip Professional Vs Individual Investor Behavior
Apr 28, 2025 -
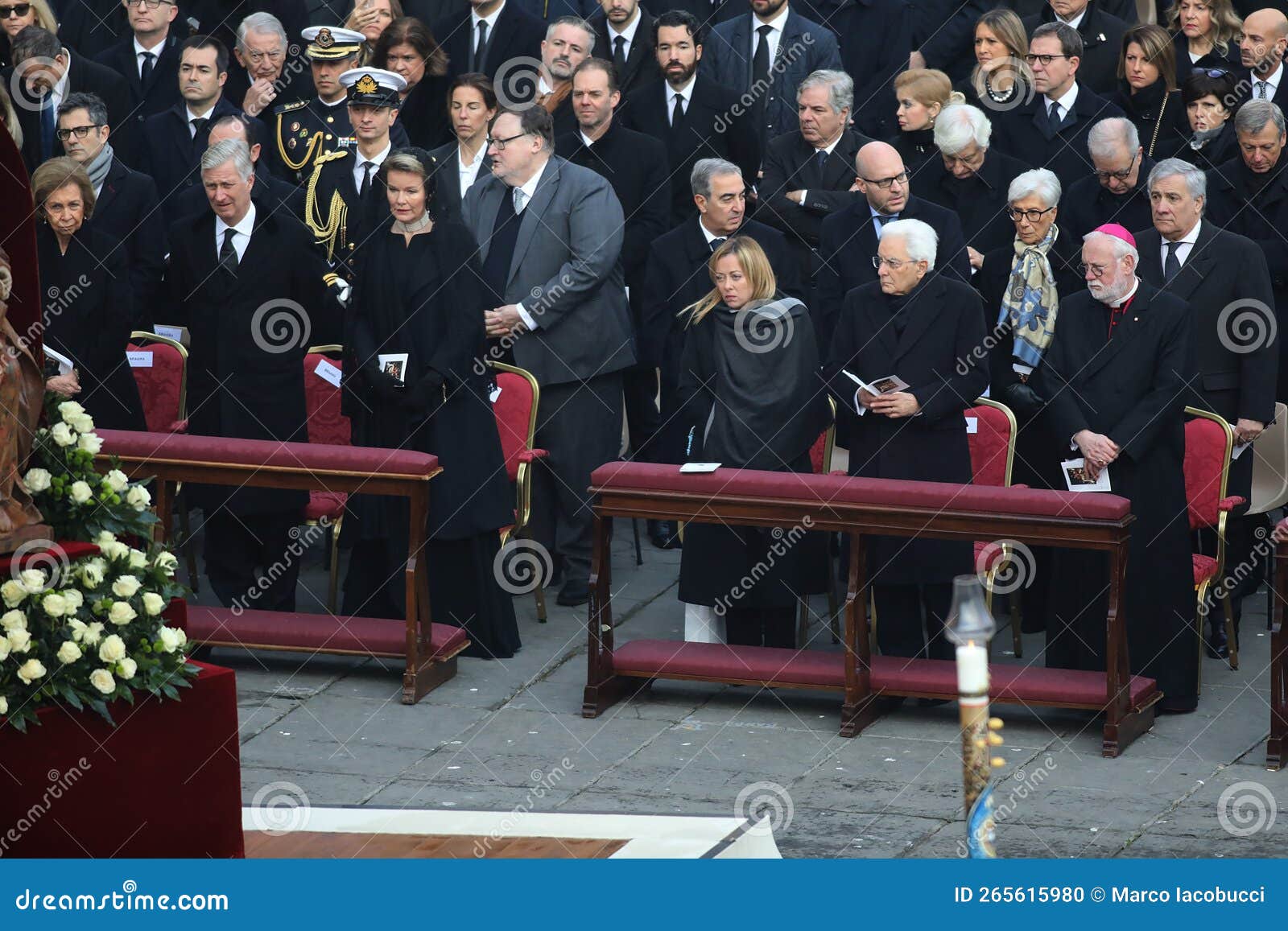 International Figures Attend Pope Francis Funeral Mass
Apr 28, 2025
International Figures Attend Pope Francis Funeral Mass
Apr 28, 2025 -
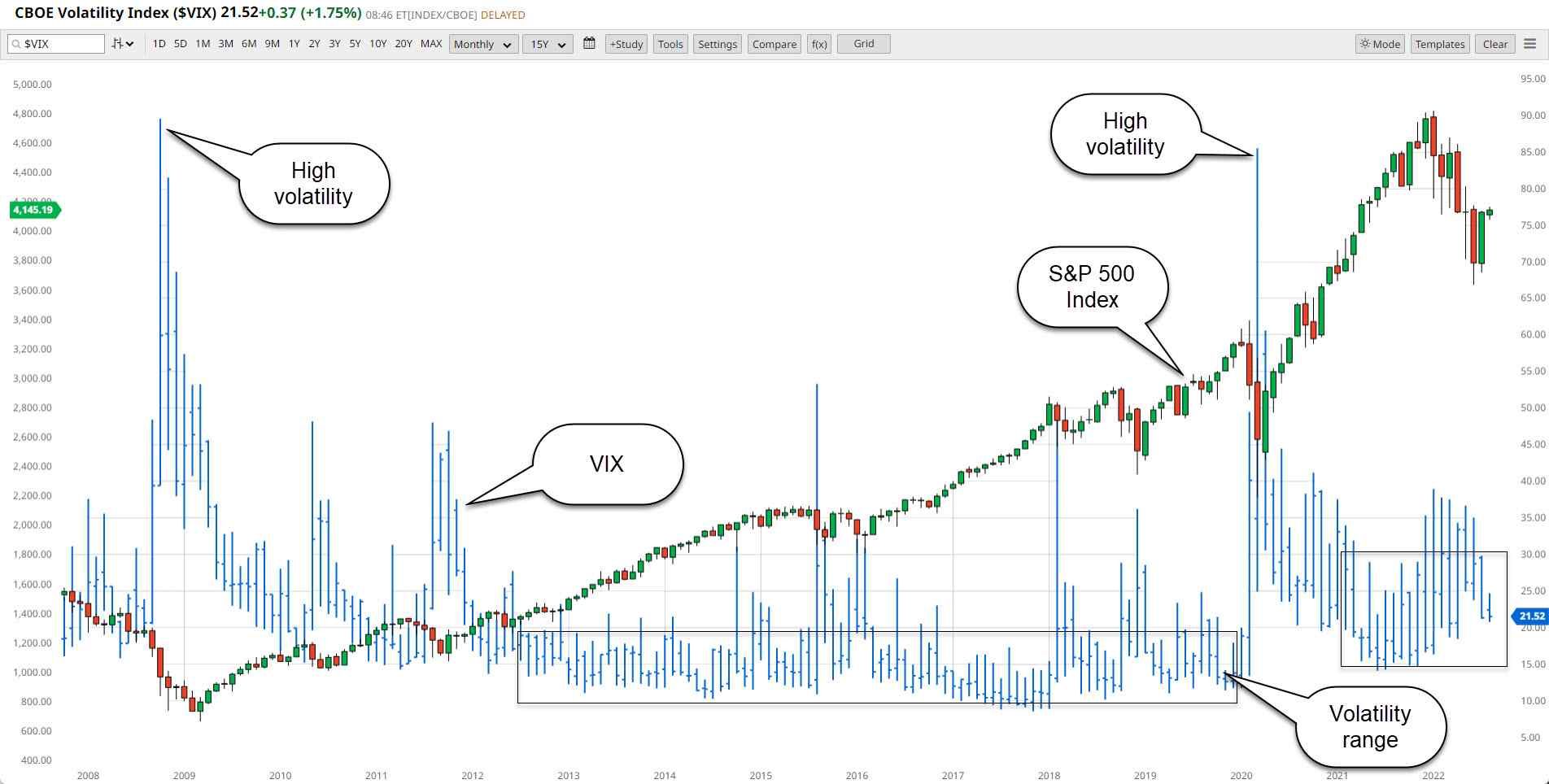 Individual Investors Response To Market Volatility A Deeper Look
Apr 28, 2025
Individual Investors Response To Market Volatility A Deeper Look
Apr 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Red Soxs Shifting Lineup Impact Of Outfielders Return And Casas Lowered Spot
Apr 28, 2025
Red Soxs Shifting Lineup Impact Of Outfielders Return And Casas Lowered Spot
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Analysis Red Sox Lineup Changes Following Outfielders Return And Casas Demotion
Apr 28, 2025
Analysis Red Sox Lineup Changes Following Outfielders Return And Casas Demotion
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Updated Red Sox Lineup Casas Position Change And Outfielders Reinstatement
Apr 28, 2025
Updated Red Sox Lineup Casas Position Change And Outfielders Reinstatement
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Red Sox Lineup Outfielder Returns Casas Moves Down In The Order
Apr 28, 2025
Red Sox Lineup Outfielder Returns Casas Moves Down In The Order
Apr 28, 2025 -
 Triston Casas Continued Slide Red Sox Lineup Adjustment And Outfielders Return
Apr 28, 2025
Triston Casas Continued Slide Red Sox Lineup Adjustment And Outfielders Return
Apr 28, 2025
