U.S. Intelligence Agencies Increase Greenland Surveillance
Table of Contents
The Strategic Importance of Greenland's Location
Greenland's immense geographic size and strategic location make it a pivotal player in Arctic geopolitics. Its proximity to North America, coupled with its position overlooking crucial shipping lanes and potential resource deposits, makes it a prime target for intelligence gathering. The island's potential to host significant military installations – air bases and naval bases – further enhances its strategic value in the context of great power competition.
- Crucial Surveillance Capabilities: Greenland's location offers unparalleled opportunities for monitoring North American airspace and maritime routes, providing early warning capabilities against potential threats.
- Proximity to Conflict Zones: Its geographical position places it near potential flashpoints, making it a vital asset for monitoring Russian and Chinese activity in the Arctic. The increasing militarization of the Arctic by Russia, in particular, has heightened concerns.
- Arctic Resource Access: The melting Arctic ice cap opens up new shipping lanes and access to valuable resources, including rare earth minerals, triggering intensified geopolitical competition and increasing the need for Arctic surveillance.
Types of Surveillance Employed by U.S. Agencies
The U.S. intelligence community employs a multi-faceted approach to Greenland surveillance, utilizing a range of sophisticated technologies and methodologies. This likely includes:
- Signals Intelligence (SIGINT): Intercepting communications to gather information on activities within and around Greenland.
- Human Intelligence (HUMINT): Utilizing human sources on the ground to gather information.
- Geospatial Intelligence (GEOINT): Analyzing satellite imagery and other geospatial data to monitor infrastructure development, military movements, and resource extraction activities.
- Open-Source Intelligence (OSINT): Gathering information from publicly available sources, such as news reports, social media, and scientific publications.
- Satellite Surveillance and Drone Surveillance: These technologies provide real-time monitoring capabilities, offering high-resolution imagery and data on various activities.
The capabilities and limitations of each technology vary, and ethical and legal considerations surrounding their deployment must be carefully weighed. While specific details of U.S. surveillance operations remain classified, the increased presence of these technologies in the region is undeniable.
Potential Reasons Behind Increased Surveillance
Several factors contribute to the intensification of U.S. intelligence activities in Greenland. These include:
- Russian Military Activity: Russia's increasing military presence in the Arctic, including the modernization of its Northern Fleet and the expansion of its air bases, is a major concern. Greenland surveillance is crucial for monitoring these developments.
- Resource Competition: The Arctic holds vast untapped resources, including rare earth minerals crucial for modern technologies. Competition for these resources among major powers fuels the need for increased intelligence gathering.
- Climate Change Impacts: The melting ice cap significantly alters the geopolitical landscape, opening new shipping routes and exposing previously inaccessible resources. This creates both opportunities and challenges, requiring enhanced surveillance.
- Chinese Investment: China's growing economic influence in the Arctic, through its Belt and Road Initiative and investments in infrastructure projects, is another factor driving increased U.S. interest in Greenland surveillance.
Greenland's Response and International Implications
Greenland's response to increased U.S. surveillance is complex. As an autonomous territory within the Kingdom of Denmark, its relationship with both the U.S. and Denmark shapes its position. The issue raises questions about Greenland's sovereignty and its ability to balance its relationship with major powers.
- Greenland's Autonomy: Greenland enjoys a considerable degree of self-governance, but its ultimate sovereignty rests with Denmark. This dynamic significantly impacts its ability to control and respond to increased surveillance.
- Denmark's Role: Denmark plays a crucial role in mediating Greenland's relationship with other nations, particularly regarding security matters.
- NATO and the Arctic Council: The implications of increased Greenland surveillance extend to broader international organizations like NATO and the Arctic Council. These organizations must navigate the complex interplay of national interests within the Arctic region.
Conclusion
The increase in U.S. intelligence agency surveillance in Greenland reflects the growing strategic importance of the Arctic region. The interplay of climate change, resource competition, and great power rivalry has created a complex geopolitical landscape. Greenland's unique geographic position makes it a key focal point for intelligence gathering, raising questions regarding sovereignty and international cooperation. The future of the Arctic hinges on careful management of these competing interests. Stay informed about the crucial developments in Greenland surveillance and the future of Arctic security. Continue to explore the complexities of this issue with further research.

Featured Posts
-
 Ps 5 Stock And Price Hike Your Action Plan
May 08, 2025
Ps 5 Stock And Price Hike Your Action Plan
May 08, 2025 -
 Predicting The Arsenal Vs Psg Semi Final A More Difficult Challenge Than Real Madrid
May 08, 2025
Predicting The Arsenal Vs Psg Semi Final A More Difficult Challenge Than Real Madrid
May 08, 2025 -
 Bitcoin And Ethereum Options Expiration Billions At Stake Market Braces For Volatility
May 08, 2025
Bitcoin And Ethereum Options Expiration Billions At Stake Market Braces For Volatility
May 08, 2025 -
 Steven Spielbergs War Movies 7 Must See Films Saving Private Ryan Is Out
May 08, 2025
Steven Spielbergs War Movies 7 Must See Films Saving Private Ryan Is Out
May 08, 2025 -
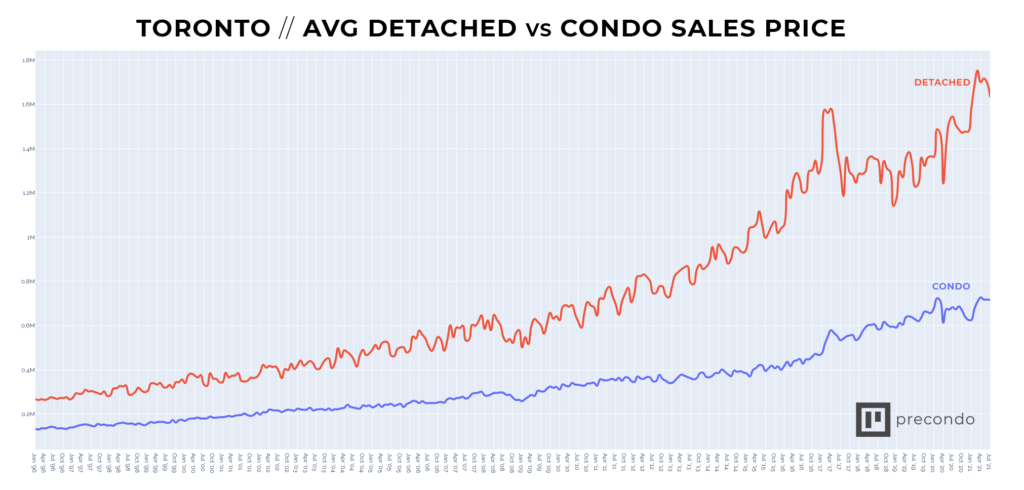 Toronto Home Sales And Prices A 23 And 4 Decline Respectively
May 08, 2025
Toronto Home Sales And Prices A 23 And 4 Decline Respectively
May 08, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Analyzing Ripples Xrp Potential Can It Break Through To 3 40
May 08, 2025
Analyzing Ripples Xrp Potential Can It Break Through To 3 40
May 08, 2025 -
 Ripples Xrp Assessing The Likelihood Of A Price Increase To 3 40
May 08, 2025
Ripples Xrp Assessing The Likelihood Of A Price Increase To 3 40
May 08, 2025 -
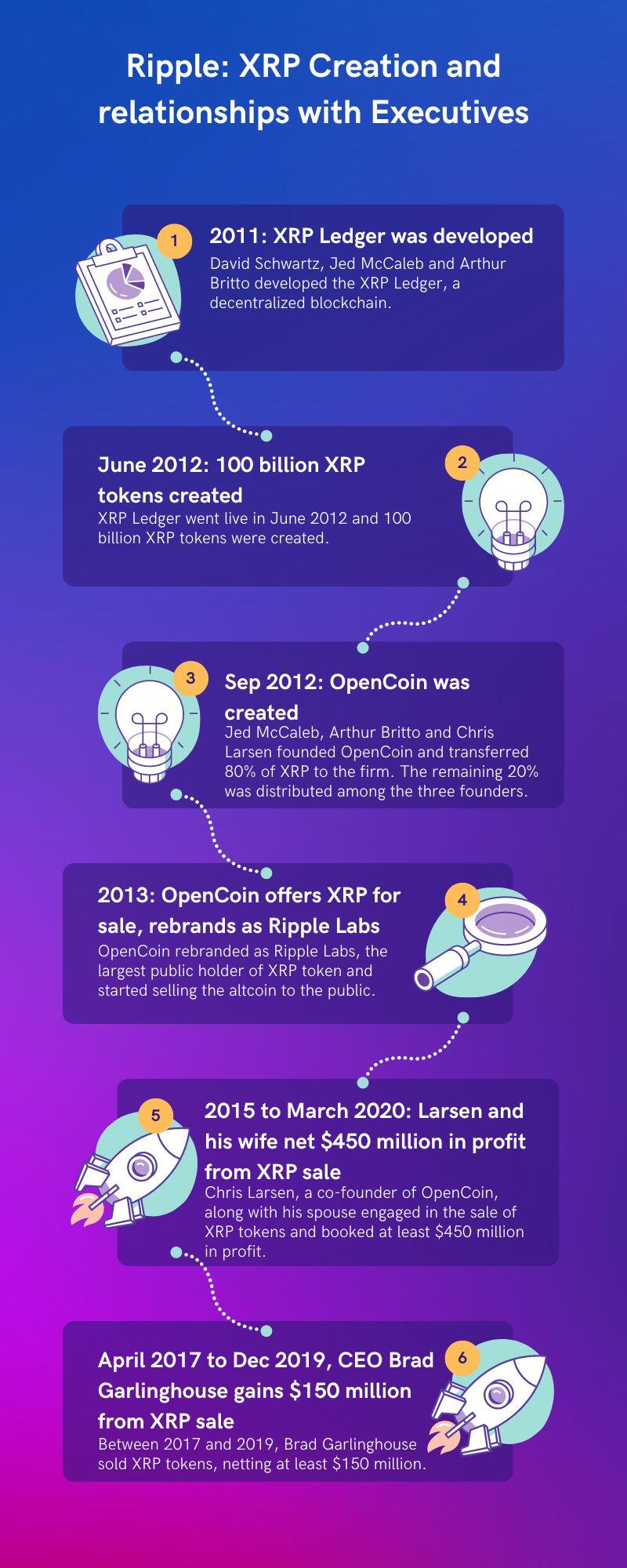 Is 3 40 A Realistic Price For Xrp Ripples Market Analysis
May 08, 2025
Is 3 40 A Realistic Price For Xrp Ripples Market Analysis
May 08, 2025 -
 Xrp Ripple A High Risk High Reward Investment Opportunity
May 08, 2025
Xrp Ripple A High Risk High Reward Investment Opportunity
May 08, 2025 -
 Analyzing The Challenges Why Xrp Etfs May Underperform Expectations
May 08, 2025
Analyzing The Challenges Why Xrp Etfs May Underperform Expectations
May 08, 2025
